Abstract
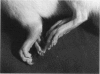
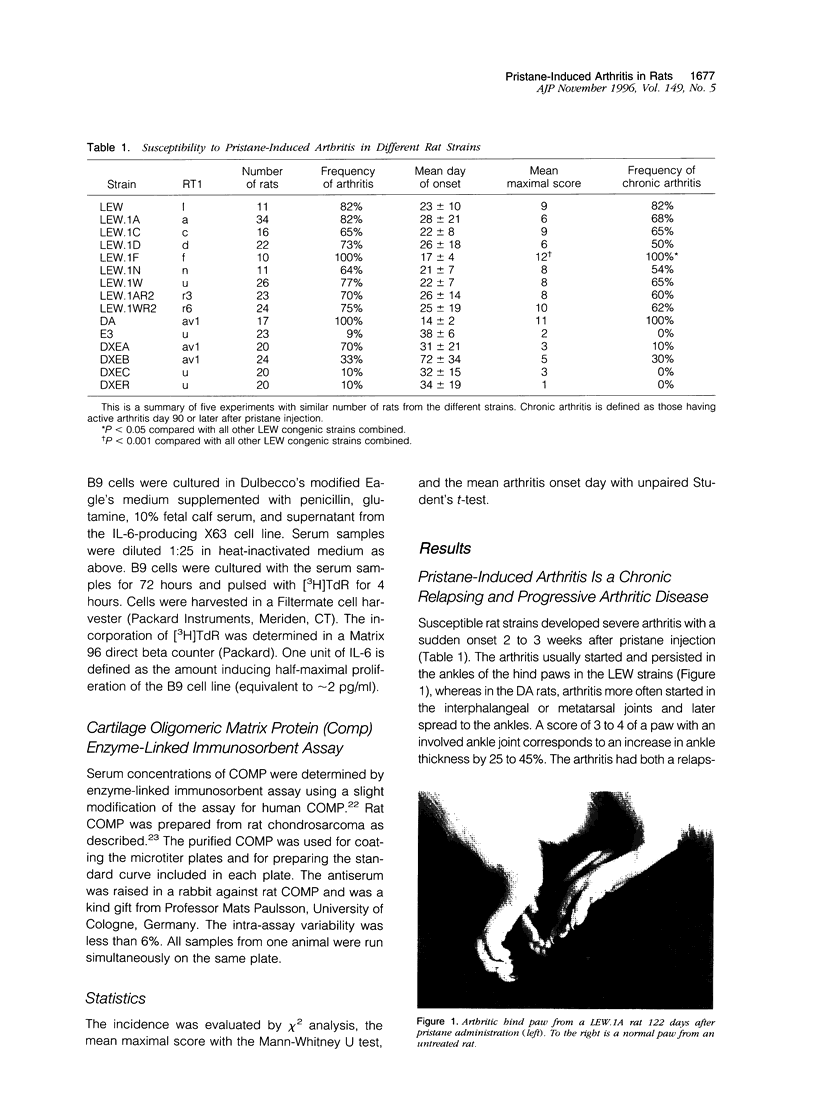
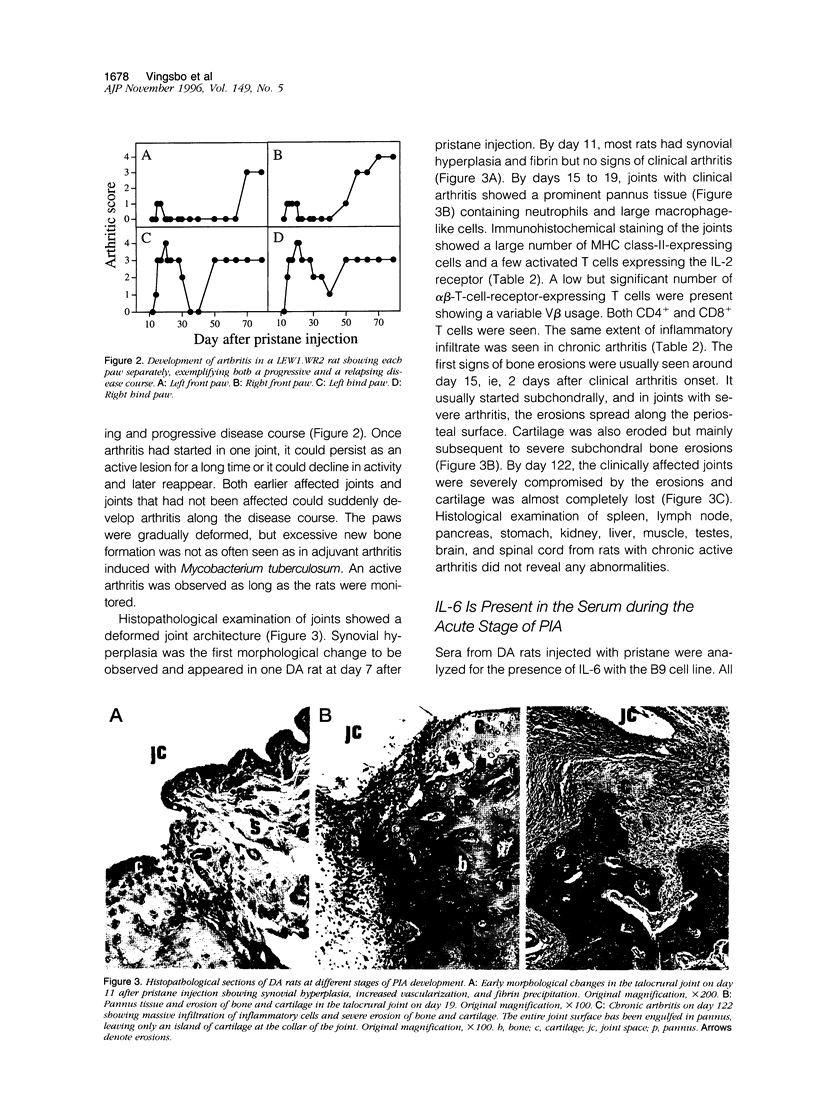
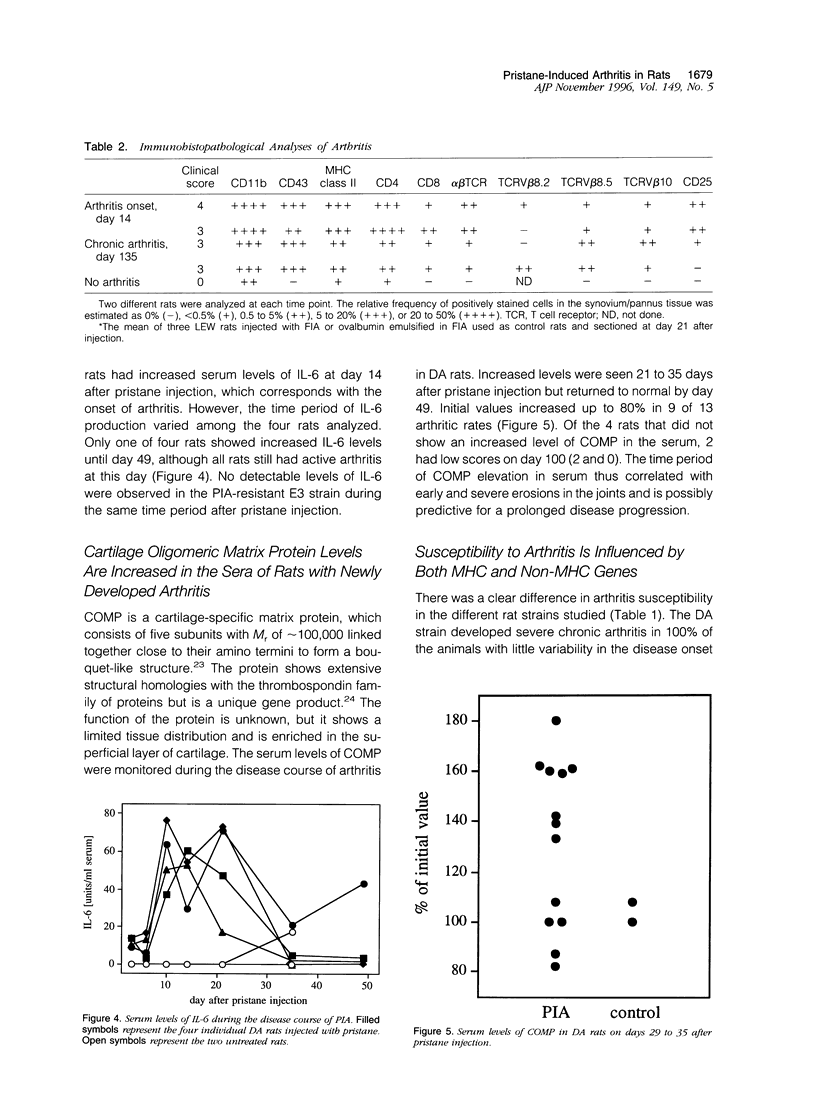
We present a novel animal model for rheumatoid arthritis induced with a well defined synthetic adjuvant oil, pristane. Two weeks after a single intradermal injection of 150 microliters of pristane, the rats developed severe and chronic arthritis. The inflammation was restricted to the joints and involved pannus formation, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II expression, and T lymphocyte infiltration. The initial development as well as the chronic stage of pristane-induced arthritis was ameliorated by treatment with antibodies to the alpha beta-T-cell receptor showing that the disease is T cell dependent. Increased levels of interleukin in serum was seen after pristane injection but not during the chronic stage of arthritis. Joint erosions were accompanied by elevated serum levels of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein. Comparison of MHC congenic LEW strains showed that the severity and chronicity of arthritis varied among the different MHC haplotypes. Rats with RT1f haplotype showed a significantly higher susceptibility to pristane-induced arthritis. A strong influence of non-MHC genes was also suggested by the variability of arthritis susceptibility among different strains with the same MHC haplotype; the most susceptible background was the DA and the least susceptible was the E3. Arthritis induced with a well defined nonimmunogenic adjuvant, with a disease course that closely resembles that of rheumatoid arthritis, makes a suitable animal model for future studies of the pathology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF

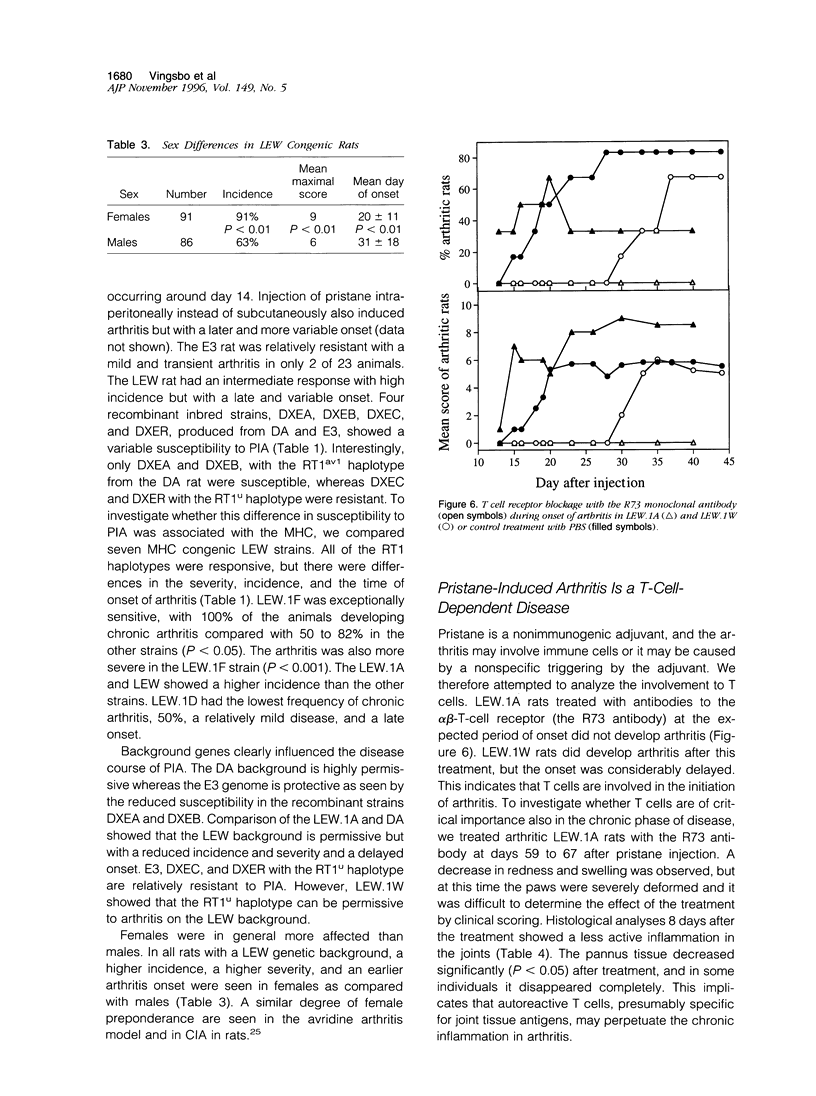


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., De Groot E. R., Schaap O. L., Lansdorp P. M. Production of hybridoma growth factor by human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Oct;17(10):1411–1416. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedwell A. E., Elson C. J., Hinton C. E. Immunological involvement in the pathogenesis of pristane-induced arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Apr;25(4):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Pearson C. M., Abe C. Adjuvant polyarthritis. IV. Induction by a synthetic adjuvant: immunologic, histopathologic, and other studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jan;23(1):62–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassbender H. G., Simmling-Annefeld M. The potential aggressiveness of synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. J Pathol. 