Abstract
A short neuropeptide F (sNPF) precursor and a sNPF receptor (sNPFR) were characterized for the mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. The sNPFR was expressed in CHO-K1 cells, and it exhibited high affinity binding, IC50 ~3–5 nM, for specific sNPFs. sNPF1 potently inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP production by transfected cells, suggesting sNPFR acts via Gi/o. Transcripts for sNPF and sNPFR were present in all body regions of larvae, pupae, and adults, and immunoblots for sNPFR confirmed this distribution in females. Membranes from female heads and thoraces exhibited prototypical high affinity binding for radiolabeled sNPF, indicating sNPFR is a bona fide endogenous receptor.
Keywords: Insect, Drosophila, Aedes aegypti, G protein-coupled receptor, Neuropeptide F, Neuropeptide Y
1. Introduction
The peptide hormone family of short neuropeptide Fs (sNPF) has members identified from a broad range of insect taxa. Initially, sNPFs were isolated from insect tissue extracts based on detection by antisera that recognize the arginine-phenylalanineamide epitope, as for Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decineata [22]), American cockroach (Periplaneta americana [25]), desert locust (Schistocerca gregaria, see [5]), and yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti, see [7; 21]). Later, genomic annotations identified the gene or Expressed Sequence Tag (EST) for sNPFs in the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster [24]), African malaria mosquito (Anopheles gambiae [21]), and Ae. aegypti [7]. These genes encode a single propeptide from which four or five individual sNPFs are processed.
Studies focusing on a few insect species implicate sNPFs in physiological processes related to reproduction and feeding. Injection of the heterologous Led-sNPF1 peptide into female migratory locusts, Locusta migratoria, over several days stimulates ovarian development [3; 5]. In D. melanogaster, manipulation of the sNPF gene affects food consumption in larvae and in adults [14]. Gain-of-function sNPF mutants display increased food intake, resulting in flies larger than the wild type; whereas loss-of-function sNPF mutants exhibit reduced food intake [14]. In a specific, in vitro assay, Aea-sNPF24–11 inhibits peristalsis of the isolated anterior midgut of larval Ae. aegypti [17].
Identification of the cognate receptor for sNPFs is an important step in defining the actions of sNPFs in insects. With the completion of the genome database for D. melanogaster, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) having high sequence similarity to neuropeptide Y receptors in mammals were identified and expressed in heterologous cell systems to determine their peptide ligands. This strategy demonstrated that the sNPF receptor is Drm-NPFR76F (CG7395; GPCR60 [6; 7; 16; 20]). Specifically, Drm-NPFR76F most closely resembles the type 2 neuropeptide Y receptor of mammals (see [6; 9]). Characterization of Drm-NPFR76F allowed in silico identification of a closely-related GPCR in the genome database of An. gambiae [9]. Given that the sNPFs are known for this mosquito, this receptor, termed Ang-sNPFR, provides a useful vantage for comparing signaling components in these two distantly related dipteran species.
Feeding and reproduction are intimately intertwined in the hematophagous life style of some mosquito species. An. gambiae is such an example, and females require a blood meal to initiate vitellogenesis, completion of oogenesis, and subsequent reproductive success. Neuropeptides and peptide hormones are known to regulate aspects of these processes in female mosquitoes [21]. As described above, sNPFs are thought to regulate feeding by D. melanogaster, thus it is likely sNPFs play a role in blood feeding that directly affects reproduction by female An. gambiae and its transmission of Plasmodium parasites and the perpetuation of malaria among humans. The present study sought to characterize the activity of the putative sNPFR and its expression in different life stages and female tissues, along with that of the gene encoding sNPF, in this pernicious species.
Materials and Methods
1. Mosquito rearing, RNA isolation and cDNA synthesis
The colony of Anopheles gambiae (CDC G3 strain) was maintained at 26 ± 1° C under long-day conditions (16 h light, 8 h dark). Larvae were raised in trays with shallow water and fed pulverized Tetramin® daily. Adults had access to 8% fructose, and for egg production, females were given access to anesthetized mice for blood meals.
Body parts or tissues from various stages of An. gambiae or Ae. aegypti were dissected into RNAlater (Ambion) and stored at 4 C or −20 C prior to total RNA isolation. Preparation of total RNA from the different tissues or from dissected body parts was accomplished with the RNAeasy® total RNA extraction kit (Qiagen). Transcript RNA was subsequently converted to cDNA by AMV reverse transcriptase with pd(T)12–18 as primer for 30 min at 42 C, and stopped by treatment at 95 C for 5 min. The resultant cDNAs were stored at 4 C or −20 C prior to use.
2. Cloning sNPF cDNAs
Specific primers for PCR were designed to encompass the predicted open reading frame (ORF) of the gene encoding sNPFs in An. gambiae: forward 5' GAC CAT GTA TCG AAT AAA TCT GAC CAC G 3', and reverse 5' TGC AAA TGA CGA CGA CTG GAT G 3'. The Ang-sNPF ORF product was amplified from female head cDNA by PCR with the primers and the following conditions; initial denaturation for 5 min at 95 C, then amplification for 1 min at 95 C, 1 min at 56 C, 1 min at 72 C for 30 cycles, followed by a 10 min 72 C incubation. PCR products were separated on 1.2% agarose gels, and excised bands were purified using GenElute minus EtBr spin columns (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Purified PCR products were cloned into pCR®II-TOPO with TOP 10 Escherichia coli competent cells (TOPO TA cloning® kit; Invitrogen, Carlsbad CA). Plasmid DNA was purified from picked colonies (QIAprep® spin miniprep kit, QIAGEN Inc., Valencia, CA), and the cDNA clones sequenced at the Integrated Biotech Labs (IBT, University of Georgia, Athens, GA).
