Abstract
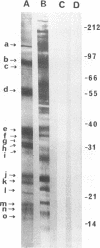
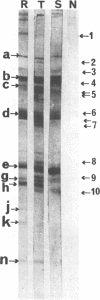
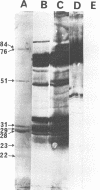
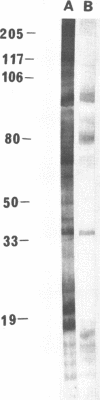
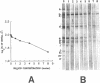
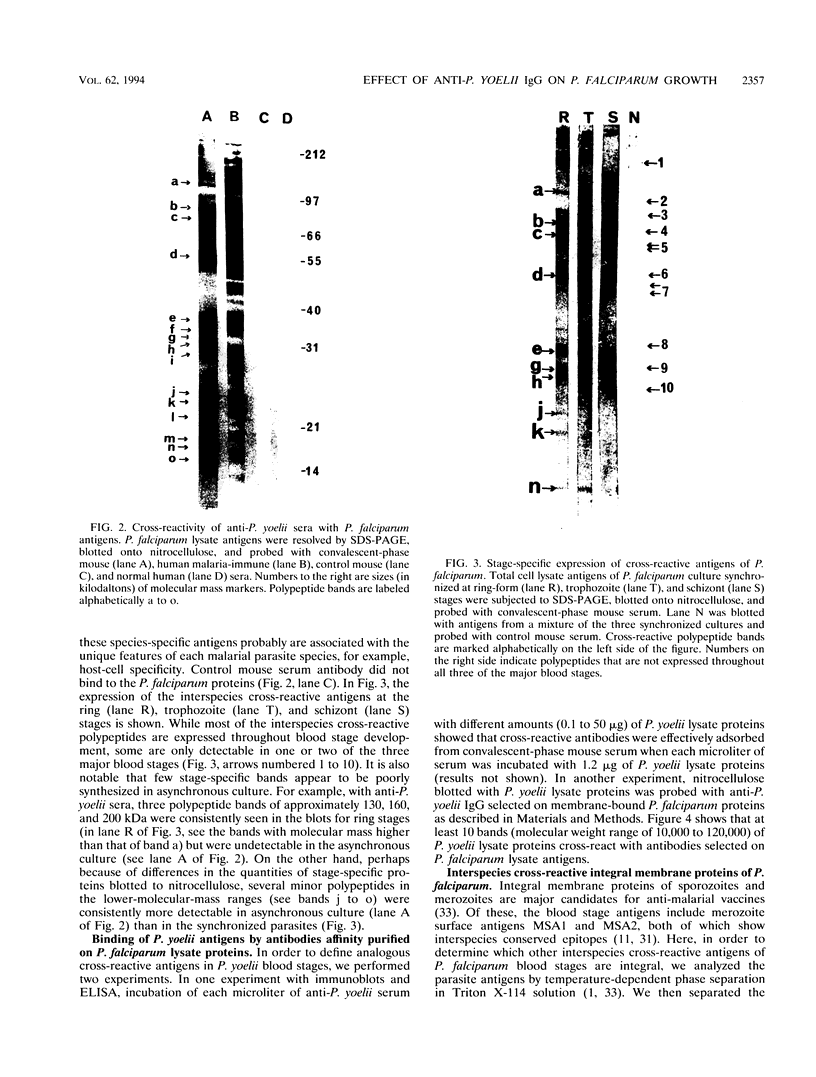
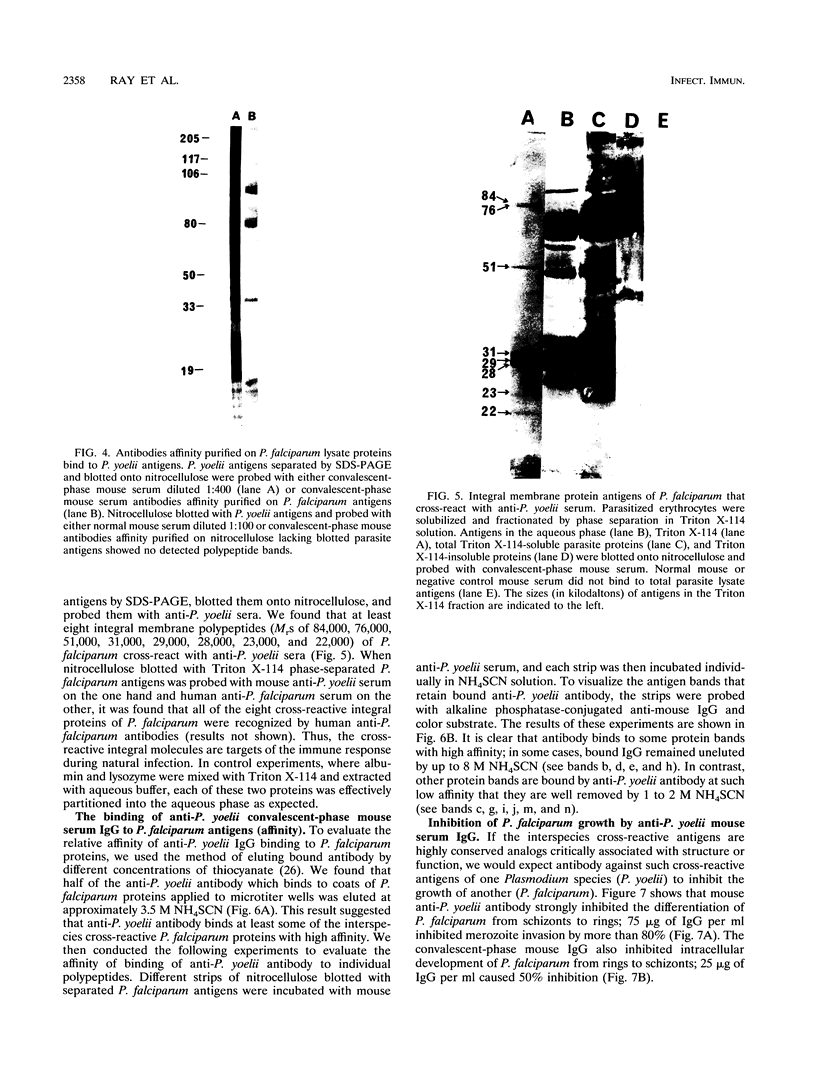
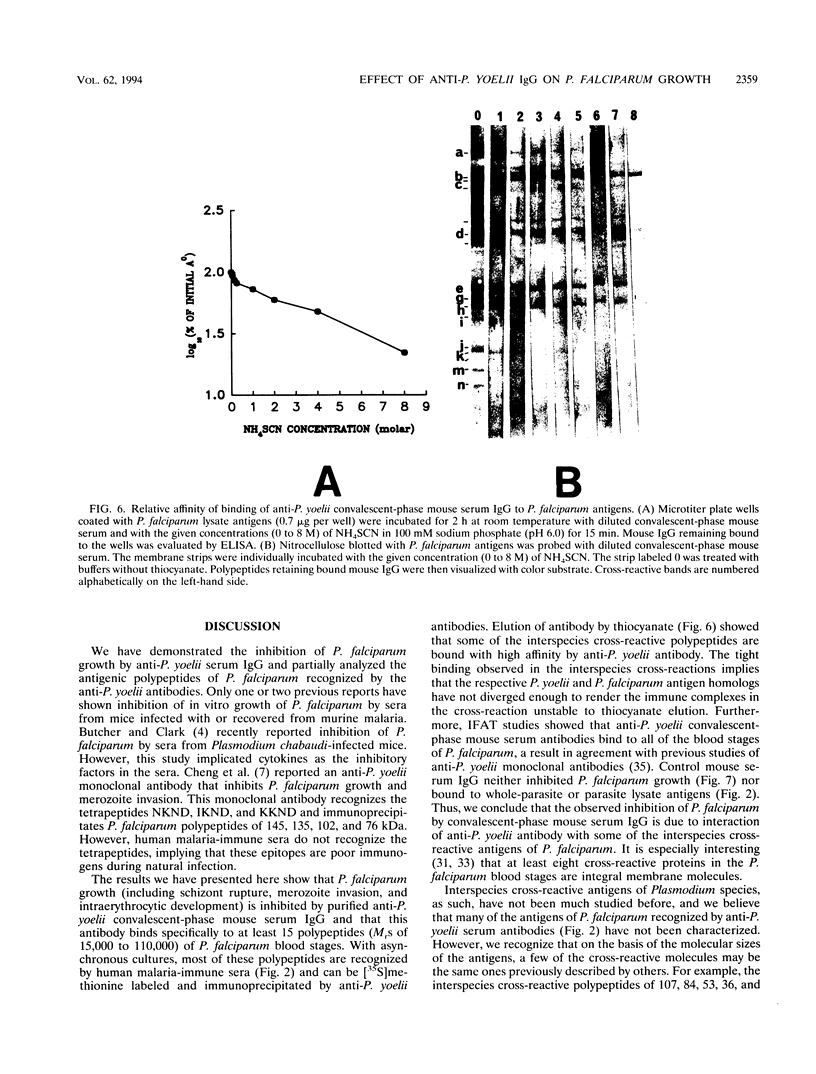
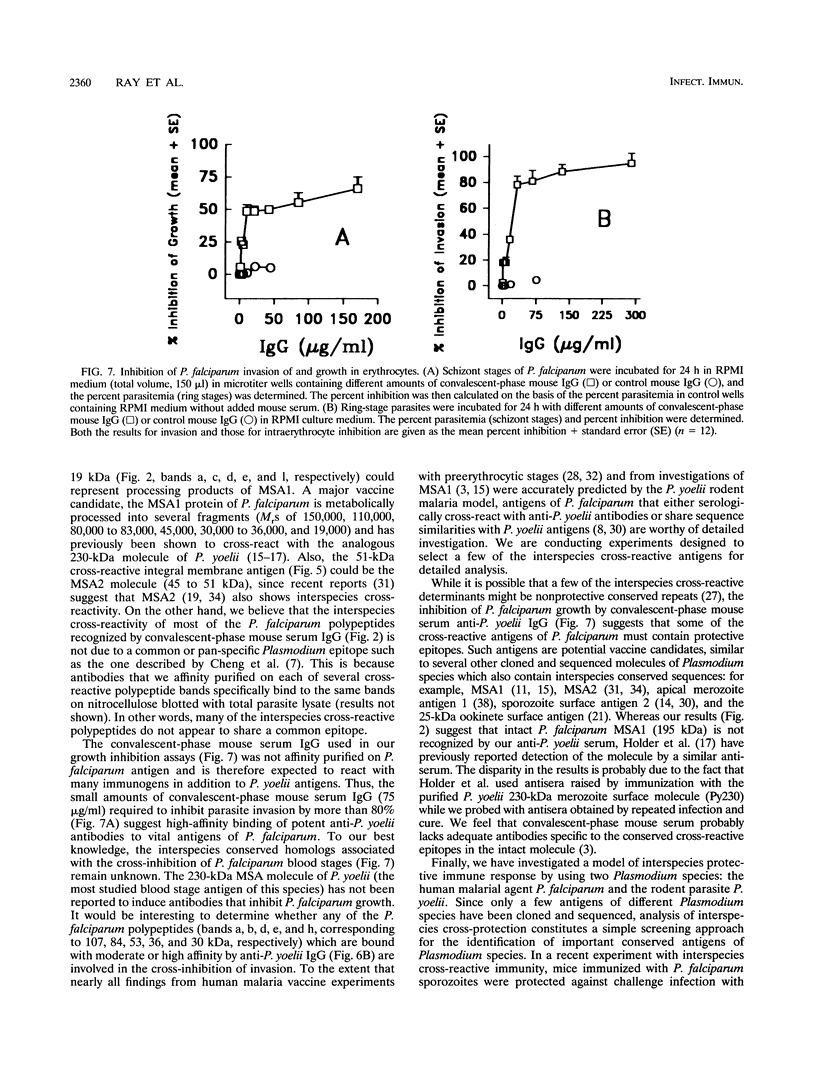
We demonstrated that antibodies in the serum of BALB/c mice convalescent from Plasmodium yoelii infection inhibit the in vitro growth of Plasmodium falciparum. Blood stage P. falciparum antigens that cross-react with the convalescent-phase mouse serum antibodies were identified and partially characterized. Convalescent-phase mouse serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) reacted with P. falciparum lysates at up to a 1:15,000 dilution of the immune sera and bound to P. falciparum-parasitized erythrocytes at up to a 1:5,000 dilution of the sera. The cross-reactive moieties of antigens in parasite lysates were resistant to oxidation by periodate but sensitive to trypsinization. About 15 polypeptides (M(r)s of 15,000 to 110,000) of P. falciparum blood stages were recognized by the convalescent-phase mouse anti-P. yoelii sera; many of these antigens were metabolically 35S labeled and specifically immunoprecipitated. Also, virtually all of the cross-reactive antigens were recognized by human malaria-immune sera. The anti-P. yoelii serum antibodies bound, with high affinity, to at least five of the cross-reactive antigens (M(r)s of 107,000, 84,000, 53,000, 36,000, and 30,000). By phase separation in Triton X-114, eight interspecies cross-reactive antigens (M(r)s of 84,000, 76,000, 51,000, 31,000, 29,000, 28,000, 23,000, and 22,000) were found to be integral membrane proteins. Convalescent-phase mouse serum IgG strongly inhibited the differentiation of P. falciparum from schizonts to rings; 75 micrograms of IgG per ml caused 80% inhibition of release of merozoites and their invasion into erythrocytes. On the other hand, the anti-P. yoelii serum antibodies also inhibited intracellular development of P. falciparum from rings to schizonts; 25 micrograms of IgG per ml caused 50% inhibition. Inhibition of P. falciparum growth by anti-P. yoelii serum IgG suggests that some of the interspecies cross-reactive antigens contain important conserved epitopes and induce protective antibodies against P. falciparum.