1983 Mar;139(3):399–406. doi: 10.1002/path.1711390314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glant T. T., Mikecz K., Arzoumanian A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycan-induced arthritis in BALB/c mice. Clinical features and histopathology. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Feb;30(2):201–212. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt T. J., Holmdahl R. Anti-T cell receptor antibody treatment of rats with established autologous collagen-induced arthritis: suppression of arthritis without reduction of anti-type II collagen autoantibody levels. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Matsuda T., Turner M., Miyasaka N., Buchan G., Tang B., Sato K., Shimizu M., Maini R., Feldmann M. Excessive production of interleukin 6/B cell stimulatory factor-2 in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1797–1801. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitsumoto Y., Thompson S. J., Zhang Y. W., Rook G. A., Elson C. J. Relationship between interleukin 6, agalactosyl IgG and pristane-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. 1992;11(4):247–254. doi: 10.3109/08916939209035162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R. Female preponderance for development of arthritis in rats is influenced by both sex chromosomes and sex steroids. Scand J Immunol. 1995 Jul;42(1):104–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1995.tb03632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Goldschmidt T. J., Kleinau S., Kvick C., Jonsson R. Arthritis induced in rats with adjuvant oil is a genetically restricted, alpha beta T-cell dependent autoimmune disease. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):197–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jonsson R., Larsson P., Klareskog L. Early appearance of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes and class II antigen-expressing cells in joints of DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Kvick C. Vaccination and genetic experiments demonstrate that adjuvant-oil-induced arthritis and homologous type II collagen-induced arthritis in the same rat strain are different diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):96–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Dencker L., Gustafson G., Larsson E. Appearance of different lymphoid cells in synovial tissue and in peripheral blood during the course of collagen II-induced arthritis in rats. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Mar;21(3):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Vingsbo C., Hedrich H., Karlsson M., Kvick C., Goldschmidt T. J., Gustafsson K. Homologous collagen-induced arthritis in rats and mice are associated with structurally different major histocompatibility complex DQ-like molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):419–424. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Vingsbo C., Mo J. A., Michaëlsson E., Malmström V., Jansson L., Brunsberg U. Chronicity of tissue-specific experimental autoimmune disease: a role for B cells? Immunol Rev. 1995 Apr;144:109–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1995.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssiau F. A., Devogelaer J. P., Van Damme J., de Deuxchaisnes C. N., Van Snick J. Interleukin-6 in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jun;31(6):784–788. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Wallny H. J., Hartley J. K., Lawetzky A., Tiefenthaler G. A monoclonal antibody to a constant determinant of the rat T cell antigen receptor that induces T cell activation. Differential reactivity with subsets of immature and mature T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):73–86. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson R., Tarkowski A., Klareskog L. A demineralization procedure for immunohistopathological use. EDTA treatment preserves lymphoid cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 3;88(1):109–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Scheynius A., Kabelitz D., Wigzell H. Evidence in support of a self-perpetuating HLA-DR-dependent delayed-type cell reaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3632–3636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konttinen Y. T., Bergroth V., Nordström D., Koota K., Skrifvars B., Hagman G., Friman C., Hämäläinen M., Slätis P. Cellular immunohistopathology of acute, subacute, and chronic synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Aug;44(8):549–555. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.8.