A partial cDNA sequence encoding sNPFs was identified using TBLASTN homology searches of the Ae. aegypti EST database (TC# NABP734TR; http://www.tigr.org/tigr-scripts/tgi/T_index.cgi?species=a_aegypti). As above, total RNA prepared from female Ae. aegypti heads was converted to cDNA using a dT anchored primer 5’ GGT TGC AGT GGG TGA ATA GGT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT 3’. To obtain a cDNA clone of the 3’ end of the mRNA encoding sNPFs in this species, a 3’ RACE procedure were used to amplify products from the head cDNA with a gene specific, forward primer 5’ TGC CGG ATA AAC TTT ACA ACG 3’ and an anchor, reverse primer 5’ GGT TGC AGT GGG TGA ATA GG 3’ using the PCR conditions above. The products of interest were TA cloned and sequenced as above. The signal peptides for the translated mosquito sNPF prepropeptide sequences were predicted with the SignalP program (Center for Biological Sequence Analysis, BioCentrum-DTU, Technical University of Denmark, www.cbs.dtu.dk)
3. Ang-sNPF receptor cloning and expression in CHO cells
The nucleotide sequence for the ORF encoding a putative homolog of the D. melanogaster sNPFR (DrmNPFR76F) was identified in the An. gambiae genome database [11], allowing for the design of two specific primers spanning the ORF: forward 5' GAC GCC TCG GAA TGC TGA CG 3' and reverse 5' CGG TTG AAT GTC CTT CGC AAG CTC 3'. The ORF product was amplified by PCR from female head cDNA with these primers and the following conditions; initial denaturation for 5 min at 95 C, then amplification for 1 min at 95 C, 1 min at 56 C, 2 min at 72 C for 30 cycles, followed by a 10 min 72 C incubation. The products of interest were cloned and sequenced as above.
For expression of the putative sNPFR, the cloned PCR products were digested with Eco RI, and the resulting fragment containing the ORF was ligated into the mammalian expression vector pcDNA 3.1(+). The ligated products were transformed into TOP 10 E. coli competent cells, and the plasmid DNA from picked colonies was analyzed for directionality. As described by Garczynski et al. [8], products with the proper orientation were used to transfect CHO-K1 cells, and stable cell lines expressing the putative sNPFR were generated. For clonal selection, approximately 105 cells from the stable lines were plated in 96 well plates, and a series of 10-fold dilutions performed. Growth of selected cells was monitored, and wells containing single colonies were propagated. Clonal lines were analyzed by RT-PCR as above and used for binding and cAMP assays below.
4. Identification of the putative Ae. aegypti sNPFR homolog and ClustalW analysis of the dipteran receptors
The deduced amino acid sequence for the putative sNPFR homolog in An. gambiae was used in TBLASTN homology searches of the Ae. aegypti assembled genome deposited in ENSEMBL (http://pre.ensembl.org/Aedes_aegypti/index.html) to identify and assemble nucleotide sequences for the putative sNPFR ORF. The nucleotide sequences encoding this ORF are located on Supercontigs 1.289 (nt region 1420678 – 1419089) and 1.858 (nt region 412509 – 414098). Prediction of the transmembrane domains, glycosylation sites, and amino acid phosphorylation sites for the homolog sNPFRs in the two mosquitoes was accomplished with programs at the website for the Center for Biological Sequence Analysis (BioCentrum-DTU, Technical University of Denmark, www.cbs.dtu.dk). The deduced amino acid sequences for the mosquito sNPFR homologs were aligned with that of the known D. melanogaster sNPFR using the ClustalW 1.8 program (http://searchlauncher.bcm.tmc.edu/multi-align/multi-align.html). Percent identity and similarity was determined using the sequence manipulation suite at www.ualberta.ca/~stothard/javascript/ident_sim.html.
5. Detection of sNPF and sNPFR transcription by RT-PCR
To determine when and where the Ang-sNPF and Ang-sNPFR genes are expressed, the PCR products from their respective transcripts were amplified from the cDNAs prepared from total RNA isolated from heads, thoraces, and abdomens of An. gambiae life stages (see above) with new sets of gene specific primers. For this analysis, the respective cDNAs from three different cohorts of An. gambiae were subjected to RT-PCR. The following primers that surround a predicted intron were used to obtain an Ang-NPF product: internal forward 5' GCG GTT CGA TCT CCT TCG C 3' and internal reverse 5' GAA CGG CCC CAT CGA AGC C 3'. The following primers were used to obtain the Ang-sNPFR product: internal forward 5’ GAG CTT CCG CTG GCG GGA AC 3’ and internal reverse 5’ CCG TCC CAT TCA AGG CGA CAC C 3’. The same conditions were used for PCR with both primer sets: initial denaturation for 4 min at 95 C, then amplification for 20 sec at 94 C, 20 sec at 65 C, 45 sec at 72 C for 30 cycles, and followed by a 10 min 72 C incubation. PCR products were separated on 1.2% agarose gels and imaged with the GeneGenius documentation station (Synoptics, Inc.; Frederick, MD).
6. Ang-NPFR antiserum production and immunoblots
To develop immunoassays for the detection of the sNPFR in An. gambiae, two rabbits were immunized with a mixed antigen of synthetic peptides from the amino- (ELLRPNSSTVAPPNC) and carboxy- (CFDPSRGRAGTVGGN) terminal regions of Ang-sNPFR that were covalently linked to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (custom peptide synthesis, conjugation, and immunization by Sigma-Genosys, The Woodlands, TX). After testing the sera for immunoreactivity, one serum (rabbit 298, bleed 4) was chosen to use on immunoblots. Membrane extracts were prepared from body parts, tissues, or CHO cells transfected with the Ang-sNPFR cDNA, as described for receptor binding assays. Pelleted membranes were resuspended in reducing sample buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 25% glycerol, 2% SDS, 0.01% bromophenol blue, 5% β -mercaptoethanol; Biorad) and boiled for 10 min. After treatment, the membrane protein samples and MW markers (Magik Markers, Invitrogen) were separated on 10% Tris-glycine gels (BioRad) by electrophoresis (25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine 0.1% SDS, pH 8.3; National Diagnostics) and then tank transferred to methanol-activated polyvinylidine difluoride (PVDF) filters (BioRad) in transfer buffer (25 mM Tris, 192 mM glycine, 20% methanol, pH 8.3; BioRad). After transfer, the PVDF filters were rinsed with Tris-buffered (50 mM, pH 7.5) saline (150 mM) containing 0.1% Tween 20 (TBST) and then blocked with a solution of 2% BSA, 2% non-fat dry milk and 1% goat serum in TBST at 4 C, 1 h. The antiserum (rabbit 298 bleed 4) or preimmune serum was added directly to the blocking solution (final dilution 1:10,000) and incubated at 4 C overnight. After rinsing with TBST, the blots were washed four times, 20 min each, with fresh TBST, and then transferred to fresh blocking solution. Secondary antibody (goat anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to horseradish peroxidase, Sigma) was added to a final dilution of 1:50,000 v/v for incubation 4 h at room temperature. After washing four times, 20 min each, with fresh TBST, the immunoreactive proteins were detected with the ECL™ Western Blotting System (GE Healthcare), and the chemiluminescence was visualized with the GeneGnome system (Synoptics, Inc.).
