Abstract
Malaria infection is accompanied by the production of a number of autoantibodies, including some that react with DNA. Epidemiological evidence implicates these in the nephritides that arise in human quartan malaria and in experimental malaria infections in mice. Through parallels with the involvement of DNA-reactive antibodies in the autoimmune syndrome systemic lupus erythematosus, a role for DNA-reactive antibodies in forming phlogistic immune deposits in the kidneys is implied. To more fully understand the relationship between antibodies of this specificity made in malaria and systemic lupus erythematosus, we prepared monoclonal DNA-reactive antibodies from BALB/c mice infected with Plasmodium berghei (clone RC) and compared their properties with those of other antibodies previously isolated from lupous MRL/Mp lpr/lpr and (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. Antibodies from malarial mice were all immunoglobulin M class and bound to single-stranded but not double-stranded DNA in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. They also reacted with synthetic polyribonucleotides in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and with parasitized erythrocytes and parasite pigment in kidney sections. None of the antibodies from lupous mice had identical specificities. The potential involvement of the DNA-reactive antibodies in malarial nephritis was demonstrated, by use of immunocytochemical methods, on the basis of their binding to existing immune deposits in kidney sections from malarial mice, a similar property having been previously demonstrated for antibodies from lupous mice. Furthermore, antibodies from malarial mice expressed public idiotypes, notably Id.V-88, which is a member of the Id.16/6 family, commonly found on DNA-reactive antibodies in lupus and other infectious and connective tissue diseases. This study indicates that DNA-reactive antibodies in malaria have immunochemical properties similar but not identical to those of such antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and that they have the potential to participate in the formation of immune deposits in nephritic malarial kidneys.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adu D., Williams D. G., Quakyi I. A., Voller A., Anim-Addo Y., Bruce-Tagoe A. A., Johnson G. D., Holborow E. J. Anti-ssDNA and antinuclear antibodies in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):310–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J., Ossi E., Albini B., Sepulveda M., Kano K., Sheffer J., Vasilion P., Marine E., Baliah T., Jockin H. Disseminated immune deposits in lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 May;20(4):962–968. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman K., Termaat R. M., de Jong J., van den Brink H. G., Berden J. H., Smeenk R. J. Cross-reactive binding patterns of monoclonal antibodies to DNA are often caused by DNA/anti-DNA immune complexes. Res Immunol. 1989 Jun-Aug;140(5-6):595–612. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronze-da-Rocha E., Machado C., Staines N. A., Sunkel C. E. Systemic lupus erythematosus murine monoclonal DNA-binding antibodies recognize cytoplasmic and nuclear phosphorylated antigens that display cell cycle redistribution in HEp-2 cells. Immunology. 