Abstract
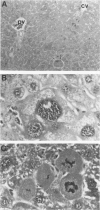
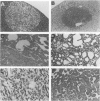
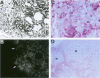
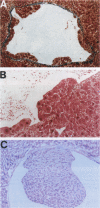
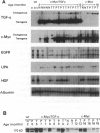
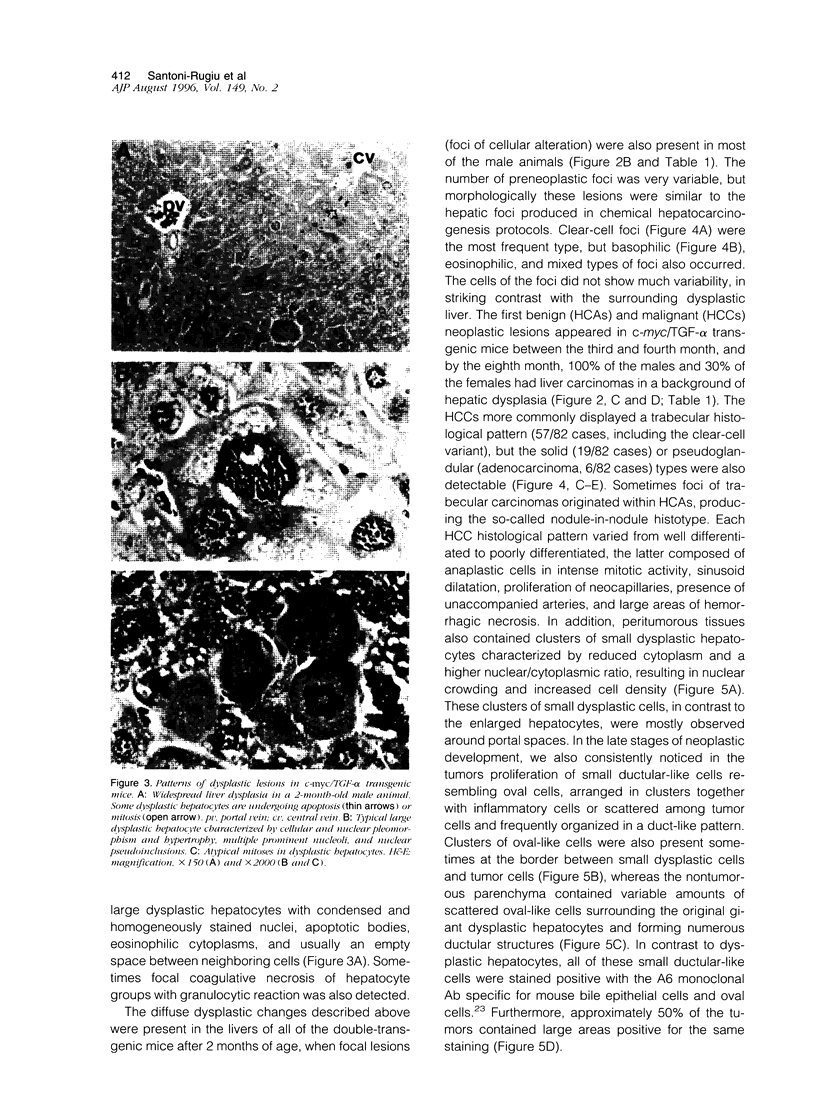
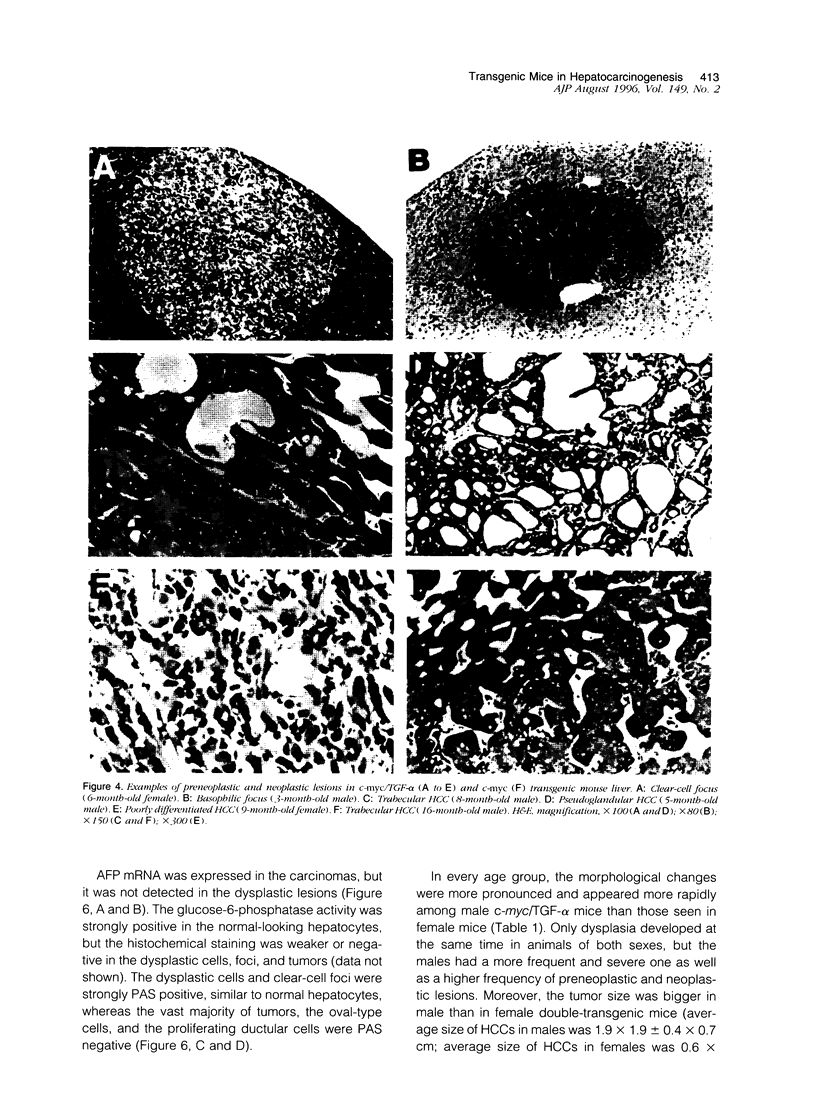
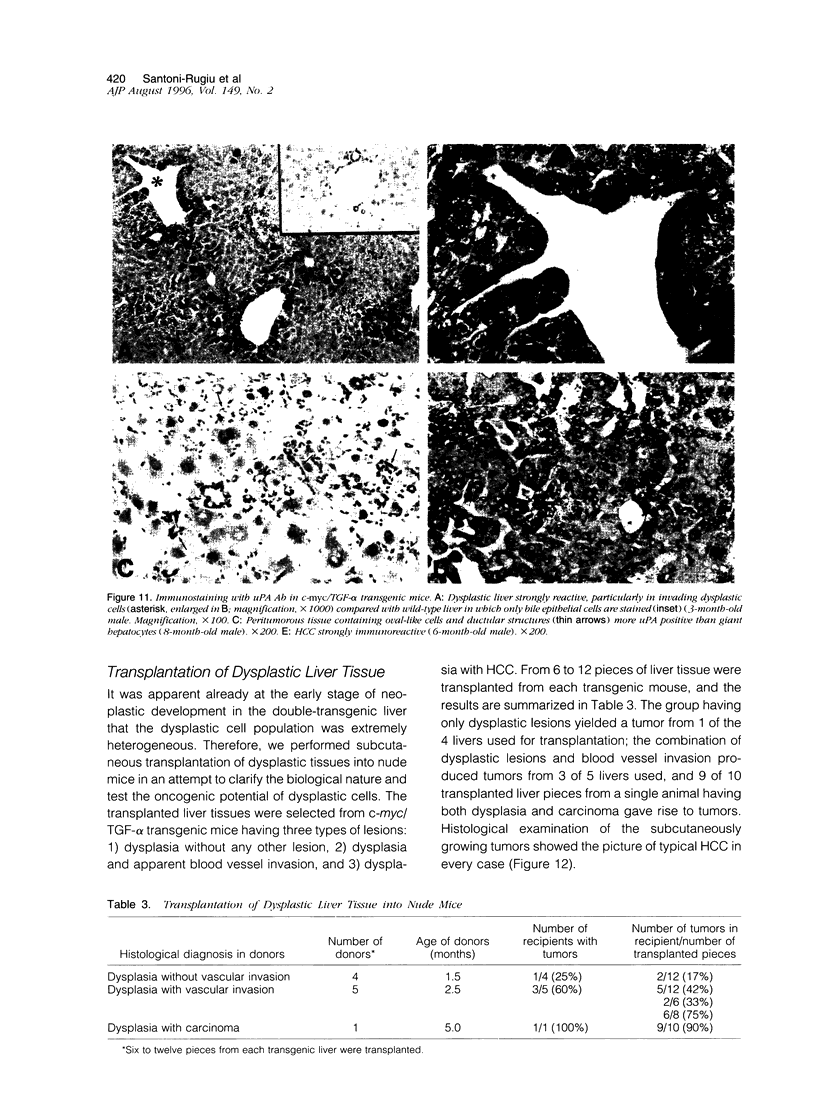
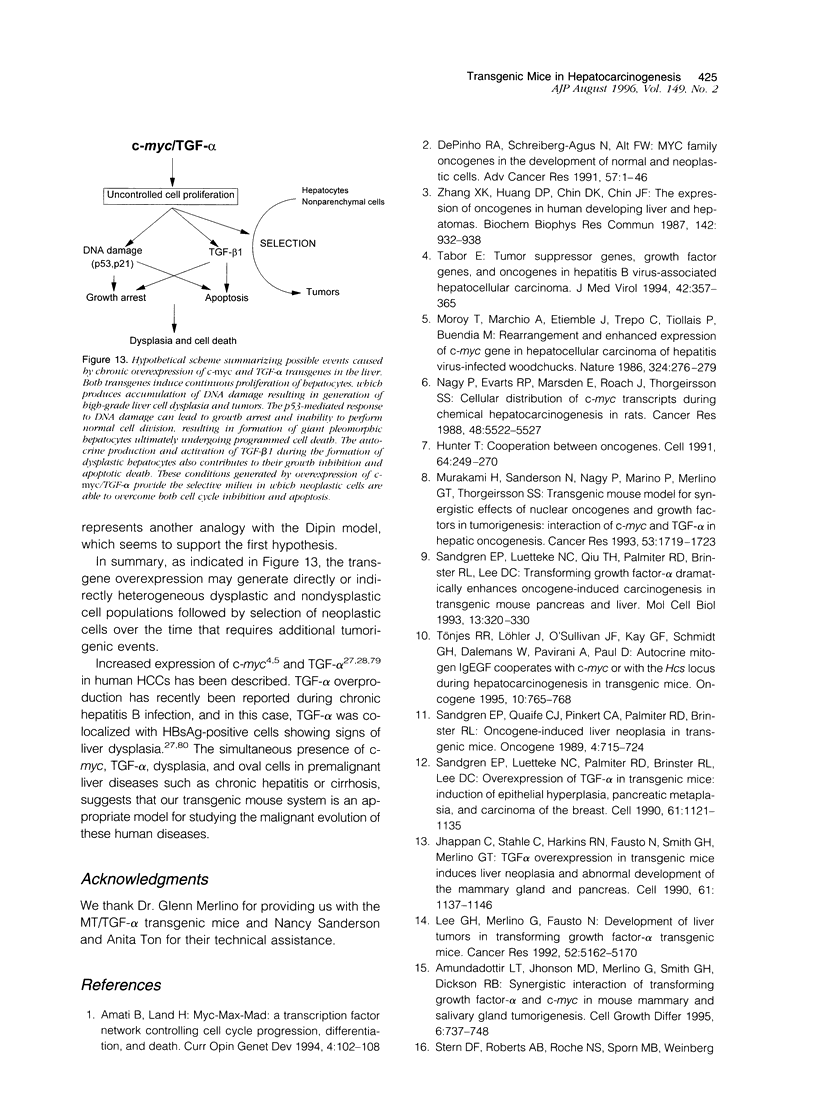
We have previously shown that co-expression of c-myc and transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha as transgenes in mouse liver results in major enhancement of neoplastic development in this organ as compared with expression of either of these transgenes alone. In this report we describe in detail the progression from liver cell dysplasia to hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) occurring in the liver of c-myc/TGF-alpha and c-myc transgenic mice. Despite morphological similarities in the sequence of events between the two transgenic lines, the dramatic acceleration, extent, and severity of hepatic lesions in c-myc/TGF-alpha mice clearly demonstrated the synergistic effects of this transgenic combination. Although c-myc/TGF-alpha and c-myc females displayed longer latency and lower tumor incidence, the pathological changes were the same as those seen in the male mice, including the formation of HCCs, which are absent in TGF-alpha single-transgenic females. Tumors in single- and double-transgenic mice showed induction of the endogenous c-myc and TGF-alpha and, most frequently, unchanged or decreased epidermal growth factor receptor, further indicating the collaborative role of c-myc and TGF-alpha in providing a selective growth advantage to tumor cells independently of the epidermal growth factor receptor levels. To identify possible tumor precursors, we focused particularly on the dysplastic changes preceding and accompanying the appearance of preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions in the double-transgenic mice. Early on, these changes were characterized by the appearance of large dysplastic hepatocytes, mostly pericentrally, expressing high levels of TGF-alpha and uPA, as well as TGF-beta 1, particularly in apoptotic cells. After a short period of replication and expansion into the liver parenchyma, as well as penetration into the central veins, these cells underwent apoptotic cell death while preneoplastic and neoplastic lesions were forming. The peritumorous tissues also contained small dysplastic hepatocytes and oval-like cells, similar to those found in the tumors. Transplantation of the transgenic liver tissues harboring only dysplasia with or without vascular lesions onto nude mice was able to yield HCCs composed of small diploid cells, suggesting that initiated cells are generated during the early dysplastic phase and can progress to HCC. It is therefore likely that