7. Peptide synthesis and radiolabelling
The amino acid sequences for the processed forms of Ang-sNPFs were deduced from the ORF of the cloned cDNA, and these peptides (see Table 1) and the Aedes head peptides I and III were chemically synthesized (> 80% pure; Dr. Kevin Clark, University of Georgia; [7]). Synthetic forms of Ang-NPF [9] and the Drm-sNPFs (86% pure; Quality Controlled Biochemicals Inc., Hopkinton, MA; Table 1) were obtained, and D-Y0-Drm-sNPF1 (D-YAQRSPSLRLRFamide) was iodinated by a lactoperoxidase—hydrogen peroxide method [4; 7].
Table 1.
Peptide sequences, abbreviations, and activities in radioreceptor assay.
| Abbreviation | Sequence | IC50 (nM)1 |
|---|---|---|
| A. gambiae sNPF2 | ||
| Ang-sNPF1 | AVRSPSLRLRFa | 3.0 |
| Ang-sNPF13–11 | RSPSLRLRFa | 46.7 |
| Ang-sNPF14–11 | SPSLRLRFa | 336.0 |
| Ang-sNPF2 | AIRAPQLRLRFa | 4.9 |
| Ang-sNPF24–11 | APQLRLRFa | 653.0 |
| Ang-sNPF3 | APSQRLRWa | 360.0 |
| Ang-sNPF4 | TIRAPQLRLRFa | 4.5 |
| Ang-sNPF5 | APTQRLRWa | 380.0 |
| Analog | ||
| Ang-sNPF13–11R3A | ASPSLRLRFa | 187.0 |
| A. aegypti Head Peptide3 | ||
| Aea-HPI | pERPhPSLKTRFa | n.a.4 |
| Aea-HPIII | pERPPSLKTRFa | n.a. |
8. Receptor binding assays
Membranes from CHO-K1 cells transfected with Ang-sNPFR cDNA and tissues from adult An. gambiae were prepared using differential centrifugation through sucrose for use in the peptide binding assays and the immunoblots. The Ang-sNPFR expressing CHO cells were grown to confluence in RPMI 1640 medium containing 800 μg /ml G418, and then membranes from these cells were prepared as previously described [9]. The body parts or tissues were dissected into 350 μl of homogenization buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 250 mM sucrose, with one Roche complete mini protease inhibitor tablet /1 ml buffer) and then homogenized in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube first with a motorized pestle and second by passage through an 18 ga needle. The homogenate was centrifuged (2,000 x g) for 2 min at 4 C. The supernatant was transferred to a tube on ice, and another 350 μl of homogenization buffer was added to the pellet for processing as above. After the final spin, the supernatants were pooled, and membranes collected by centrifugation at 34,500 x g for 16 to 18 h at 4 C in a Beckman JA-21 rotor. The pelleted membranes were used for immunoblots (see above) or resuspended in homogenization buffer (30 μl/5 body parts), sheared through a 25-gauge needle, and stored at −80 C for binding assays.
The binding assays were set up as follows. Membranes equivalent to 2 x 105 CHO cells or five body parts were added to a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube containing 100 pM 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1X Hank's Balanced Salt solution, 3% BSA, and protease inhibitor tablet (1 tablet /10 ml buffer) in the presence of various amounts of unlabeled peptide (0 to 1 μM). The binding reaction went for 3 h at room temperature, and tubes were vortexed every 30 min. To end the reaction, the tubes were centrifuged at 14,000 x g for 5 min at 4 C. After the supernatant was aspirated, the pellets were washed three times with ice cold PBS, and then the bottoms of the tubes were cut off and counted on a Packard GammaII counter. The raw counts obtained from the binding assays were converted to percent total binding, and these data were analyzed by non-linear regression analysis with GraphPad Prism software (v3.0 GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA) to obtain curves, IC50 values (the concentration of sNPF that reduces specific binding of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 by 50%), and statistics, including values of R2 and standard errors.
9. Cyclic AMP Assay
Measurement of cyclic AMP in the cytosol of CHO cells expressing Ang-sNPFR was accomplished with the cAMP-Screen Direct kit™ (Applied Biosystems Tropix Division). Cells were seeded into the 96 well tissue culture plate provided in the kit and then grown to confluence (2 days) in RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 800 μg /ml G418. For the assay, cells were washed three times with RPMI 1640 medium and then incubated for 1 h at 37 C in media with or without 10 μ M forskolin, 50 mM Ro-20-1724 (phosphodiesterase inhibitor) and different concentrations (0 to 10 μ M) of Ang-sNPF1 or Ang-sNPF3. After the incubation, cells were washed once with RPMI 1640 and then cytosolic cAMP was measured following the kit instructions. Chemiluminescent signals were measured for 1 s/well on a TR717™ luminometer (Applied Biosystems Tropix Division). The cAMP supplied with the kit was used to generate a standard curve, and data was analyzed using the determination of unknowns from a standard curve function with GraphPad Prism software (v3.0 GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA). Determined values were converted to percent forskolin-stimulated cAMP then analyzed by non-linear regression analysis (as described above) to obtain curves, IC50 values (the concentration of sNPF that reduces forskolin-stimulated cAMP by 50%) and statistics, including values of R2 and standard errors.
Results
1. Analysis of cDNA transcripts encoding sNPFs and sNPFR in mosquitoes
After DNA sequences encoding potential sNPF and sNPFR transcripts were identified in the An. gambiae genome database [9; 21], their cDNAs were characterized from PCR products obtained from cDNAs prepared from heads and abdomens of non-blood fed females. A prepropeptide of 234 amino acids is encoded by the ORF of 705 bp in the Ang-sNPF cDNA (GenBank DQ437578; Fig. 1A). The signal peptide is predicted to encompass the first 22 amino acids, and further processing of the propeptide by proteolysis at mono- or dibasic residue sites and enzymatic amidation at the C-terminus would yield five putative peptide messengers (Fig. 1A and Table 1). Comparison of the sequence for the Ang-sNPF cDNA with that of the putative gene revealed the positions of four introns (Fig 1A).
Figure 1.
