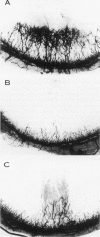
Abstract
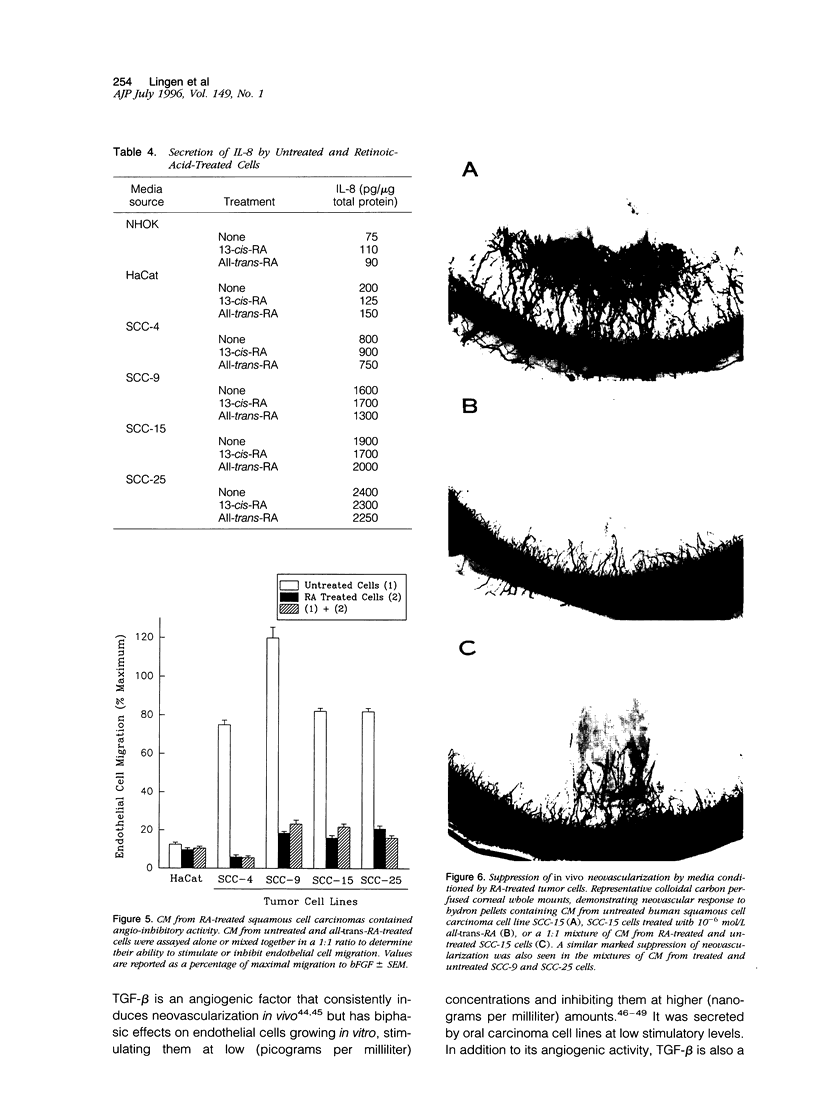
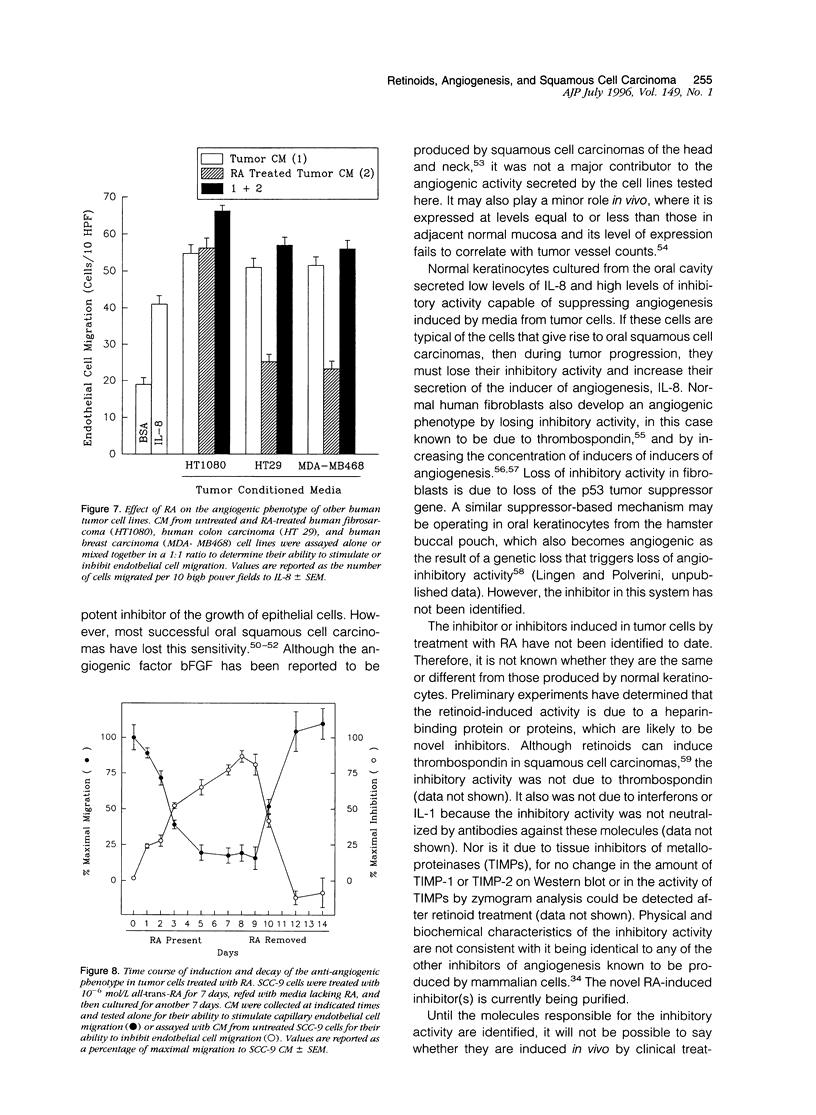
Retinoids have shown great promise as chemopreventive against the development of squamous cell carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract. However, the exact mechanism by which they block new tumors from arising is unknown. Here, we report that 13-cis- and all-trans-retinoic acid, used at clinically achievable doses of 10(-6) mol/L or less, can directly and specifically affect cell lines cultured from oral squamous cell carcinomas, inducing them to switch from an angiogenic to an anti-angiogenic phenotype. Although retinoic-acid-treated and untreated tumor cells make the same amount of interleukin-8, the major inducer of neovascularization produced by such tumor lines, they vary in production of inhibitory activity. Only the retinoic-acid-treated cells produce a potent angio-inhibitory activity that is able to block in vitro migration of endothelial cells toward tumor cell conditioned media and to halt neovascularization induced by such media in the rat cornea. Anti-angiogenic activity is induced in the tumor cells by low doses of retinoids in the absence of toxicity with a kinetics that suggest that it could be contributing to the effectiveness of the retinoids as chemopreventive agents.