large dysplastic hepatocytes undergo apoptosis, which may be closely associated with the up-regulation of TGF-beta 1 and uPA, whereas other cells evolve into the precursor population for HCC. Due to the simultaneous presence of c-myc, TGF-alpha, and dysplasia in premalignant human liver diseases, our transgenic mouse system appears to be an appropriate model for studying human hepatocarcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati B., Land H. Myc-Max-Mad: a transcription factor network controlling cell cycle progression, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):102–108. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amundadottir L. T., Johnson M. D., Merlino G., Smith G. H., Dickson R. B. Synergistic interaction of transforming growth factor alpha and c-myc in mouse mammary and salivary gland tumorigenesis. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Jun;6(6):737–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony P. P., Vogel C. L., Barker L. F. Liver cell dysplasia: a premalignant condition. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Mar;26(3):217–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcellos-Hoff M. H., Ehrhart E. J., Kalia M., Jirtle R., Flanders K., Tsang M. L. Immunohistochemical detection of active transforming growth factor-beta in situ using engineered tissue. Am J Pathol. 1995 Nov;147(5):1228–1237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedossa P., Peltier E., Terris B., Franco D., Poynard T. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) and TGF-beta 1 receptors in normal, cirrhotic, and neoplastic human livers. Hepatology. 1995 Mar;21(3):760–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennoun M., Rissel M., Engelhardt N., Guillouzo A., Briand P., Weber-Benarous A. Oval cell proliferation in early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis in simian virus 40 large T transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1993 Nov;143(5):1326–1336. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun L., Mead J. E., Panzica M., Mikumo R., Bell G. I., Fausto N. Transforming growth factor beta mRNA increases during liver regeneration: a possible paracrine mechanism of growth regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1539–1543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Oberhammer F., Jirtle R. L., Askari M., Sedivy R., Grasl-Kraupp B., Purchio A. F., Schulte-Hermann R. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 as a signal for induction of cell death by apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1993 Mar;67(3):531–536. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. Y., Tsai J. H., Yeh Y. C., Chang C. C., Yeh H. W., Guh J. Y., Tsai J. F. Epidermal growth factor-related transforming growth factors in the urine of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1991 Jun;13(6):1112–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Berson S. D., Geddes E. W. Liver cell dysplasia: association with hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhosis and hepatitis B antigen carrier status. Cancer. 1979 Nov;44(5):1671–1676. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197911)44:5<1671::aid-cncr2820440521>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Berson S. D. Liver cell dysplasia in normal, cirrhotic, and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer. 1986 Apr 15;57(8):1535–1538. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860415)57:8<1535::aid-cncr2820570816>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. D., Guo K., Gullick W. J., Bassendine M. F., Burt A. D. Expression of transforming growth factor alpha in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver. 1993 Jun;13(3):151–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1993.tb00623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalal B. I., Keown P. A., Greenberg A. H. Immunocytochemical localization of secreted transforming growth factor-beta 1 to the advancing edges of primary tumors and to lymph node metastases of human mammary carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):381–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePinho R. A., Schreiber-Agus N., Alt F. W. myc family oncogenes in the development of normal and neoplastic cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:1–46. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60994-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt N. V., Factor V. M., Yasova A. K., Poltoranina V. S., Baranov V. N., Lasareva M. N. Common antigens of mouse oval and biliary epithelial cells. Expression on newly formed hepatocytes. Differentiation. 1990 Oct;45(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor V. M., Radaeva S. A., Thorgeirsson S. S. Origin and fate of oval cells in dipin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in the mouse. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):409–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausto N. Multifunctional roles for transforming growth factor-beta 1. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanders K. C., Thompson N. L., Cissel D. S., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Baker C. C., Kass M. E., Ellingsworth L. R., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta 1: histochemical localization with antibodies to different epitopes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):653–660. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilović J., Moens G., Thiery J. P., Jouanneau J. Expression of transfected transforming growth factor alpha induces a motile fibroblast-like phenotype with extracellular matrix-degrading potential in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell Regul. 