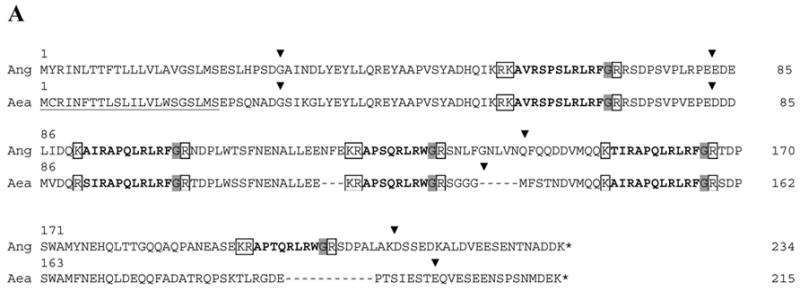
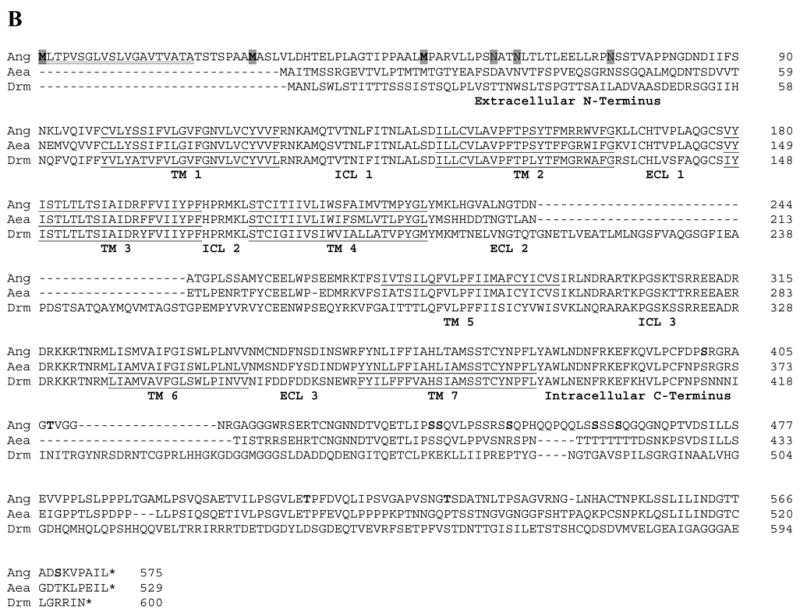
ClustalW alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of the Open Reading Frames (ORFs) of dipteran sNPFs and sNPFRs. (A) Alignment of the deduced sNPF prepropeptides of An. gambiae (GenBank DQ437578) and Ae. aegypti (GenBank DQ459411). The predicted signal peptides are underlined, processed form of sNPFs are in bold, convertase cleavage sites are boxed and C-terminal amide donors are shaded. Locations of introns are denoted by a ▾placed above the amino acid sequences. For the D. melanogaster prepropeptide (CG13968-RA), see [24]. (B) Alignment of the deduced sNPFR ORFs of An. gambiae (Ang; GenBank DQ437579), Ae. aegypti (Aea; ENSEMBL Supercontigs 1.289 and 1.858) and D. melanogaster (Drm; CG7395). The predicted transmembrane domains (TM) are underlined, and intracellular (ICL) and extracellular (ECL) loops labeled. For Ang-SNPFR, predicted start methionines are in bold shaded, signal peptide is double underlined, potential N-glycosylation sites are shaded and phosphorylation sites in bold.
The nucleotide sequence of the Ang-sNPFR cDNA (GenBank DQ437579) has an ORF of 1728 bp with three potential translational start sites having scores of 0.763, 0.692 and 0.598 respectively (scores > 0.5 represent a probable translation start; see [18]; Fig. 1B). Depending on where translation starts, there are three possible forms of the Ang-sNPFR: 575 residues – 62.5 kDa, 548 residues – 60 kDa, or 526 residues – 57.8 kDa. Although the extracellular N-terminus would vary from 49 to 98 amino acids in length, the forms have the same seven predicted transmembrane domains along with the corresponding intracellular and extracellular loops and the intracellular C-terminus of 196 amino acids, consistent with known GPCRs (Fig. 1B). In addition, there are three potential N-glycosylation sites present on the predicted extracellular N-terminus, and nine phosphorylation sites (Fig. 1B). No introns were evident after comparison of the sequence for the Ang-sNPFR cDNA with that of the putative gene.
Putative homologs of the Ang-sNPF and Ang-sNPFR genes were identified with TBLASTN searches of the EST and genome databases for Ae. aegypti. An EST containing a partial 5’ cDNA sequence with similarity to the Ang-sNPF gene was identified in the TIGR database (TC# NABP734TR), which allowed for the PCR amplification and cloning of an Aea-sNPF cDNA with an ORF of 648 bp (GenBank DQ459411). The Aea-sNPF ORF encodes a prepropeptide of 215 amino acids. The signal peptide is predicted to encompass the first 22 amino acids, and further processing of the propeptide as for Ang-sNPF would yield four putative peptide messengers (Fig. 1A and Table 1). Comparison of the sequence for the Aea-sNPF cDNA with that of the putative gene revealed the positions of four introns (Fig 1A).
The putative Aea-sNPFR gene was located in the supercontigs 1.289 and 1.858 of the Ae. aegypti genome database (http://pre.ensembl.org/Aedes_aegypti/index.html). Like the An. gambiae and D. melanogaster sNPFR genes, it does not appear to have introns and has the predicted features of a GPCR. The amino acid sequences for the three dipteran sNPFRs were aligned using the ClustalW program (Fig. 1B). The three sNPFRs share significant sequence identity and similarity. The Ang- and Aea-sNPFRs have 61.5 % identity and 71% similarity, while the Ang-sNPFR shares 39.1% identity and 49.8% similarity with its D. melanogaster counterpart.
2. Analysis of sNPF and sNPFR transcription in mosquito life stages
Based on the results from RT-PCR of cDNAs from three cohorts of An. gambiae, transcript expression of the Ang-sNPF and Ang-sNPFR genes was evident consistently in all body regions of larvae, pupae, and both sexes of An. gambiae (Fig. 2). The presence of both transcripts was more variable in eggs with embryos: Ang-sNPF products were present in two of the three cohorts and Ang-sNPFR products in only one cohort. Due to the lack of introns in the Ang-sNPFR gene, total RNA from all body regions of the life stages was used as template in RT-PCR reactions to test for contamination by genomic DNA. Because no PCR products were detected (Fig. 2, lower panel), the above results for Ang-sNPFR gene expression are supported.
Figure 2.