Full text
PDF


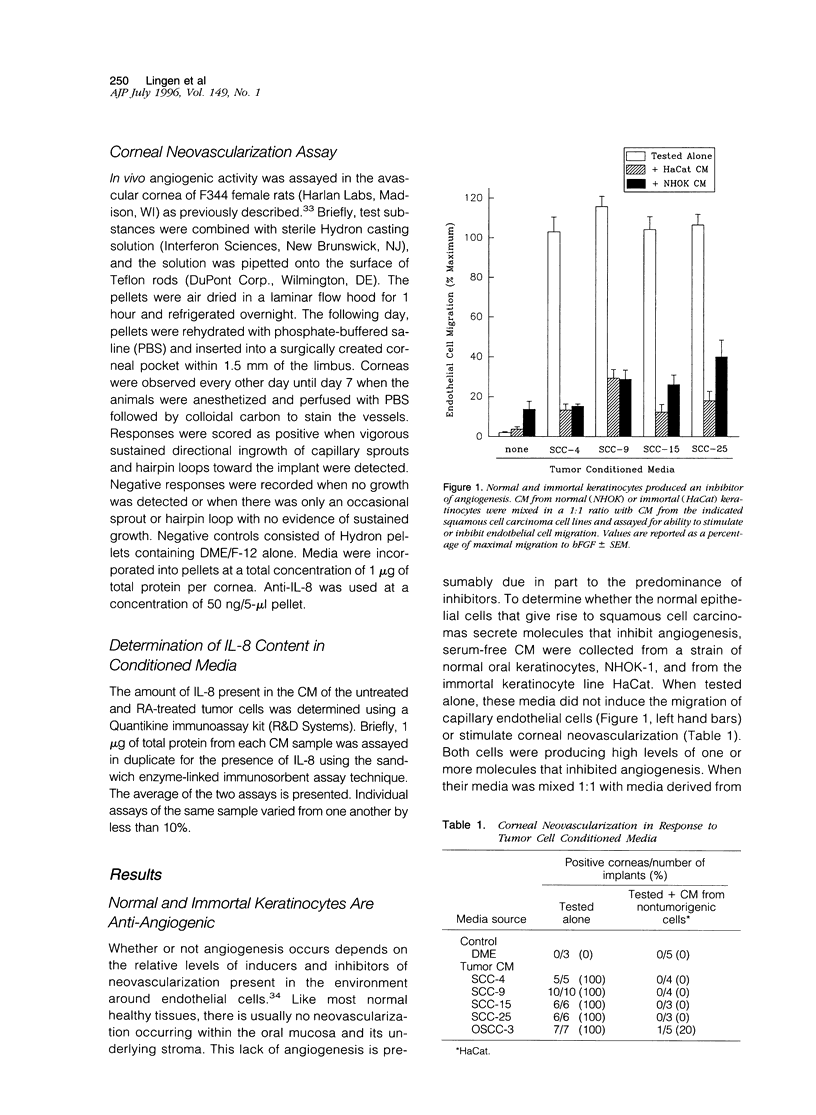

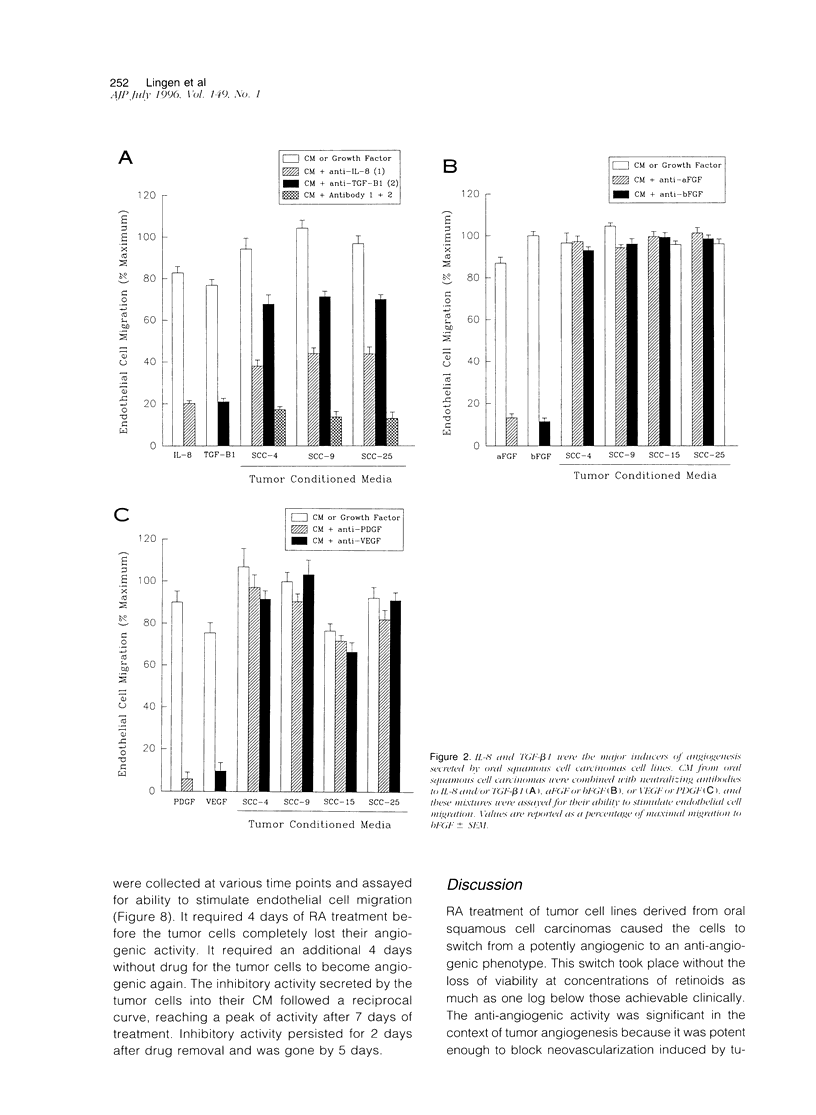
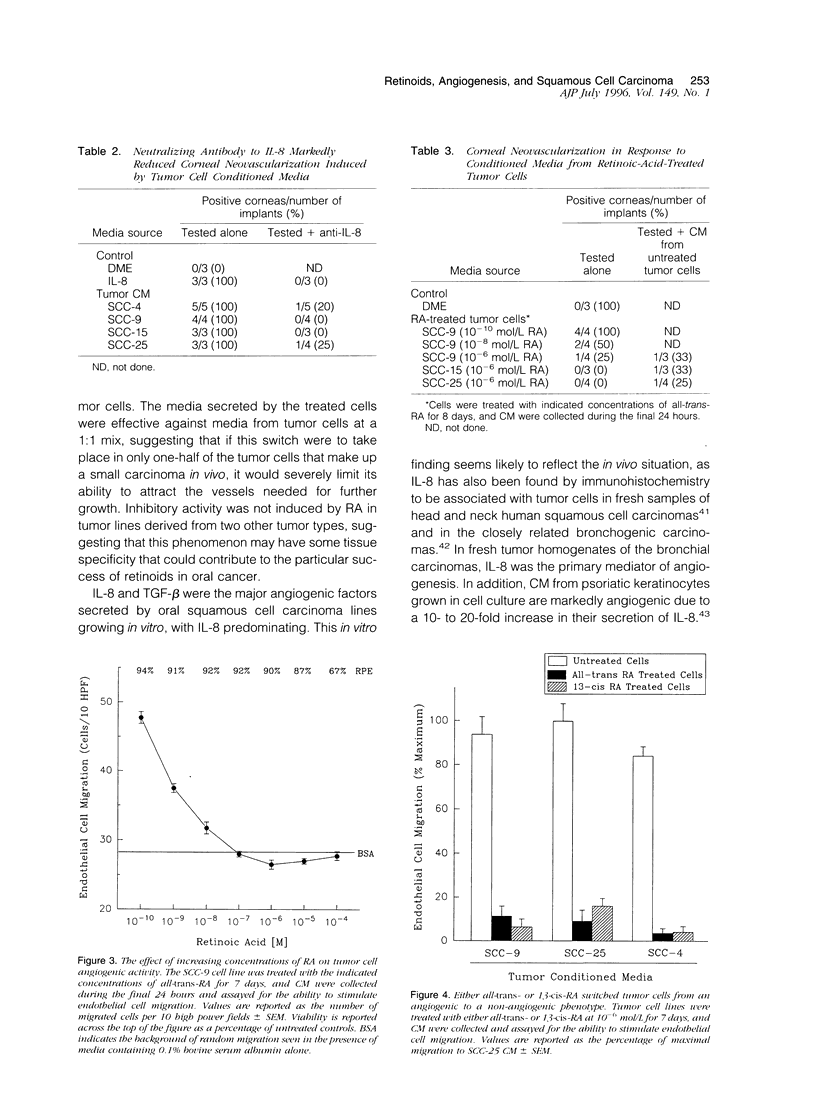



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos B., Lotan R. Retinoid-sensitive cells and cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1990;190:217–225. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)90026-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arensman R. M., Stolar C. J. Vitamin A effect on tumor angiogenesis. J Pediatr Surg. 1979 Dec;14(6):809–813. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(79)80271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan J. A., Boyle J. O., Koch W. M., Goodman S. N., Hruban R. H., Eby Y. J., Couch M. J., Forastiere A. A., Sidransky D. Association between cigarette smoking and mutation of the p53 gene in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 16;332(11):712–717. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503163321104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. Y., Mukhopadhyay T., Kim J., Casson A., Ro J. Y., Goepfert H., Hong W. K., Roth J. A. Discordant p53 gene mutations in primary head and neck cancers and corresponding second primary cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 1;53(7):1676–1683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. F., Contrino J., Spiro J. D., Mann E. A., Chen L. L., Kreutzer D. L. Interleukin-8 expression by head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995 Feb;121(2):202–209. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1995.01890020064013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dameron K. M., Volpert O. V., Tainsky M. A., Bouck N. Control of angiogenesis in fibroblasts by p53 regulation of thrombospondin-1. Science. 1994 Sep 9;265(5178):1582–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.7521539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank S., Hübner G., Breier G., Longaker M. T., Greenhalgh D. G., Werner S. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured keratinocytes. Implications for normal and impaired wound healing. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12607–12613. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game S. M., Stone A., Scully C., Prime S. S. Tumour progression in experimental oral carcinogenesis is associated with changes in EGF and TGF-beta receptor expression and altered responses to these growth factors. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jun;11(6):965–973. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.6.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Weidner N., Maluta S., Pozza F., Boracchi P., Mezzetti M., Testolin A., Bevilacqua P. Intratumoral microvessel density and p53 protein: correlation with metastasis in head-and-neck squamous-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993 Nov 11;55(5):739–744. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910550507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. J., Polverini P. J., Rastinejad F., Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Frazier W. A., Bouck N. P. A tumor suppressor-dependent inhibitor of angiogenesis is immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from a fragment of thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas L. J. Retinoids, retinoid-responsive genes, cell differentiation, and cancer. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Sep;3(9):655–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W. K., Endicott J., Itri L. M., Doos W., Batsakis J. G., Bell R., Fofonoff S., Byers R., Atkinson E. N., Vaughan C. 13-cis-retinoic acid in the treatment of oral leukoplakia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 11;315(24):1501–1505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612113152401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W. K., Lippman S. M., Itri L. M., Karp D. D., Lee J. S., Byers R. M., Schantz S. P., Kramer A. M., Lotan R., Peters L. J. Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 20;323(12):795–801. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009203231205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D., Folkman J. Inhibition of angiogenesis through modulation of collagen metabolism. Lab Invest. 1988 Jul;59(1):44–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janot F., el-Naggar A. K., Morrison R. S., Liu T. J., Taylor D. L., Clayman G. L. Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck is associated with degree of histologic differentiation. Int J Cancer. 1995 Apr 21;64(2):117–123. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Ishizaki A., Hellman U., Wernstedt C., Kyogoku M., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H., Funa K. A human keratinocyte cell line produces two autocrine growth inhibitors, transforming growth factor-beta and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6, in a calcium- and cell density-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12373–12379. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. E., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Harlow L. A., DiPietro L. A., Elner V. M., Elner S. G., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1798–1801. doi: 10.1126/science.1281554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingen M. W., Polverini P. J., Bouck N. P. Inhibition of squamous cell carcinoma angiogenesis by direct interaction of retinoic acid with endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1996 Feb;74(2):476–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman S. M., Batsakis J. G., Toth B. B., Weber R. S., Lee J. J., Martin J. W., Hays G. L., Goepfert H., Hong W. K. Comparison of low-dose isotretinoin with beta carotene to prevent oral carcinogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jan 7;328(1):15–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199301073280103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman S. M., Hong W. K. Second malignant tumors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: the overshadowing threat for patients with early-stage disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Sep;17(3):691–694. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Lotan D., Sacks P. G. Inhibition of tumor cell growth by retinoids. Methods Enzymol. 1990;190:100–110. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)90014-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S., Marczak M., Szmurlo A., Jablonska S., Bollag W. Retinoids, interferon alpha, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and their combination inhibit angiogenesis induced by non-HPV-harboring tumor cell lines. RAR alpha mediates the antiangiogenic effect of retinoids. Cancer Lett. 1995 Feb 10;89(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S., Szmurlo A., Marczak M., Jablonska S., Bollag W. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced angiogenesis by retinoids, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and their combination. Cancer Lett. 1993 Nov 30;75(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(93)90204-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski S., Szmurlo A., Marczak M., Jablonska S., Bollag W. Synergistic effect of retinoids and interferon alpha on tumor-induced angiogenesis: anti-angiogenic effect on HPV-harboring tumor-cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1994 Apr 1;57(1):81–85. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyskens F. L., Jr, Gilmartin E., Alberts D. S., Levine N. S., Brooks R., Salmon S. E., Surwit E. A. Activity of isotretinoin against squamous cell cancers and preneoplastic lesions. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Jun;66(6):1315–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missero C., Ramon y Cajal S., Dotto G. P. Escape from transforming growth factor beta control and oncogene cooperation in skin tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9613–9617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamadzadeh M., Müller M., Hultsch T., Enk A., Saloga J., Knop J. Enhanced expression of IL-8 in normal human keratinocytes and human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT in vitro after stimulation with contact sensitizers, tolerogens and irritants. Exp Dermatol. 1994 Dec;3(6):298–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1994.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroco J. R., Solt D. B., Polverini P. J. Sequential loss of suppressor genes for three specific functions during in vivo carcinogenesis. Lab Invest. 1990 Sep;63(3):298–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nees M., Homann N., Discher H., Andl T., Enders C., Herold-Mende C., Schuhmann A., Bosch F. X. Expression of mutated p53 occurs in tumor-distant epithelia of head and neck cancer patients: a possible molecular basis for the development of multiple tumors. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4189–4196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Mitra R. S., Varani J., Dixit V. M., Polverini P. J. Aberrant production of interleukin-8 and thrombospondin-1 by psoriatic keratinocytes mediates angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):820–828. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M. S., Holmgren L., Shing Y., Chen C., Rosenthal R. A., Moses M., Lane W. S., Cao Y., Sage E. H., Folkman J. Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa T., Hirotani K., Nakamura O., Shudo K., Hiragun A., Iwaguchi T. A highly potent antiangiogenic activity of retinoids. Cancer Lett. 1989 Nov 30;48(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(89)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper M. S., Vassalli J. D., Orci L., Montesano R. Biphasic effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on in vitro angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Feb;204(2):356–363. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli G. J., Snyderman C. H., Johnson J. T., Myers E. N. Angiogenesis induced by head and neck squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in the chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane model. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1993 Mar;102(3 Pt 1):215–221. doi: 10.1177/000348949310200309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouët J., Gospodarowicz D. Transforming growth factor beta-1 positively modulates the bioactivity of fibroblast growth factor on corneal endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Nov;141(2):392–399. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Bouck N. P., Rastinejad F. Assay and purification of naturally occurring inhibitor of angiogenesis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;198:440–450. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)98044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss M., Muñoz-Antonia T., Cowan J. M., Wilkins P. C., Zhou Z. L., Vellucci V. F. Resistance of human squamous carcinoma cells to transforming growth factor beta 1 is a recessive trait. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6280–6284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Beckett M. A. Tumorigenic keratinocyte lines requiring anchorage and fibroblast support cultured from human squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1657–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicka L., Marczak M., Szmurło A., Makieła B., Skiendzielewska A., Skopinska M., Majewski S., Jabłonska S. Acitretin decreases tumor cell-induced angiogenesis. Skin Pharmacol. 1991;4(3):150–153. doi: 10.1159/000210941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAUGHTER D. P., SOUTHWICK H. W., SMEJKAL W. Field cancerization in oral stratified squamous epithelium; clinical implications of multicentric origin. Cancer. 1953 Sep;6(5):963–968. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(195309)6:5<963::aid-cncr2820060515>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks P. G., Harris D., Chou T. C. Modulation of growth and proliferation in squamous cell carcinoma by retinoic acid: a rationale for combination therapy with chemotherapeutic agents. Int J Cancer. 1995 May 4;61(3):409–415. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910610322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz-Hector S., Haghayegh S. Beta-fibroblast growth factor expression in human and murine squamous cell carcinomas and its relationship to regional endothelial cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1444–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalinsky D. R., Bischoff E. D., Gregory M. L., Gottardis M. M., Hayes J. S., Lamph W. W., Heyman R. A., Shirley M. A., Cooke T. A., Davies P. J. Retinoid-induced suppression of squamous cell differentiation in human oral squamous cell carcinoma xenografts (line 1483) in athymic nude mice. Cancer Res. 1995 Jul 15;55(14):3183–3191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Polverini P. J., Kunkel S. L., Orringer M. B., Whyte R. I., Burdick M. D., Wilke C. A., Strieter R. M. Inhibition of interleukin 8 attenuates angiogenesis in bronchogenic carcinoma. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1409–1415. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Parkinson D. R., Cheson B. D., Friedman M. A. Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1992 May;10(5):839–864. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.5.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Parkinson D. R., Cheson B. D., Friedman M. A. Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1992 May;10(5):839–864. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.5.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolsma S. S., Volpert O. V., Good D. J., Frazier W. A., Polverini P. J., Bouck N. Peptides derived from two separate domains of the matrix protein thrombospondin-1 have anti-angiogenic activity. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):497–511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Gibbs D. F., Inman D. R., Shah B., Fligiel S. E., Voorhees J. J. Inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion by retinoic acid. Relationship to reduced extracellular matrix production and alterations in Ca2+ levels. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):887–895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. K., Carlson G. W., Cohen C., Derose P. B., Hunter S., Jurkiewicz M. J. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic factor in oral cavity tumors. Am J Surg. 1994 Nov;168(5):373–380. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang E. Y., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1-induced changes in cell migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis in the chicken chorioallantoic membrane. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):731–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zariwala M., Schmid S., Pfaltz M., Ohgaki H., Kleihues P., Schäfer R. p53 gene mutations in oropharyngeal carcinomas: a comparison of solitary and multiple primary tumours and lymph-node metastases. Int J Cancer. 1994 Mar 15;56(6):807–811. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou C. P., Clifford J. L., Xu X. C., Sacks P. G., Chambon P., Hong W. K., Lotan R. Modulation by retinoic acid (RA) of squamous cell differentiation, cellular RA-binding proteins, and nuclear RA receptors in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 15;54(20):5479–5487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]