Abstract
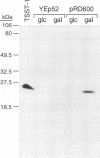
In order to search for an occult cytotoxic enzymatic activity of the toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 (TSST-1), we placed the gene encoding TSST-1 (tstH) under the control of an inducible promoter in the eukaryotic yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Under similar circumstances, the known bacterial enzymatic cytotoxins Shiga-like toxin and diphtheria toxin are both highly lethal to the yeast host. Although full-length stable TSST-1 was demonstrated within the yeast cells and although it retained mitogenicity for human T cells, it had no apparent effect on the yeast cells' growth kinetics or on their gross morphology. Retrieval and sequencing of the toxin gene revealed the wild-type sequence throughout, thus demonstrating that the apparent lack of toxicity for the yeast cells was not due to a serendipitous attenuating mutation within the coding region of the toxin gene. Similar results obtained after a second transformation of the same strain and after transformation of an unrelated strain demonstrate that neither chance permissive host mutation nor intrinsic host resistance was likely to have obscured an existing cytotoxic property of TSST-1. We conclude that TSST-1 probably does not possess a discrete enzymatic property cytotoxic for eukaryotic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomster-Hautamaa D. A., Kreiswirth B. N., Kornblum J. S., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequence of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15783–15786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohach G. A., Fast D. J., Nelson R. D., Schlievert P. M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illnesses. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):251–272. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deresiewicz R. L., Calderwood S. B., Robertus J. D., Collier R. J. Mutations affecting the activity of the Shiga-like toxin I A-chain. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3272–3280. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drumm A., de Azavedo J. C., Arbuthnott J. P. Damaging effect of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 on chick embryo cells in vitro. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S275–S281. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R. W., White W., Nicholson-Weller A. Decay-accelerating factor expression on either effector or target cells inhibits cytotoxicity by human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):2055–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A., Schlossman D., Welsh P., Hertler A., Withers D., Johnston S. Selection and characterization of ricin toxin A-chain mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):415–420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H., Coburn J., Collier R. J. The eukaryotic host factor that activates exoenzyme S of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a member of the 14-3-3 protein family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2320–2324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., Bergdoll M. S., MacDonald H. S., Vellinga J., Reiser R. Study of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin in human epithelial cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):535–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushnaryov V. M., MacDonald H. S., Reiser R., Bergdoll M. S. Staphylococcal toxic shock toxin specifically binds to cultured human epithelial cells and is rapidly internalized. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):566–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.566-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. K., Deringer J. R., Kreiswirth B. N., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Fluid replacement protection of rabbits challenged subcutaneous with toxic shock syndrome toxins. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):879–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.879-884.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. K., Kreiswirth B. N., Deringer J. R., Projan S. J., Eisner W., Smith B. L., Carlson E., Novick R. P., Schlievert P. M. Nucleotide sequences and biologic properties of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 from ovine- and bovine-associated Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;165(6):1056–1063. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.6.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. K., Vercellotti G. M., Deringer J. R., Schlievert P. M. Effects of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 on aortic endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):711–719. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J. Mediators in the pathogenesis of toxic shock syndrome: overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S263–S269. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. B., Broach J. R. Propagation and expression of cloned genes in yeast: 2-microns circle-based vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:234–279. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85024-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M., Shands K. N., Dan B. B., Schmid G. P., Nishimura R. D. Identification and characterization of an exotoxin from Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic-shock syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):509–516. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaizumi M., Mekada E., Uchida T., Okada Y. One molecule of diphtheria toxin fragment A introduced into a cell can kill the cell. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]