RT-PCR detection of transcript expression of Ang-sNPF and Ang-sNPFR genes in body regions of An. gambiae life stages. Embryos (E), and heads (H), thoraces (T) and abdomens (A) of 4th instar larvae (L4), pupae, males and non-blood fed females are shown. The size of RT-PCR products for Ang-sNPF is 445 bp and for Ang-sNPFR is 620 bp. The presence (+) or absence (−) of PCR products in each of the three cohorts tested is shown below each representative gel photo panel. Control PCR reactions included template with forward (FP) or reverse (RP) primers only, and primers with no template (NT).
3. Functional assays: competitive binding and inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP
Radioreceptor binding assays were used to establish the functional interaction of Ang-sNPFs and the Ang-sNPFR expressed in CHO cells, and the proximal signaling step resulting from this interaction was revealed with cAMP assays. The first efforts to detect Ang-sNPF binding to CHO cells expressing the Ang-sNPFR were unsuccessful, so the stably transfected cells were clonally selected and transcription of the Ang-sNPFR cDNA was monitored by RT-PCR to obtain a greater proportion of cells presenting the receptor on the membrane surface. Finally, a clonal, stable cell line was established that showed specific Ang-sNPF binding. To verify the suitability of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 as a tracer, membranes from these cells were first tested for the ability to bind the radiolabeled peptide, and its binding was displaced by the addition of Drm-sNPF1 in a concentration-dependent manner (data not shown). Subsequent binding assays with membranes from these cells showed that the Ang-sNPFs displaced this radiolabeled peptide in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 3). The rank order of potency was Ang-sNPF1 ~ Ang-sNPF2 ~ Ang-sNPF4 > Ang-sNPF13-11 > Ang-sNPF13–11R3A> Ang-sNPF14–11 ~ Ang-sNPF3 ~ Ang-sNPF5 > Ang-sNPF24–11 (Table 1). Other peptides having limited sequence similarity, Ang-NPF and Aedes head peptides I and III, did not displace the binding of the radiolabeled peptide to the membranes of Ang-sNPFR expressing cells (data not shown).
Figure 3.
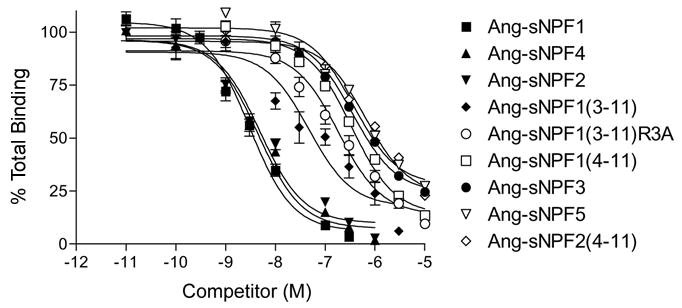
Competitive inhibition of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 binding by Ang-sNPFs to membranes prepared from CHO-K1 cells stably expressing Ang-sNPFR. Membranes were incubated with 100 pM 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 and various concentrations of Ang-sNPF1, Ang-sNPF13–11, Ang-sNPF13–11R3A, Ang-sNPF14–11, Ang-sNPF2, Ang-sNPF24–11, Ang-sNPF3, Ang-sNPF4, and Ang-sNPF5 for 3 h at room temperature. Values indicate means ± S.E. (N=6).
Once the Ang-sNPFs were shown to bind the expressed Ang-sNPFR, the next question to answer was whether this interaction affected cAMP signaling in the CHO-K1 cells expressing this GPCR. This assay was performed directly on the cells seeded and grown in wells of plates that were subsequently assayed for cAMP stimulation or inhibition. Ang-sNPF1 and Ang-sNPF3 failed to stimulate cAMP production in the Ang-sNPFR expressing cells (data not shown). Both, however, inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 4) with IC50 values of 1.5 nM and 196 nM, respectively. These values are consistent with those from the binding assays (Table 1), thus suggesting that the binding of sNPFs to the sNPFR may inhibit cAMP production in target insect cells.
Figure 4.
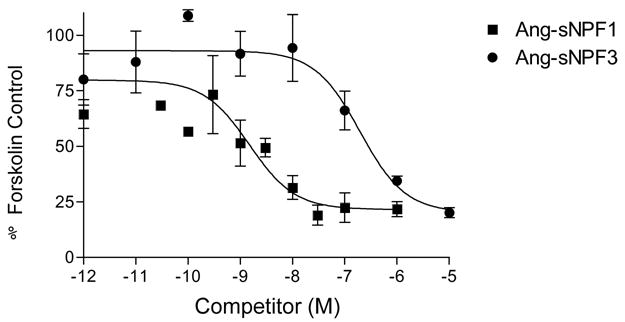
Competitive inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation to CHO-K1 cells expressing Ang-sNPFR by Ang-sNPF1 and Ang-sNPF3. Cells were treated with 10 μM forskolin and various concentrations of Ang-sNPF1 or Ang-sNPF3 for 1 hr at 37 C. Values indicate means ± S.E. (N=3).
4. Detection of Ang-sNPFR by immunoblot analysis
Antisera were produced to specific regions in the N- and C-terminal regions of the sNPFR and used on immunoblots to determine which body regions and tissues of An. gambiae express the Ang-sNPFR. A 50 kDa protein was detected consistently in membrane extracts from heads, thoraces, and abdomens of males and non-blood fed females (Fig. 5A), and the same size band was present in CHO cells expressing the Ang-sNPFR and shown to bind the sNPFs. This immunoreactive protein was most abundant in the thorax extracts of both sexes. A more abundant immunoreactive protein of 60 kDa also was detected in male and female head extracts, and similarly a 30 kDa protein was predominant in abdomen extracts (Fig. 5A). In subsequent immunoblots of more defined regions and tissues of non-blood fed females, these results were verified (Fig. 5B). Again, the 50 kDa form of Ang-sNPFR was present in membrane extracts of all sampled body regions or tissues, except the ovaries. Interestingly, only a single immunoreactive band is evident in abdominal walls, consisting largely of integument, muscles, and fat body (free of other internal organs), and hindgut, and it is most abundant in the dorsal thorax, which is filled with flight muscles, and less so in the ventral thorax. Only this region of the thorax, which contains the thoracic ganglia, and heads with the brain show the 60 kDa immunoreactive band. The immunoreactive 30 kDa band is present only in midgut extracts, suggesting that this form is a product of midgut enzyme degradation. The immunoreactive bands detected by rabbit antibody 298 bleed 4 were not present on immunoblots probed with pre-immune serum (data not shown).
Figure 5.
