Abstract
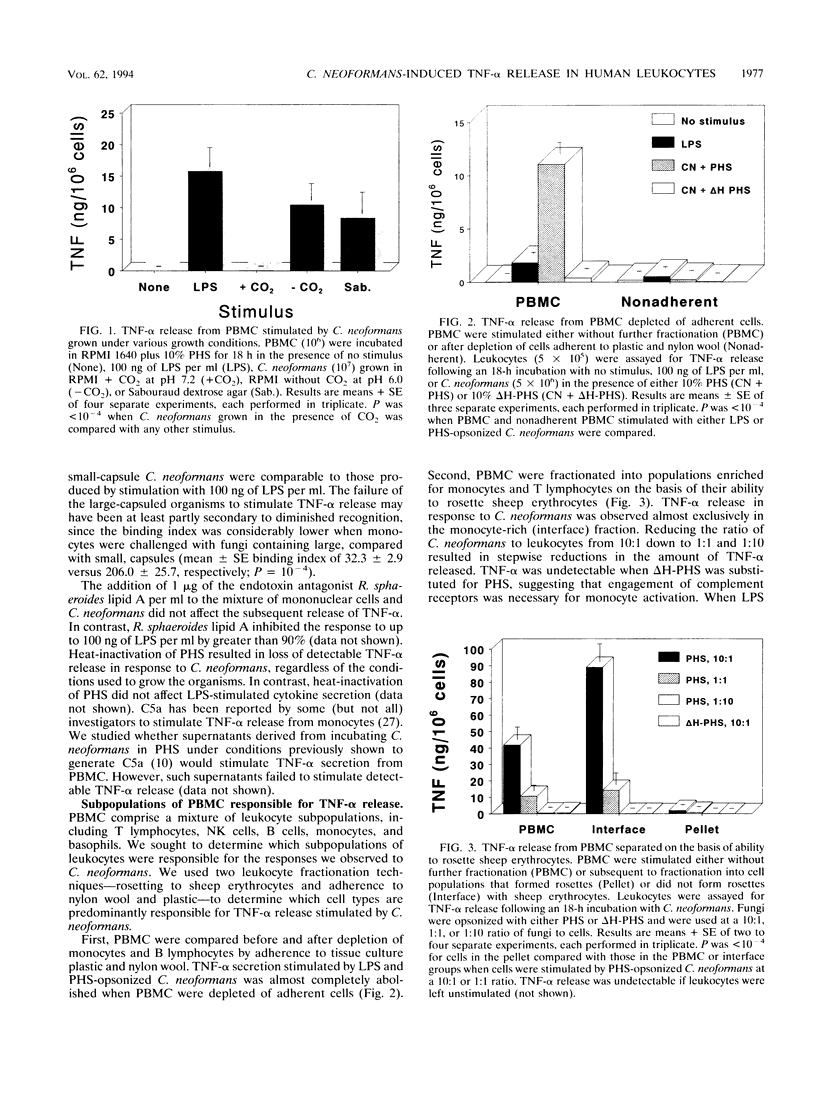
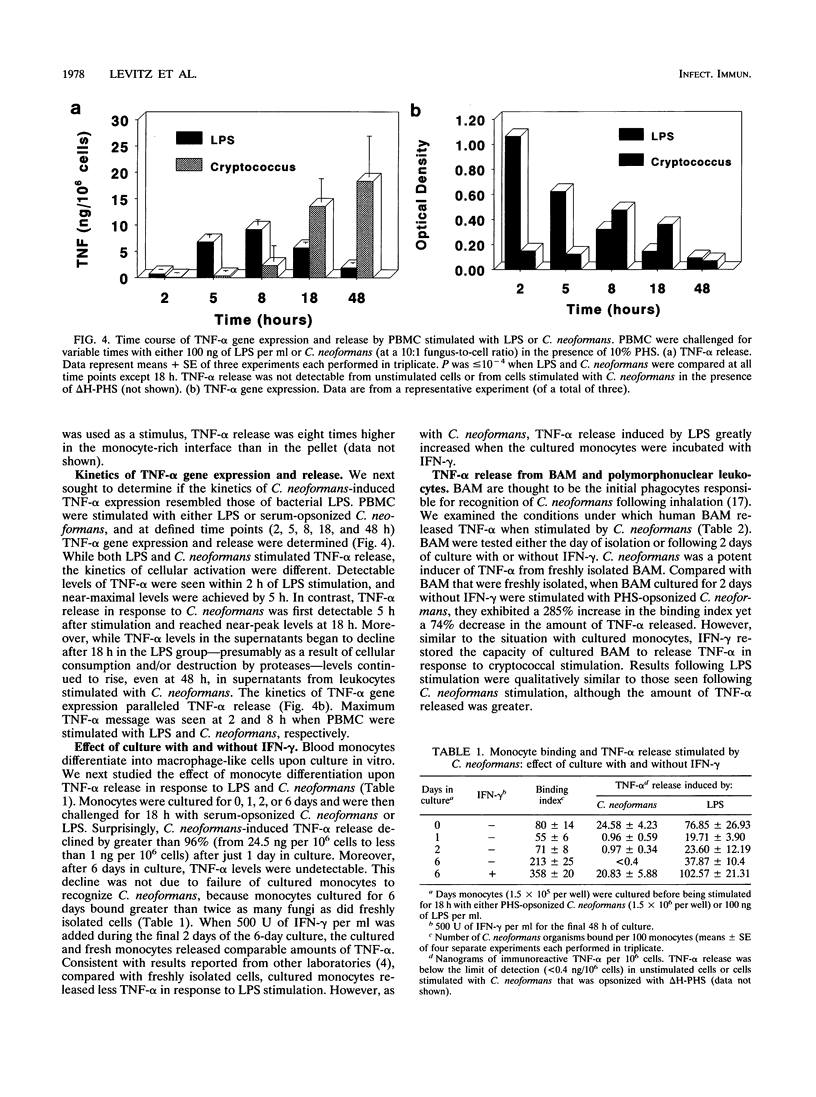
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is a key mediator of inflammation and may promote human immunodeficiency virus replication in latently infected cells. Since cryptococcosis often is associated with aberrations in the host inflammatory response and occurs preferentially in persons with AIDS, we defined the conditions under which human leukocytes produce TNF-alpha when stimulated by Cryptococcus neoformans. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) produced comparable amounts of TNF-alpha following stimulation with C. neoformans and lipopolysaccharide. Detectable TNF-alpha release in response to C. neoformans occurred only when fungi with small-sized capsules were used and complement-sufficient serum was added. Fractionation of PBMC established that monocytes were the predominant source of TNF-alpha. TNF-alpha gene expression and release occurred significantly later in PBMC stimulated with C. neoformans than in PBMC stimulated with LPS. C. neoformans was also a potent inducer of TNF-alpha from freshly isolated bronchoalveolar macrophages (BAM). Upon in vitro culture, BAM and monocytes bound greater numbers of fungal cells, yet their capacity to produce TNF-alpha following cryptococcal stimulation declined by 74 to 100%. However, this decline was reversed if the BAM and monocytes were cultured with gamma interferon. These data establish that C. neoformans can potently stimulate TNF-alpha release from human leukocytes. However, several variables profoundly affected the amount of TNF-alpha released, including the type of leukocyte and its state of activation, the size of the cryptococcal capsule, and the availability of opsonins.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazzoni F., Cassatella M. A., Laudanna C., Rossi F. Phagocytosis of opsonized yeast induces tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA accumulation and protein release by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Sep;50(3):223–228. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.3.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J., Toma M., Johansson B. E., Wormser G. P. Poorly encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans from patients with AIDS. I: Preliminary observations. AIDS Res. 1986 Summer;2(3):211–218. doi: 10.1089/aid.1.1986.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandes M. E., Wakefield L. M., Wahl S. M. Modulation of monocyte type I transforming growth factor-beta receptors by inflammatory stimuli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19697–19703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuck S. L., Sande M. A. Infections with Cryptococcus neoformans in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 21;321(12):794–799. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909213211205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse K. A., Powell D., Washington I., Poli G., Strebel K., Farrar W., Barstad P., Kovacs J., Fauci A. S., Folks T. M. Monokine regulation of human immunodeficiency virus-1 expression in a chronically infected human T cell clone. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins H. L., Bancroft G. J. Cytokine enhancement of complement-dependent phagocytosis by macrophages: synergy of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1447–1454. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuturi M. C., Murphy M., Costa-Giomi M. P., Weinmann R., Perussia B., Trinchieri G. Independent regulation of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin production by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1581–1594. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Interferon-gamma. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90083-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Erickson N. F., 3rd Chemotaxis of human neutrophils and monocytes induced by Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):380–382. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.380-382.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Clouse K. A., Justement J., Rabson A., Duh E., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2365–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golenbock D. T., Hampton R. Y., Qureshi N., Takayama K., Raetz C. R. Lipid A-like molecules that antagonize the effects of endotoxins on human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19490–19498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. Regulation of capsule synthesis by carbon dioxide. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):508–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI112000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R. A., Song K., Fan N., Chang D. J. The p70 tumor necrosis factor receptor mediates cytotoxicity. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90532-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann D., Gallay P., Barras C., Zaech P., Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S., Glauser M. P., Baumgartner J. D. Control of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding and LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor secretion in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 1;148(11):3505–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Dupont M. P. Phenotypic and functional characterization of human lymphocytes activated by interleukin-2 to directly inhibit growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1490–1498. doi: 10.1172/JCI116354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Dupont M. P., Smail E. H. Direct activity of human T lymphocytes and natural killer cells against Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1994 Jan;62(1):194–202. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.1.194-202.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M. Macrophage-Cryptococcus interactions. Immunol Ser. 1994;60:533–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M., Tabuni A. Binding of Cryptococcus neoformans by human cultured macrophages. Requirements for multiple complement receptors and actin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):528–535. doi: 10.1172/JCI115027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitz S. M. The ecology of Cryptococcus neoformans and the epidemiology of cryptococcosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Nov-Dec;13(6):1163–1169. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.6.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. A., Liu Y., Golenbock D. T. Neither CD14 nor serum is absolutely necessary for activation of mononuclear phagocytes by bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4452–4461. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4452-4461.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macher A. M., Bennett J. E., Gadek J. E., Frank M. M. Complement depletion in cryptococcal sepsis. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1686–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G., Storkus W. J., Dawson J. R. Human natural killer cells do not inhibit growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in the absence of antibody. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):639–645. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.639-645.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina J. M., Schindler R., Ferriani R., Sakaguchi M., Vannier E., Dinarello C. A., Groopman J. E. Production of cytokines by peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):888–893. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. W., Kelley T. G., Gan H., Kandil O., Newman M. J., Pinkston P., Rose R. M., Remold H. G. Concurrent infection of human macrophages with HIV-1 and Mycobacterium avium results in decreased cell viability, increased M. avium multiplication and altered cytokine production. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 15;151(4):2261–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Yancey K. B., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Hefter K., Frank M. M., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A., Gelfand J. A. C5a stimulates secretion of tumor necrosis factor from human mononuclear cells in vitro. Comparison with secretion of interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):443–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Gekker G., Chao C. C., Hu S. X., Edelman C., Balfour H. H., Jr, Verhoef J. Human cytomegalovirus-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells induce HIV-1 replication via a tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated mechanism. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):574–580. doi: 10.1172/JCI115623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettoello-Mantovani M., Casadevall A., Kollmann T. R., Rubinstein A., Goldstein H. Enhancement of HIV-1 infection by the capsular polysaccharide of Cryptococcus neoformans. Lancet. 1992 Jan 4;339(8784):21–23. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90142-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi N., Honovich J. P., Hara H., Cotter R. J., Takayama K. Location of fatty acids in lipid A obtained from lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5502–5504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Ng W., Wilson C. B., McMaster W. R., Burchett S. K. Modulation of in vitro monocyte cytokine responses to Leishmania donovani. Interferon-gamma prevents parasite-induced inhibition of interleukin 1 production and primes monocytes to respond to Leishmania by producing both tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1914–1924. doi: 10.1172/JCI114654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Keller U., Brockhaus M. Release of soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in relation to circulating TNF during experimental endotoxinemia. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1172/JCI115891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Lee T. H. Tumor necrosis factor. New insights into the molecular mechanisms of its multiple actions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7313–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voth R., Rossol S., Klein K., Hess G., Schütt K. H., Schröder H. C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Müller W. E. Differential gene expression of IFN-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with AIDS related complex and AIDS. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):970–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. P., Levitz S. M., Tabuni A., Kornfeld H. HIV-1 envelope protein (gp120) inhibits the activity of human bronchoalveolar macrophages against Cryptococcus neoformans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Dec;146(6):1434–1438. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.6.1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei S., Blanchard D. K., Liu J. H., Leonard W. J., Djeu J. Y. Activation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production from human neutrophils by IL-2 via IL-2-R beta. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 1;150(5):1979–1987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