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle D. B., Newbold C. I., Wilson R. J., Brown K. N. Intraerythrocytic development and antigenicity of Plasmodium falciparum and comparison with simian and rodent malaria parasites. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Nov;9(3):227–240. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J. M., Jr, Parke L. A., Daly T. M., Cavacini L. A., Weidanz W. P., Long C. A. A protective monoclonal antibody recognizes a variant-specific epitope in the precursor of the major merozoite surface antigen of the rodent malarial parasite Plasmodium yoelii. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;142(8):2835–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Clark I. A. The inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum growth in vitro by sera from mice infected with malaria or treated with TNF. Parasitology. 1990 Dec;101(Pt 3):321–326. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000060509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami C., Frevert U., Sinnis P., Takacs B., Clavijo P., Santos M. J., Nussenzweig V. The basolateral domain of the hepatocyte plasma membrane bears receptors for the circumsporozoite protein of Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan V. S., Chatterjee S., Johar P. K. Synthetic peptides based on conserved Plasmodium falciparum antigens are immunogenic and protective against Plasmodium yoelii malaria. Parasite Immunol. 1993 Apr;15(4):239–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1993.tb00606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Q., Jones G., Liu E. X., Kidson C., Saul A. Identification of a common Plasmodium epitope (CPE) recognised by a pan-specific inhibitory monoclonal antibody. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Nov;49(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90131-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan G., Krishna S., Crisanti A., Robson K. Expression of thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites. Lancet. 