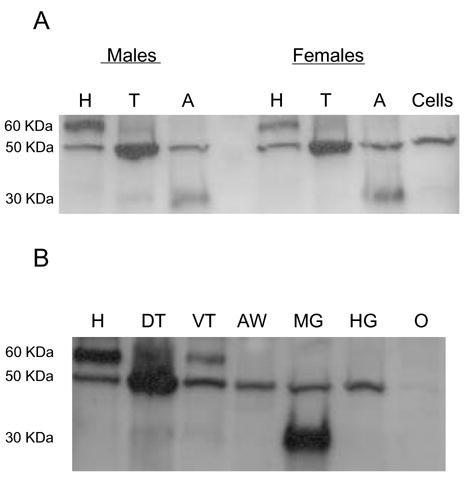
Immunoblot detection of Ang-sNPFR in membrane preparations from body regions and tissues of An. gambiae. Upper panel. Membranes prepared from heads (H), thoraces (T) and abdomens (A) of adult males and non-blood fed females or CHO-K1 cells expressing Ang-sNPFR (Cells). Lower panel. Membranes prepared from heads (H), dorsal thorax (DT), ventral thorax (VT), abdomen wall (AW), midgut (MG), hindgut and Malphigian tubules (HG) and ovaries (O) of non-blood fed females. Apparent protein masses are given to the left of each panel.
5. Competitive binding of sNPFs to membranes prepared from mosquito tissues
The apparent abundance of Ang-sNPFR in the head and thorax of females indicated that membranes prepared from these body regions may be sufficient to demonstrate specific and native sNPF binding in the radioreceptor assay. After a preliminary demonstration of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 binding to these membrane extracts was displaced with 1 μM Ang-sNPF1 (data not shown), it was shown that Ang-sNPF1 and Ang-sNPF3 displaced binding of the radiolabeled peptide to the membranes in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 6), with IC50 values of 0.58 nM and 108 nM, respectively. These values are consistent with those obtained for each peptide in the assays using membranes prepared from CHO cells expressing the Ang-sNPFR (Table 1).
Figure 6.
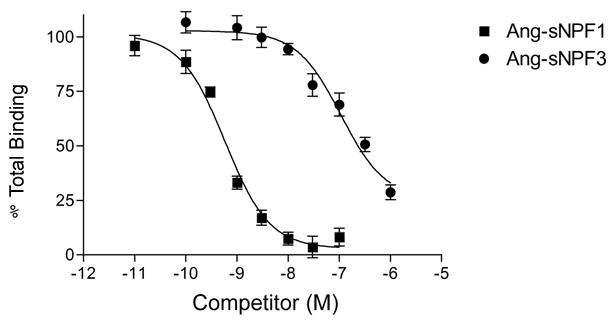
Competitive inhibition of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 binding to membranes prepared from dissected heads and thoraces of non-blood fed An. gambiae females. Membranes were incubated with 100 pM 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 and various concentrations of Ang-sNPF1 or Ang-sNPF3 for 3 h at RT. Values indicate means ± S.E. (N=6).
Discussion
Genes for the sNPF prepropeptide and a candidate sNPFR receptor were identified by homology searches of the genome of An. gambiae (see [7; 9]). The authenticity of the predicted genes now has been confirmed by sequencing their cDNAs obtained from An. gambiae tissues, along with a functional examination of the actions of Ang-sNPFs on Ang-sNPFR. The organization of the Ang-sNPF prepropeptide and its encoding gene in general resembles those of Ae. aegypti (Fig. 1A) and D. melanogaster [24], but there are some differences. The sNPF propeptide of An. gambiae contains five sNPFs whereas those of Ae. aegypti and D. melanogaster contain four sNPFs; for each a straightforward nomenclature [24] has been applied. The canonical GPCR structure is evident for the Ang-sNPFR, as well as its counterparts in D. melanogaster (Drm-NPFR76F; see [6; 7; 16; 20]) and Ae. aegypti (Aea-sNPFR; present report, Fig. 1B). Interestingly, none of the sNPFR ORFs possesses introns. Activities of sNPFs on Drm-NPFR76F have been characterized previously [6; 7; 16; 20]. In the present investigation, radioreceptor assays were used to substantiate Ang-sNPFR as a bona fide receptor for Ang-sNPFs, to examine structure-function relations preliminarily, and to determine binding in native tissues.
Ang-sNPFs vary in their interactions with the Ang-sNPFR, as revealed by their ability to displace binding of 125I-[D-Y0]-Drm-sNPF1 to membranes prepared from stably transfected cells. The labeled Drm-sNPF1 was used for these studies because it exhibited a substantially reduced non-specific binding relative to the corresponding An. gambiae analog (data not shown), and hence was preferred. Among the various An. gambiae sNPFs examined in the radioreceptor assay, two distinctive types of activity were evident (Fig. 3; Table 1). Among full-length sNPFs, peptides comprised of 11 amino acids – sNPF1, sNPF2, and sNPF4 – each exhibited high affinity binding, as judged by an IC50 < 5 nM. In contrast, the shorter sNPF3 and sNPF5, each having 8 residues and a tryptophan-amide C-terminus, exhibited lower affinity, with IC50 values > 100 nM. Such low affinity binding also characterized other forms of Ang-sNPF peptides comprised of fewer than 9 amino acids. Ang-sNPF13–11 exhibited an intermediate IC50 of 46.7 nM, which was diminished substantially for its alanine-substituted analog, Ang-sNPF13–11R3A, indicating an importance of the arginine in position 3 for binding of sNPF1, sNPF2, sNPF4, and Ang-sNPF13–11 to Ang-sNPFR. Because Aea-HPI and Aea-HPIII share limited sequence similarity with the sNPFs, they were tested at concentrations of 1 μM and found to have no activity in the Ang-sNPFR radioreceptor assay (Table 1). The contrasting activities of sNPF1 and sNPF3 also were evident in cAMP assays and in binding studies with mosquito membranes (see below).
Information about structural requirements for binding of sNPFs to sNPFR is relatively sparse. One study [7] examined the D. melanogaster sNPF receptor, Drm-NPFR76F, by a comparable radioreceptor assay using cell membranes. Similar overall findings were observed, but a few differences were notable. Like Ang-sNPFR, Drm-NPFR76F exhibits a clear preference for longer sNPF peptides. In contrast for Drm-NPFR76F, a peptide corresponding to Ang-sNPF13–11 was relatively active; Aea-HPI, but not Aea-HPIII, was weakly active. The findings suggest subtle differences in the selectivity of Drm-NPFR76F compared to Ang-sNPFR.
