Abstract
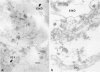
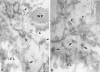
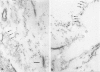
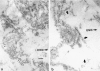
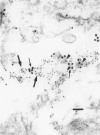
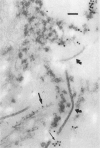
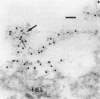
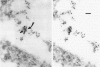
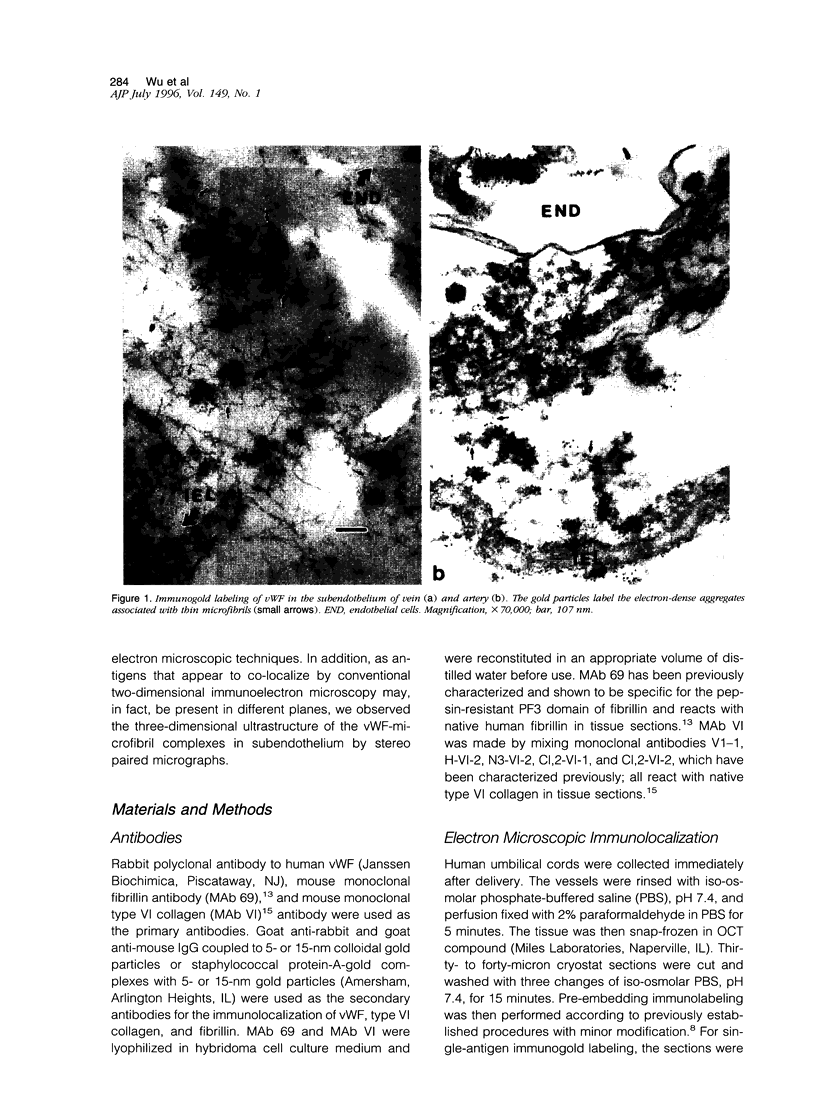
von Willebrand factor (vWF) plays an important role in the process of platelet adhesion after endothelial injury by serving as a bridge between constituents of the vascular subendothelium and platelet membrane receptors. We previously presented evidence that type VI collagen microfibrils serve as a binding site for vWF in human vascular subendothelium. However, others have proposed that vWF is not associated with type VI collagen but rather with the thicker elastin-associated microfibrils, which contain several proteins including fibrillin. We therefore investigated the relationships among vWF, type VI collagen, and fibrillin in human vascular subendothelium by immunoelectron microscopy using single- and double-labeling immunogold localization techniques. In addition, we observed the three-dimensional ultrastructure of vWF-microfibril complexes by stereo paired micrographs and stereo viewer. We found that vWF co-localizes only with the type VI collagen microfibrils in subendothelium but not with fibrillin microfibrils or striated collagen. The vWF is present in subendothelium in the form of electron-dense aggregates having diameters varying between 65 and 80 nm that are closely associated with, and enmesh, the type VI collagen microfibrils and have structural similarities to intracellular Weibel-Palade bodies. The occasional co-localization of type VI collagen and fibrillin adjacent to internal elastic lamina was observed. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that type VI collagen, but not fibrillin-containing microfibrils, serves as a physiologically relevant binding site for vWF in the vascular subendothelium, where the type VI collagen-vWF complex may play an important role modulating the hemostatic response to vascular injury.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denis C., Baruch D., Kielty C. M., Ajzenberg N., Christophe O., Meyer D. Localization of von Willebrand factor binding domains to endothelial extracellular matrix and to type VI collagen. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Mar;13(3):398–406. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel-Lafeve F., Legrand Y. J. Immunochemical identification of a thrombospondin-like structure in an arterial microfibrillar extract. Thromb Res. 1988 Apr 15;50(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel-Lafève F., Legrand Y. J. Binding of plasma von Willebrand factor by arterial microfibrils. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Aug 13;64(1):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel F., Grant M. E., Legrand Y. J., Souchon H., Tobelem G., Jackson D. S., Caen J. P. Interaction of blood platelets with a microfibrillar extract from adult bovine aorta: requirement for von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):551–554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Engvall E., Glanville R. W. Ultrastructure of type VI collagen in human skin and cartilage suggests an anchoring function for this filamentous network. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1995–2006. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene D. R., Maddox B. K., Kuo H. J., Sakai L. Y., Glanville R. W. Extraction of extendable beaded structures and their identification as fibrillin-containing extracellular matrix microfibrils. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Apr;39(4):441–449. doi: 10.1177/39.4.2005373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Harlan J. M., Harker L. A., Joseph M. L., Counts R. B. Thrombin-mediated release of factor VIII antigen from human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):531–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perris R., Kuo H. J., Glanville R. W., Leibold S., Bronner-Fraser M. Neural crest cell interaction with type VI collagen is mediated by multiple cooperative binding sites within triple-helix and globular domains. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Nov;209(1):103–117. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Gordon R. E., Sussman I. I., Chu S. V., Solomon V. Electron microscopic localization of factor-VIII-related antigen in adult human blood vessels. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):627–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Patel N. D., Schwartz E., Zhou S. L., Potter B. J. 150-kD von Willebrand factor binding protein extracted from human vascular subendothelium is type VI collagen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):253–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI115285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Sussman I. I., Gordon R. E., Chu S. V., Solomon V. Localization of factor-VIII-related antigen in human vascular subendothelium. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):752–756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand J. H., Wu X. X., Potter B. J., Uson R. R., Gordon R. E. Co-localization of von Willebrand factor and type VI collagen in human vascular subendothelium. Am J Pathol. 1993 Mar;142(3):843–850. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes J. A., Francis C. W., Wagner D. D. Fibrin induces release of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):117–123. doi: 10.1172/JCI112771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Ware J. The structure and function of von Willebrand factor. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Jun 1;67(6):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelman E. U., Kehrel B., Hese K. M., de Groot P. G., Sixma J. J., Nieuwenhuis H. K. Platelet adhesion to collagen and endothelial cell matrix under flow conditions is not dependent on platelet glycoprotein IV. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3240–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saelman E. U., Nieuwenhuis H. K., Hese K. M., de Groot P. G., Heijnen H. F., Sage E. H., Williams S., McKeown L., Gralnick H. R., Sixma J. J. Platelet adhesion to collagen types I through VIII under conditions of stasis and flow is mediated by GPIa/IIa (alpha 2 beta 1-integrin). Blood. 1994 Mar 1;83(5):1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Bolhuis P. A., Sixma J. J. Human blood platelet adhesion to artery subendothelium is mediated by factor VIII-Von Willebrand factor bound to the subendothelium. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):636–638. doi: 10.1038/279636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Inducible secretion of large, biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90735-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stel H. V., Sakariassen K. S., de Groot P. G., van Mourik J. A., Sixma J. J. Von Willebrand factor in the vessel wall mediates platelet adherence. Blood. 1985 Jan;65(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman I. I., Rand J. H. Subendothelial deposition of von Willebrand's factor requires the presence of endothelial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Oct;100(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turitto V. T., Weiss H. J., Zimmerman T. S., Sussman I. I. Factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in subendothelium mediates platelet adhesion. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):823–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Drosenberg L. Platelet interaction with modified articular cartilage. Its possible relevance to joint repair. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):641–651. doi: 10.1172/JCI108682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]