1992 Jun 6;339(8806):1412–1413. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Thomas A. W., Inge P. M., Cohen S. Stage-specific protein synthesis by asexual blood stage parasites of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 May;8(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone G. L., Winguth S. D. Immunoprecipitation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:688–700. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco Da Silveira J., Sibilli L., Brunet E., Mercereau-Puijalon O. Cloning of cDNAS that code for Plasmodium chabaudi antigens of the erythrocytic forms and cross-hybridize with P. falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:133–143. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R. C., Campbell J. R., Leef M. L., Charoenvit Y., Carter M., Sedegah M., Beaudoin R. L., Hoffman S. L. A malaria sporozoite surface antigen distinct from the circumsporozoite protein. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68 (Suppl):152–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. Biosynthesis and processing of a Plasmodium falciparum schizont antigen recognized by immune serum and a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1528–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R., Newbold C. I. Serological cross-reaction between high molecular weight proteins synthesized in blood schizonts of Plasmodium yoelii, Plasmodium chabaudi and Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Nov;9(3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A. The precursor to major merozoite surface antigens: structure and role in immunity. Prog Allergy. 1988;41:72–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Aikawa M., Atkinson C. T., Ballou W. R., Chen G. X., Li J., Meis J. F., Sina B., Wright C., Zhu J. D. Non-CS pre-erythrocytic protective antigens. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. L., Edmundson H. M., Lord R., Spencer L., Mollard R., Saul A. J. Immunological fine structure of the variable and constant regions of a polymorphic malarial surface antigen from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Sep;48(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamboj K. K., Barnwell J. W., Nussenzweig R. S., Cochrane A. H. Characterization of cross-reactive blood-stage antigens of the Plasmodium cynomolgi complex using anti-Plasmodium vivax monoclonal antibodies. J Parasitol. 1988 Jun;74(3):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow D. C., Syin C., McCutchan T. F., Miller L. H. Comparison of the primary structure of the 25 kDa ookinete surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium gallinaceum reveal six conserved regions. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 15;33(3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kironde F. A., Kumar A., Nayak A. R., Kraikov J. L. Antibody recognition and isoelectrofocusing of antigens of the malaria parasite Plasmodium yoelii. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3909–3916. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3909-3916.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald R. A., Hosking C. S., Jones C. L. The measurement of relative antibody affinity by ELISA using thiocyanate elution. J Immunol Methods. 1988 Feb 10;106(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moelans I. I., Schoenmakers J. G. Crossreactive antigens between life cycle stages of plasmodium falciparum. Parasitol Today. 1992 Apr;8(4):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(92)90278-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardin E. H., Nussenzweig R. S. T cell responses to pre-erythrocytic stages of malaria: role in protection and vaccine development against pre-erythrocytic stages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:687–727. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy R., Reese R. T. A role for carbohydrate moieties in the immune response to malaria. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1952–1955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers W. O., Malik A., Mellouk S., Nakamura K., Rogers M. D., Szarfman A., Gordon D. M., Nussler A. K., Aikawa M., Hoffman S. L. Characterization of Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite surface protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9176–9180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul A., Lord R., Jones G. L., Spencer L. Protective immunization with invariant peptides of the Plasmodium falciparum antigen MSA2. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):208–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe J. A., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Ramasamy R., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Identification of two integral membrane proteins of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe J. A., Peterson M. G., Coppel R. L., Saul A. J., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Structural diversity in the 45-kilodalton merozoite surface antigen of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Mar;39(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90061-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. W., Kim K. J., Munoz P. A., Evans C. B., Asofsky R. Monoclonal antibodies to stage-specific, species-specific, and cross-reactive antigens of the rodent malarial parasite, Plasmodium yoelii. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):563–570. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.563-570.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters A. P., Thomas A. W., Deans J. A., Mitchell G. H., Hudson D. E., Miller L. H., McCutchan T. F., Cohen S. A merozoite receptor protein from Plasmodium knowlesi is highly conserved and distributed throughout Plasmodium. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17974–17979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. M., Oppenheim J. D., Vanderberg J. P. Plasmodium falciparum: assay in vitro for inhibitors of merozoite penetration of erythrocytes. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Jun;51(3):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Portillo H. A., Longacre S., Khouri E., David P. H. Primary structure of the merozoite surface antigen 1 of Plasmodium vivax reveals sequences conserved between different Plasmodium species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4030–4034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]