In other heterologous systems used for expression of Drm-NPFR76F, the profile of sNPF activities varies somewhat according to the methodology (see [7]). One approach has involved co-expression of Drm-NPFR76F in Xenopus oocytes with either the promiscuous G-protein Gα16 [6] or G-protein coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels [20]. When receptor activation is measured by either inwardly directed chloride currents [6] or inwardly directed potassium currents [20], longer Drm-sNPF peptides were found to be both more potent, as judged by EC50, and more effective, at a test dose of 1 μM, than were shorter sNPFs. A similar co-expression scheme in CHO-K1 cells utilized a bioluminescent calcium response as an indicator of Drm-NPFR76F activation [16]. In this system, active Drm-sNPFs tested were approximately equipotent, based on comparable EC50 values. However, the longer Drm-sNPF1 peptide elicited a higher maximum response than the shorter Drm-sNPF3 and sNPF4 peptides.
With the exception of the present study, little is known about downstream signaling events for the insect sNPF receptors. In our system, Ang-sNPF1 potently inhibited forskolin-stimulated cAMP production (Fig. 4), suggesting Ang-sNPFR acts via Gi/o, at least in CHO-K1 cells. Consistent with its rank order in the radioreceptor assay, Ang-sNPF3 was substantially less effective in inhibition of the actions of forskolin (Fig. 4). Structurally, Ang-sNPFR and Drm-NPFR76F most closely resemble the vertebrate neuropeptide Y2 receptor subtype (see [6; 9]). Prototypically, activation of Y2 receptors proceeds via functional coupling to G-proteins of the Gi/o class [13].
Co-expression of sNPF receptors with the promiscuous G-protein Gα16 [6; 16] is useful for screening assays, but is not revealing for signaling partners. With co-expression of Drm-NPFR76F and G-protein coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channels, the insightful observation was made that responses to sNPFs were markedly reduced by pretreatment with pertussis toxin [20]. Such toxin sensitivity is indicative of the involvement of Gi/o-type G-proteins in signaling. Specification of Gi/o as the signaling partner for Ang-sNPFR parallels similar findings with the neuropeptide F receptor from D. melanogaster (Drm-NPFR; [8]), which has a close structural resemblance to Drm-NPFR76F and Ang-sNPFR [9]. Together these results suggest that the apparent conservative evolution of functional coupling across mammalian neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes [13] likely extends to the structurally related receptors of insects.
Expression of the Ang-sNPF gene occurs in all body regions of the life stages examined for An. gambiae, as judged from the detection of corresponding transcripts by RT-PCR (Fig. 2), and presumably, this expression reflects the distribution of the nervous system in all body regions. Such an occurrence of sNPFs has been reported for other insects. In a recent study of D. melanogaster by Lee et al. [14], Northern blots and immunoblots of whole body extracts showed that the Drm-NPF gene is expressed in all life stages. Furthermore, sNPFs were localized in specific cells in all regions of the nervous system, including thoracic neurohemal glands, as revealed by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. There was no mention that the gut of this insect was examined for Drm-sNPF transcripts, but it was reported that no immunoreactive cells were observed in the adult gut. Application of tandem mass spectrometry to D. melanogaster found predicted sNPF masses in extracts of pooled CNS of wandering larvae [1; 2], as well as individual nerve tissues and abdominal neurohemal organs [19] and body and hemolymph [7] of adult flies. The localization of sNPFs in neurohemal organs and hemolymph indicates that these peptides likely function as hormones, in addition to possible roles as neuromodulators, but no direct effect on a specific process has been reported for D. melanogaster.
Earlier structural characterizations of sNPFs resulted from the isolation of peptides from extracts of brains from L. decineata [22] and S. gregaria (see [5]), abdomens from Ae. aegypti (M. Brown, unpublished data cited in [21]), and midguts from P. americana [25]. In contrast, sNPFs were absent from nervous system extracts of diapausing L. decineata, but present in ones for non-diapausing beetles [12]. The GGRSPSLRLRFa sequence of a peptide isolated from the nervous system of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus [10], suggests that the sNPF family occurs in other arthropods as well.
As revealed by RT-PCR (Fig. 2), the pattern of Ang-sNPFR gene expression, in general, resembled that of Ang-sNPF in the life stages of An. gambiae, although variability of incidence was evident in eggs and in heads of larvae. Prior information about sNPF receptor distribution in insects is limited to the detection of transcripts for D. melanogaster. Transcripts for Drm-NPFR76F were detected by RT-PCR in brain, Malpighian tubules, fat body and gut of larvae, and in heads, bodies, and ovaries of adults [16]. Northern blots revealed such transcripts in heads, bodies, and appendages (legs and antennae) of adult flies, and the transcripts also were localized in the peripheral and central nervous system of embryos [6].
Most importantly, the expression of the Ang-sNPFR gene in mosquito tissues was confirmed with the detection of the encoded protein in corresponding tissues subjected to immunoblots with an antiserum produced specifically for this GPCR. In both males and females, an immunoreactive protein of 50 kDa size was detected in membrane extracts of heads, thoraces, and abdomens (Fig. 5 upper panel). A single immunostained band of the same size was present in membranes of Ang-sNPFR cDNA transfected CHO-K1 cells (Fig. 5 upper panel), used as a positive control. In a more detailed examination of protein expression in females, a corresponding immunoreactive band was most abundant in the dorsal thorax, which is packed with flight muscles, and was less but consistently present in head, ventral thorax, abdomen wall, midgut, and hindgut, but was absent from ovary (Fig. 5 lower panel; note that same number of tissue equivalents were loaded in each lane).
An immunoreactive protein of larger molecular weight was present only in heads and ventral thorax of females (Fig. 5 lower panel), both of which contain the largest ganglia of the nervous system. Because the sNPFR ORF contains three predicted start codons (Fig. 1B), this larger immunoreactive band may represent another form of the receptor. Tissue-specific usage of alternative start codons by nervous tissue [23] could produce proteins of such a size; however, identification of this larger band as an authentic sNPFR would require further protein purification and N-terminal sequencing for confirmation. In contrast, an immunoreactive protein of lower molecular weight was detected only in abdomens (midguts present; Fig. 5 upper panel) or midguts alone (Fig 5 lower panel). This lower immunoreactive band was greatly reduced in immunoblots when the amount of protease inhibitor was increased during preparation of abdomen/midgut membranes (data not shown), suggesting that proteases readily degrade GPCRs of interest in such tissues.