1992 Dec;77(4):582–591. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Clark I. A. SLE and malaria: another look at an old idea. Parasitol Today. 1990 Aug;6(8):259–261. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Frampton G., Staines N. A., Hobby P., Perry G. J., Cameron J. S. Different mechanisms by which anti-DNA MoAbs bind to human endothelial cells and glomerular mesangial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):68–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel Ribeiro C. T., de Roquefeuil S., Druilhe P., Monjour L., Homberg J. C., Gentilini M. Abnormal anti-single stranded (ss) DNA activity in sera from Plasmodium falciparum infected individuals. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(6):742–746. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton G., Hobby P., Morgan A., Staines N. A., Cameron J. S. A role for DNA in anti-DNA antibodies binding to endothelial cells. J Autoimmun. 1991 Jun;4(3):463–478. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90159-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood B. M., Voller A. Suppression of autoimmune disease in New Zealand mice associated with infection with malaria. I. (NZBxNZW) F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Dec;7(6):793–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V., Allsopp C. E., Kwiatkowski D., Anstey N. M., Twumasi P., Rowe P. A., Bennett S., Brewster D., McMichael A. J., Greenwood B. M. Common west African HLA antigens are associated with protection from severe malaria. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):595–600. doi: 10.1038/352595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V. Immunologic aspects of renal lesions associated with malaria. Kidney Int. 1979 Jul;16(1):3–8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. In vitro demonstration of a particular affinity of glomerular basement membrane and collagen for DNA. A possible basis for a local formation of DNA-anti-DNA complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):428–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazyumba G., Berney M., Brighouse G., Cruchaud A., Lambert P. H. Expression of the B cell repertoire and autoantibodies in human African trypanosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jul;65(1):10–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight A., Sinden R. E. The purification of gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum and P. yoelii nigeriensis by colloidal silica (Percoll) gradient centrifugation. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(4):503–509. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. A., Morgan A., Henderson B., Staines N. A. A key role for fibronectin in the sequential binding of native dsDNA and monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies to components of the extracellular matrix: its possible significance in glomerulonephritis. Immunology. 1985 Feb;54(2):389–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Buchanan R. R., Lew A. M., Olsen I., Staines N. A. Five groups of antigenic determinants on DNA identified by monoclonal antibodies from (NZB X NZW)F1 and MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. Immunology. 