Abstract
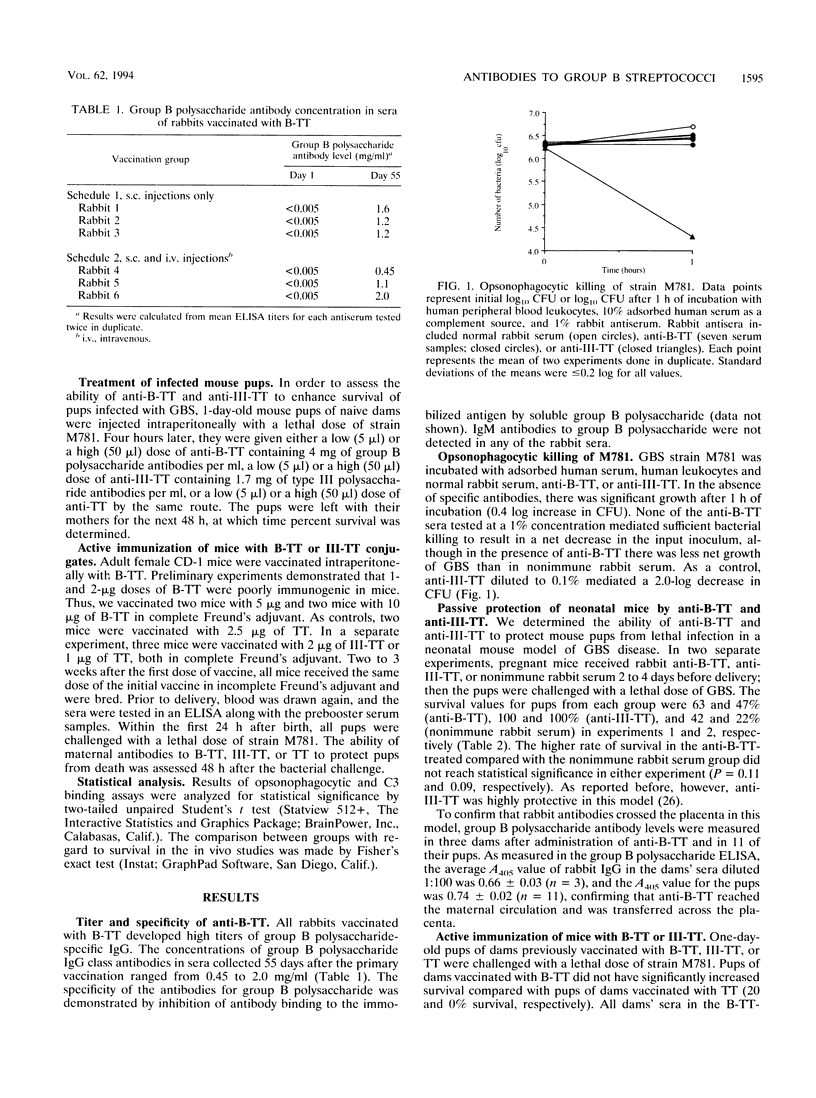
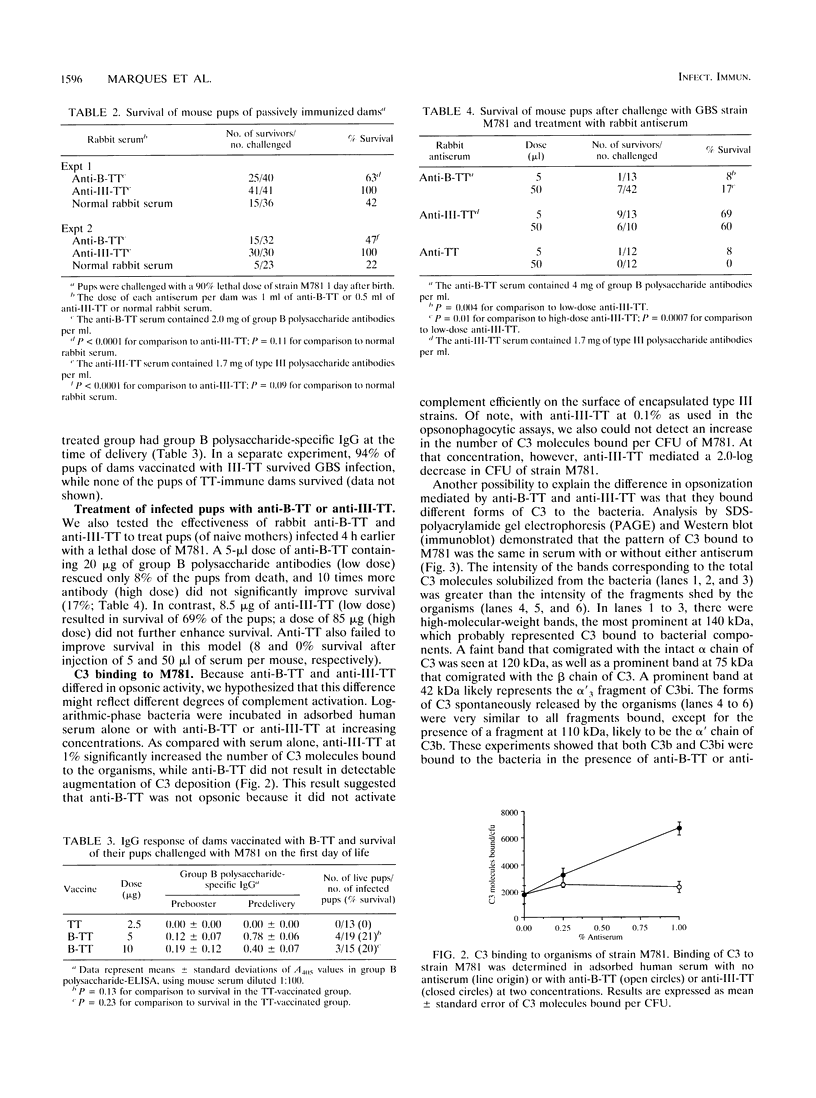
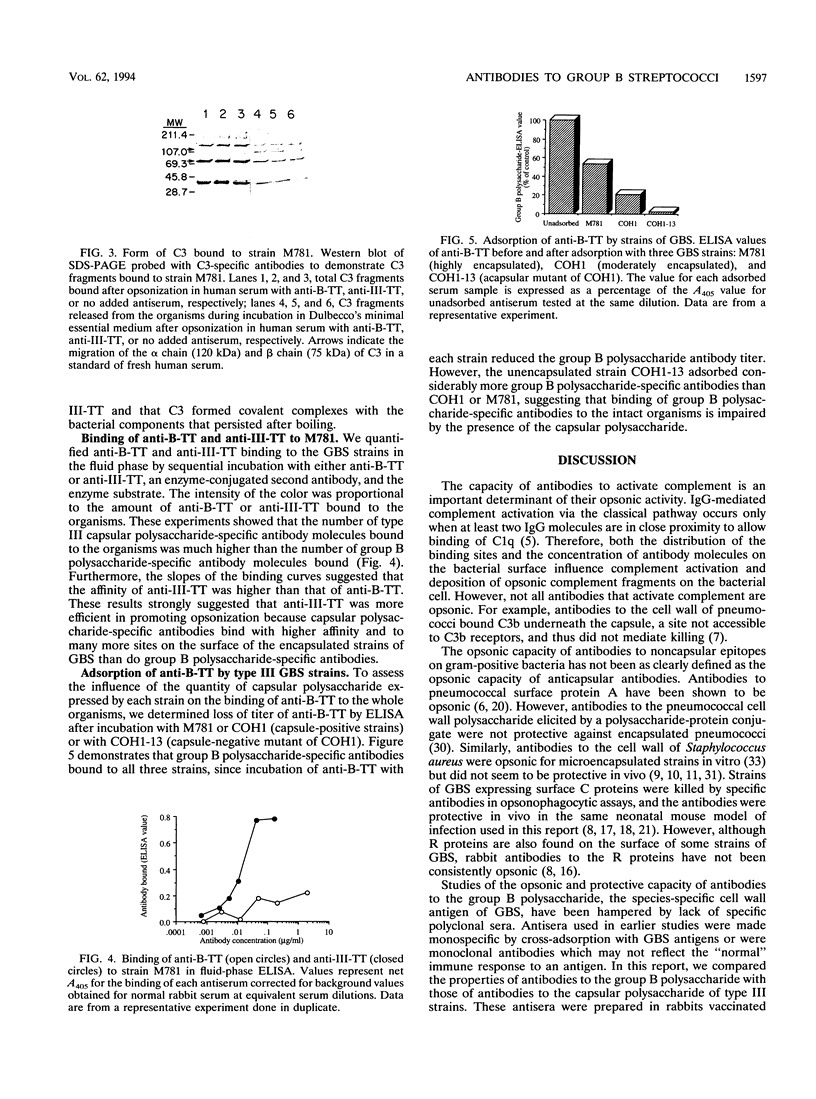
Group B streptococci (GBS) are a major cause of sepsis and meningitis in infants. While antibodies directed to the type-specific GBS capsule have been shown to be protective, it is less clear whether antibodies to the group B polysaccharide, a noncapsular, cell wall-associated antigen, may play a role in immunity. To investigate the functional activity of group B polysaccharide-specific antibodies, we tested sera from rabbits vaccinated with group B polysaccharide coupled to tetanus toxoid (B-TT). Anti-B-TT was weakly opsonic in vitro for a highly encapsulated type III strain, while antiserum elicited by vaccination with type III capsular polysaccharide linked to tetanus toxoid (III-TT) was a very effective opsonin. In contrast to anti-III-TT, anti-B-TT given before or after bacterial challenge was only marginally effective in protecting newborn mice against lethal infection with type III GBS. The number of C3 molecules bound to type III GBS was augmented by anti-III-TT but not by high antibody concentrations of anti-B-TT. These results suggest that the difference in opsonic activity between anti-B-TT and anti-III-TT may be due to a difference in their ability to deposit C3. In addition, the maximum number of antibody molecules bound to the bacterial surface was greater for anti-III-TT than for anti-B-TT. That anti-B-TT binds to fewer sites than anti-III-TT may explain the differences in complement activation and in opsonic and protective efficacy of antibodies to group B polysaccharide compared with antibodies to the type-specific capsular polysaccharide.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony B. F., Concepcion N. F., Concepcion K. F. Human antibody to the group-specific polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):221–226. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohnsack J. F., Zhou X. N., Gustin J. N., Rubens C. E., Parker C. J., Hill H. R. Bacterial evasion of the antibody response: human IgG antibodies neutralize soluble but not bacteria-associated group B streptococcal C5a-ase. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):315–321. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Complement fixation on cell surfaces by 19S and 7S antibodies. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):505–506. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Yother J., McDaniel L. S. Role of pneumococcal surface protein A in the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S372–S374. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Hosea S. W., Hammer C. H., Burch C. G., Frank M. M. A quantitative analysis of the interactions of antipneumococcal antibody and complement in experimental pneumococcal bacteremia. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):85–98. doi: 10.1172/JCI110444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrieri P. Surface-localized protein antigens of group B streptococci. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S363–S366. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granström M., Julander I. G., Hedström S. A., Möllby R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for antibodies against teichoic acid in patients with staphylococcal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):640–646. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.640-646.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. P., Bayer A. S., Turner D., Ward J. I. Antibody responses to protein A in patients with Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):458–462. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.458-462.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. P., Ward J. I., Bayer A. S. Influence of Staphylococcus aureus antibody on experimental endocarditis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3030–3034. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3030-3034.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancefield R. C., McCarty M., Everly W. N. Multiple mouse-protective antibodies directed against group B streptococci. Special reference to antibodies effective against protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):165–179. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindén V. Mouse-protective effect of rabbit anti-R-protein antibodies against group B streptococci type II carrying R-protein. Lack of effect on type III carrying R-protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):145–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Gong E. W., Rodewald A. K., Kasper D. L. Protection of neonatal mice from group B streptococcal infection by maternal immunization with beta C protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):4989–4994. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.4989-4994.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoff L. C., Michel J. L., Kasper D. L. A monoclonal antibody identifies a protective C-protein alpha-antigen epitope in group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):204–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.204-210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques M. B., Kasper D. L., Pangburn M. K., Wessels M. R. Prevention of C3 deposition by capsular polysaccharide is a virulence mechanism of type III group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3986–3993. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3986-3993.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel L. S., Yother J., Vijayakumar M., McGarry L., Guild W. R., Briles D. E. Use of insertional inactivation to facilitate studies of biological properties of pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA). J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):381–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel J. L., Madoff L. C., Kling D. E., Kasper D. L., Ausubel F. M. Cloned alpha and beta C-protein antigens of group B streptococci elicit protective immunity. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2023–2028. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2023-2028.