Because of the apparent abundance of Ang-sNPFR in head and thoraces of females, membranes from these body regions were subjected to radioreceptor analysis; selection of these regions also avoided complications from protease degradation. Prototypical high affinity binding of radiolabeled sNPF was exhibited by these preparations (Fig. 6); each data point required membranes from only five head/thorax equivalents. sNPF1 was a potent inhibitor of the binding of labeled peptide to tissue membranes (IC50 ~ 0.6 nM), with sNPF3 less effective (IC50 > 100 nM). The relative activities of sNPF1 and sNPF3 resembled those observed for CHO-K1 cells in the radioreceptor assay and in inhibition of the actions of forskolin. These consistent similarities suggest that the binding observed for native membranes from adult An. gambiae reflects the presence of an authentic, endogenous sNPFR. A robust degree of binding of label also offers the possibility of further investigations of sNPFR in its native state, by techniques such as receptor autoradiography. Furthermore, these findings will advance future studies to discover the roles of sNPFs and their receptor in the regulation of feeding and reproduction in this hematophagous dipteran.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Kevin Clark for syntheses of sNPF peptides and Mr. Cory Lee for assistance with cell culture. This work was supported by grants to M.R.B. from the Georgia Experiment Station (GEO00786) and National Institutes of Health (AI33108).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errorsmaybe discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Baggerman G, Boonen K, Verleyen P, De Loof A, Schoofs L. Peptidomic analysis of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system by two-dimensional capillary liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2005;40(2):250–60. doi: 10.1002/jms.744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Baggerman G, Cerstiaens A, De Loof A, Schoofs L. Peptidomics of the larval Drosophila melanogaster central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(43):40368–74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206257200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cerstiaens A, Benfekih L, Zouiten H, Verhaert P, De Loof A, Schoofs L. Led-NPF-1 stimulates ovarian development in locusts. Peptides. 1999;20(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(98)00152-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Crim JW, Garczynski SF, Brown MR. Approaches to radioiodination of insect neuropeptides. Peptides. 2002;23(11):2045–51. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(02)00192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.De Loof A, Baggerman G, Breuer M, Claeys I, Cerstiaens A, Clynen E, Janssen T, Schoofs L, Vanden Broeck J. Gonadotropins in insects: an overview. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2001;47(3):129–38. doi: 10.1002/arch.1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Feng G, Reale V, Chatwin H, Kennedy K, Venard R, Ericsson C, Yu K, Evans PD, Hall LM. Functional characterization of a neuropeptide F-like receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18(2):227–38. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garczynski SF, Brown MR, Crim JW. Structural studies of Drosophila short neuropeptide F: occurrence and receptor binding activity. Peptides. 2006;27(3):575–82. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2005.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garczynski SF, Brown MR, Shen P, Murray TF, Crim JW. Characterization of a functional neuropeptide F receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides. 2002;23(4):773–80. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00647-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garczynski SF, Crim JW, Brown MR. Characterization of neuropeptide F and its receptor from the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Peptides. 2005;26(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gaus G, Doble KE, Price DA, Greenberg MJ, Lee TD, Battelle BA. The sequences of five neuropeptides isolated from Limulus using antisera to FMRFamide. Biol Bull. 1993;184(3):322–9. doi: 10.2307/1542450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hill CA, Fox AN, Pitts RJ, Kent LB, Tan PL, Chrystal MA, Cravchik A, Collins FA, Robertson HM, Zwiebel LJ. G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Anopheles gambiae. Science. 2002;298(5591):176–8. doi: 10.1126/science.1076196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hubrechts J, De Loof A, Schoofs L. Diapausing Colorado potato beetles are devoid of short neuropeptide F I and II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317(3):909–16. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Larhammar D, Salaneck E. Molecular evolution of NPY receptor subtypes. Neuropeptides. 2004;38(4):141–51. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2004.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee KS, You KH, Choo JK, Han YM, Yu K. Drosophila short neuropeptide F regulates food intake and body size. J Biol Chem. 2004;49(3):50781–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407842200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Matsumoto S, Brown MR, Crim JW, Vigna SR, Lea AO. Isolation and primary structure of neuropeptides from the mosquito, Aedes aegypti, immunoreactive to FMRFamide antiserum. Insect Biochem. 1989;19:277–83. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mertens I, Meeusen T, Huybrechts R, De Loof A, Schoofs L. Characterization of the short neuropeptide F receptor from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;297(5):1140–48. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Onken H, Moffett SB, Moffett DF. The anterior stomach of larval mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti): effects of neuropeptides on transepithelial ion transport and muscular motility. J Exp Biol. 2004;207(21):3731–9. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pedersen AG, Nielsen H. Neural network prediction of translation initiation sites in eukaryotes: perspectives for EST and genome analysis. ISMB. 1997;5:226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Predel R, Wegener C, Russell WK, Tichy SE, Russell DH, Nachman RJ. Peptidomics of CNS-associated neurhemal systems of adult Drosophila melanogaster: a mass spectrometric survey of peptides from individual flies. J Comp Neurol. 2004;474(3):379–92. doi: 10.1002/cne.20145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reale V, Chatwin HM, Evans PD. The activation of G-protein gated inwardly rectifying K+ channels by a cloned Drosophila melanogaster neuropeptide F-like receptor. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19(3):570–6. doi: 10.1111/j.0953-816x.2003.03141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Riehle MA, Garczynski SF, Crim JW, Hill CA, Brown MR. Neuropeptides and peptide hormones in Anopheles gambiae. Science. 2002;298(5591):172–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1076827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Spittaels K, Verhaert P, Shaw C, Johnston RN, Devreese B, Van Beeumen J, De Loof A. Insect neuropeptide F (NPF)-related peptides: isolation from Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) brain. Insect Biochem Molec Biol. 1996;26(4):375–82. doi: 10.1016/0965-1748(95)00104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Suckow AT, Sweet IR, Van Yserloo B, Rutledge EA, Hall TR, Waldrop M, Chessler SD. Identification and characterization of a novel isoform of the vesicular γ -aminobutyric acid transporter with glucose-regulated expression in rat islets. J Molec Endocrinol. 2006;36(1):187–99. doi: 10.1677/jme.1.01866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vanden Broeck J. Neuropeptides and their precursors in the fruitfly, Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides. 2001;22(2):241–54. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(00)00376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Veenstra JA. Isolation of a novel RFamide peptide from the midgut of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;213(2):519–24. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