1990 Dec;1(13):1003–1014. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.13.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Twardzik D. R., Lim G. J., Ranchalis J. E., Lee D. C. Expression and characterization of transforming growth factor alpha precursor protein in transfected mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1585–1591. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Axiotis C. A., Di Bisceglie A. M., Tabor E. Transforming growth factor-alpha in human hepatocellular carcinoma and coexpression with hepatitis B surface antigen in adjacent liver. Cancer. 1992 Sep 1;70(5):1049–1056. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920901)70:5<1049::aid-cncr2820700507>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber K., Kirchheimer J. C., Ermler D., Bell C., Binder B. R. Determination of plasma urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen in patients with primary liver cancer: characterization as tumor-associated antigen and comparison with alpha-fetoprotein. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1717–1720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Kawata S., Tamura S., Takaishi K., Shirai Y., Kiso S., Yabuuchi I., Matsuda Y., Nishioka M., Tarui S. Elevated levels of transforming growth factor beta messenger RNA and its polypeptide in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4080–4083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Stahle C., Harkins R. N., Fausto N., Smith G. H., Merlino G. T. TGF alpha overexpression in transgenic mice induces liver neoplasia and abnormal development of the mammary gland and pancreas. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90076-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaoustov V. I., Ozer A., Smith J. R., Noda A., Mearns M., Krishnan B., Slagle B. L., Yoffe B. Induction of senescent cell-derived inhibitor of DNA synthesis gene, SDI1, in hepatoblastoma (HepG2) cells arrested in the G2-phase of the cell cycle by 9-nitrocamptothecin. Lab Invest. 1995 Jul;73(1):118–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koen H., Pugh T. D., Goldfarb S. Hepatocarcinogenesis in the mouse. Combined morphologic-stereologic studies. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jul;112(1):89–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koen H., Pugh T. D., Nychka D., Goldfarb S. Presence of alpha-fetoprotein-positive cells in hepatocellular foci and microcarcinomas induced by single injections of diethylnitrosamine in infant mice. Cancer Res. 1983 Feb;43(2):702–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike K., Moriya K., Iino S., Yotsuyanagi H., Endo Y., Miyamura T., Kurokawa K. High-level expression of hepatitis B virus HBx gene and hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Hepatology. 