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michon F., Chalifour R., Feldman R., Wessels M., Kasper D. L., Gamian A., Pozsgay V., Jennings H. J. The alpha-L-(1----2)-trirhamnopyranoside epitope on the group-specific polysaccharide of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1991 May;59(5):1690–1696. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.5.1690-1696.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michon F., Katzenellenbogen E., Kasper D. L., Jennings H. J. Structure of the complex group-specific polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):476–486. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Bradley C., Brady W., Donaldson K., Lipsich L., Maloney G., Shuford W., Walls M., Ward P., Wolff E. Comparison of functional activities between IgG1 and IgM class-switched human monoclonal antibodies reactive with group B streptococci or Escherichia coli K1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):346–354. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. V., Siscoe P. J., Wolff E. A., Maloney G., Shuford W. Human monoclonal antibodies to group B streptococcus. Reactivity and in vivo protection against multiple serotypes. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):905–917. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodewald A. K., Onderdonk A. B., Warren H. B., Kasper D. L. Neonatal mouse model of group B streptococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):635–639. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens C. E., Heggen L. M., Haft R. F., Wessels M. R. Identification of cpsD, a gene essential for type III capsule expression in group B streptococci. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):843–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigeoka A. O., Pincus S. H., Rote N. S., Hill H. R. Protective efficacy of hybridoma type-specific antibody against experimental infection with group-B Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):363–372. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyur S. D., Raff H. V., Bohnsack J. F., Kelsey D. K., Hill H. R. Comparison of the opsonic and complement triggering activity of human monoclonal IgG1 and IgM antibody against group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1879–1884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szu S. C., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Rabbit antibodies to the cell wall polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae fail to protect mice from lethal challenge with encapsulated pneumococci. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):448–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.448-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels M. R., Paoletti L. C., Kasper D. L., DiFabio J. L., Michon F., Holme K., Jennings H. J. Immunogenicity in animals of a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine against type III group B Streptococcus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1428–1433. doi: 10.1172/JCI114858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Arbeit R. D., Lee J. C. Phagocytic killing of encapsulated and microencapsulated Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1358-1362.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