1985 May;55(1):75–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namboodiri M. S., Nagpal S., Rao P. V. Induction of anti-DNA IgG and IgE antibodies in BALB/c mice. J Autoimmun. 1992 Oct;5(5):653–663. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90161-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravirajan C. T., Staines N. A. Involvement in lupus disease of idiotypes Id.F-423 and Id.IV-228 defined, respectively, upon foetal and adult MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr DNA-binding monoclonal autoantibodies. Immunology. 1991 Oct;74(2):342–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlinson W. D., Basten A., Hargrave J. C. Clinical significance of changes in serum proteins, immunoglobulins, and autoantibodies in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1987 Jun;55(2):277–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Carr R. I. Anti-DNA activity of IgG F(ab')2 from normal human serum. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Ravirajan C. T., Morgan A., Belcher A. J., Henry A. J., Lake R. A., Smith D. A., Hamblin A. S., Hara M., Adu D. Expression and relationships of seven public idiotypes of DNA-binding autoantibodies on monoclonal antibodies and serum immunoglobulins. Lupus. 1993 Feb;2(1):25–33. doi: 10.1177/096120339300200106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Ward F. J., Denbury A. N., Mitchiner J., Hartley O., Eilat D., Isenberg D. A., Bansal S. Primary sequence and location of the idiotopes of V-88, a DNA-binding monoclonal autoantibody, determined by idiotope scanning with synthetic peptides on pins. Immunology. 1993 Mar;78(3):371–378. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. A., Frampton G., Isenberg D. A., Shoenfeld Y., Akinsola A., Ramzy M., Lilleywhite J., Williams D. G. A common anti-DNA antibody idiotype and anti-phospholipid antibodies in sera from patients with schistosomiasis and filariasis with and without nephritis. J Autoimmun. 1989 Dec;2(6):803–811. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
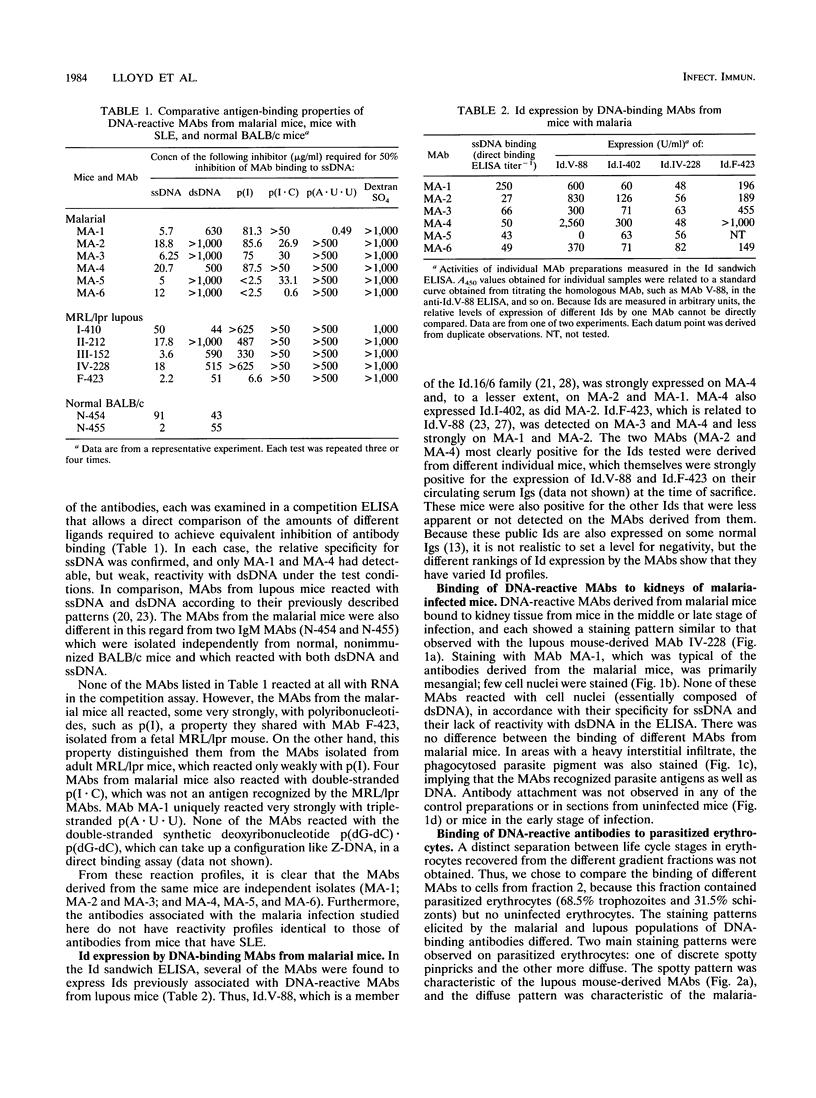
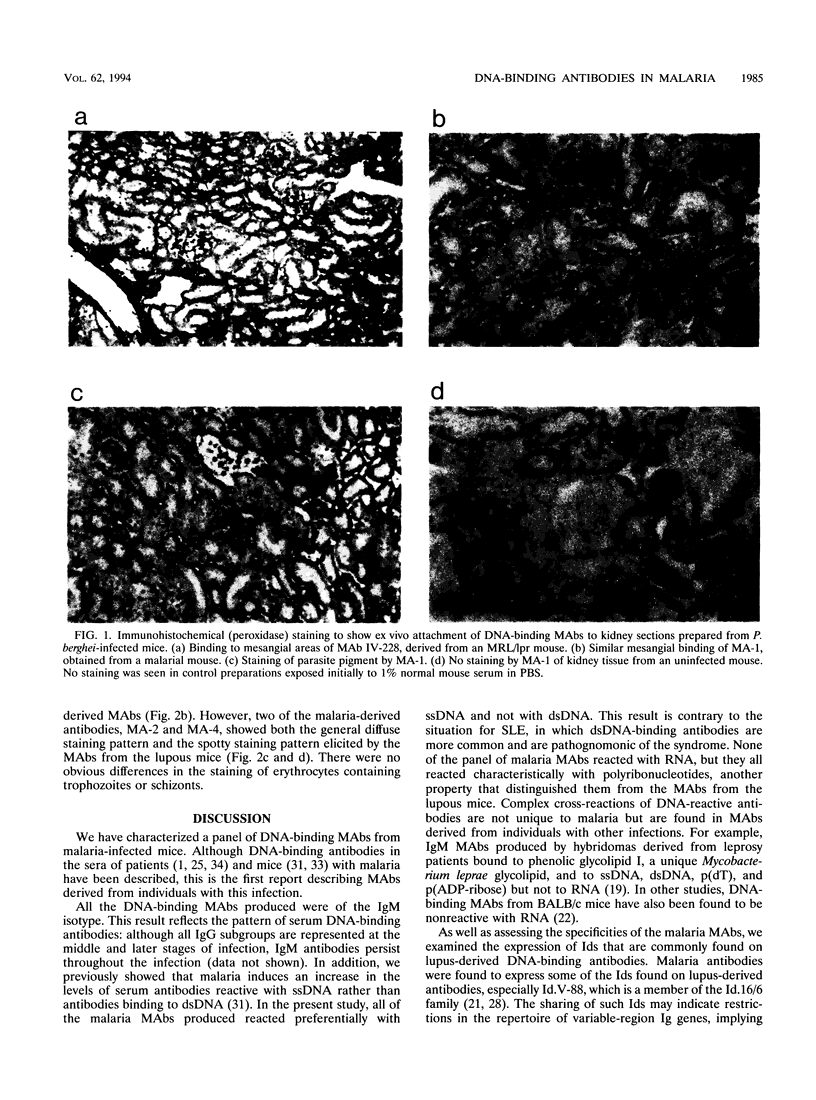
- Wozencraft A. O., Lloyd C. M., Staines N. A., Griffiths V. J. Role of DNA-binding antibodies in kidney pathology associated with murine malaria infections. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2156–2164. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2156-2164.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozencraft A. O., Staines N. A. DNA-binding antibodies and parasitic diseases. Parasitol Today. 1990 Aug;6(8):254–259. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Fossati L., Yoshida M., Abdelmoula M., Herrera S., Merino J., Lambert P. H., Izui S. Igh-C allotype-linked control of anti-DNA production and clonotype expression in mice infected with Plasmodium yoelii. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouali M., Druilhe P., Eyquem A. IgG-subclass expression of anti-DNA and anti-ribonucleoprotein autoantibodies in human malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):273–278. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]