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec-Weglinski J. W., Diamantstein T., Tilney N. L., Strom T. B. Therapy with monoclonal antibody to interleukin 2 receptor spares suppressor T cells and prevents or reverses acute allograft rejection in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2624–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Monoclonal antibodies to Ia antigens from rat thymus: cross reactions with mouse and human and use in purification of rat Ia glycoproteins. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:117–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Månsson B., Carey D., Alini M., Ionescu M., Rosenberg L. C., Poole A. R., Heinegård D., Saxne T. Cartilage and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Differences between rapid and slow progression of disease identified by serum markers of cartilage metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1995 Mar;95(3):1071–1077. doi: 10.1172/JCI117753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mörgelin M., Heinegård D., Engel J., Paulsson M. Electron microscopy of native cartilage oligomeric matrix protein purified from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma reveals a five-armed structure. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6137–6141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordan R. P., Potter M. A macrophage-derived factor required by plasmacytomas for survival and proliferation in vitro. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):566–569. doi: 10.1126/science.3726549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Antonsson P., Lindblom K., Heinegård D. COMP (cartilage oligomeric matrix protein) is structurally related to the thrombospondins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22346–22350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Development of arthritis, periarthritis and periostitis in rats given adjuvants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):95–101. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Wax J. S. Genetics of susceptibility to pristane-induced plasmacytomas in BALB/cAn: reduced susceptibility in BALB/cJ with a brief description of pristane-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1591–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. P., White T. M., Mason D. W. Macrophage heterogeneity in the rat as delineated by two monoclonal antibodies MRC OX-41 and MRC OX-42, the latter recognizing complement receptor type 3. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):239–247. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G., Thompson S., Buckley M., Elson C., Brealey R., Lambert C., White T., Rademacher T. The role of oil and agalactosyl IgG in the induction of arthritis in rodent models. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1027–1032. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita T., Furukawa O., Ueno M., Murakami T., Takata I., Tosa T. Enhanced expression of interleukin 6 in rat and murine arthritis models. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1993 May;15(4):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Seki N., Senoh H., Yokota T., Lee F., Hamaoka T., Fujiwara H. Enhanced production of interleukin-6 in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;32(5):594–600. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. S., Harper N., Bevan D. J., Staines N. A. Suppression of collagen induced arthritis by oral administration of type II collagen: changes in immune and arthritic responses mediated by active peripheral suppression. Autoimmunity. 1993;16(3):189–199. doi: 10.3109/08916939308993327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Nagel N. E., Gold D. P., Hünig T. Identification of rat Tcrb-V8.2, 8.5, and 10 gene products by monoclonal antibodies. Immunogenetics. 1993;37(4):305–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00187460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vingsbo C., Jonsson R., Holmdahl R. Avridine-induced arthritis in rats; a T cell-dependent chronic disease influenced both by MHC genes and by non-MHC genes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Mar;99(3):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb05558.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse M. W., Orr K. J., Beck F. W., Pearson C. M. Freund's adjuvants: relationship of arthritogenicity and adjuvanticity in rats to vehicle composition. Immunology. 1974 Aug;27(2):311–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):688–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Seibold J. R., Whalen J. D., Chapdelaine J. M. Pristane-induced arthritis. The immunologic and genetic features of an experimental murine model of autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Aug;32(8):1022–1030. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino S., Kinne R., Hünig T., Emmrich F. The suppressive effect of an antibody to the alpha beta cell receptor in rat adjuvant arthritis: studies on optimal treatment protocols. Autoimmunity. 1990;7(4):255–266. doi: 10.3109/08916939009087585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]