1994 Apr;19(4):810–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):341–349. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1899685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. H., Merlino G., Fausto N. Development of liver tumors in transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5162–5170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. W., Raymond V. W., Tsao M. S., Lee D. C., Earp H. S., Grisham J. W. Clonal cosegregation of tumorigenicity with overexpression of c-myc and transforming growth factor alpha genes in chemically transformed rat liver epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5238–5244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitch J. H., Apfelbaum T. F. Liver cell dysplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma in non-A, non-B hepatitis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Feb;111(2):170–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Gentry L. E., Purchio A. F., Moses H. L. Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1361–1367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mars W. M., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. Activation of hepatocyte growth factor by the plasminogen activators uPA and tPA. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):949–958. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhir J., Selfridge J., Harrison D. J., Squires S., Melton D. W. Mice with DNA repair gene (ERCC-1) deficiency have elevated levels of p53, liver nuclear abnormalities and die before weaning. Nat Genet. 1993 Nov;5(3):217–224. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Yang E. Y., Pietenpol J. A. TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami H., Sanderson N. D., Nagy P., Marino P. A., Merlino G., Thorgeirsson S. S. Transgenic mouse model for synergistic effects of nuclear oncogenes and growth factors in tumorigenesis: interaction of c-myc and transforming growth factor alpha in hepatic oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 15;53(8):1719–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möröy T., Marchio A., Etiemble J., Trépo C., Tiollais P., Buendia M. A. Rearrangement and enhanced expression of c-myc in hepatocellular carcinoma of hepatitis virus infected woodchucks. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):276–279. doi: 10.1038/324276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy P., Evarts R. P., Marsden E., Roach J., Thorgeirsson S. S. Cellular distribution of c-myc transcripts during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5522–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy P., Evarts R. P., McMahon J. B., Thorgeirsson S. S. Role of TGF-beta in normal differentiation and oncogenesis in rat liver. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(6):345–354. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsukasa H., Evarts R. P., Hsia C. C., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat. Lab Invest. 1991 Nov;65(5):511–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsukasa H., Nagy P., Evarts R. P., Hsia C. C., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1833–1843. doi: 10.1172/JCI114643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F. A., Pavelka M., Sharma S., Tiefenbacher R., Purchio A. F., Bursch W., Schulte-Hermann R. Induction of apoptosis in cultured hepatocytes and in regressing liver by transforming growth factor beta 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5408–5412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Bursch W., Tiefenbacher R., Fröschl G., Pavelka M., Purchio T., Schulte-Hermann R. Apoptosis is induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 within 5 hours in regressing liver without significant fragmentation of the DNA. Hepatology. 1993 Nov;18(5):1238–1246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odekon L. E., Blasi F., Rifkin D. B. Requirement for receptor-bound urokinase in plasmin-dependent cellular conversion of latent TGF-beta to TGF-beta. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Mar;158(3):398–407. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041580303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Ammann P., Fasciati R., Maier P. Transforming growth factor beta 1 preferentially induces apoptotic cell death in rat hepatocytes cultured under pericentral-equivalent conditions. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;132(2):227–236. doi: 10.1006/taap.1995.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradinas F. J., Bull T. B., Westaby D., Murray-Lyon I. M. Hyperplasia and prolapse of hepatocytes into hepatic veins during longterm methyltestosterone therapy: possible relationships of these changes to the developement of peliosis hepatis and liver tumours. Histopathology. 1977 Jul;1(4):225–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1977.tb01663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presnell S. C., Thompson M. T., Strom S. C. Investigation of the cooperative effects of transforming growth factor alpha and c-myc overexpression in rat liver epithelial cells. Mol Carcinog. 1995 Aug;13(4):233–244. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncalli M., Borzio M., De Biagi G., Ferrari A. R., Macchi R., Tombesi V. M., Servida E. Liver cell dysplasia in cirrhosis. A serologic and immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 1986 Apr 15;57(8):1515–1521. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860415)57:8<1515::aid-cncr2820570813>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Luetteke N. C., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lee D. C. Overexpression of TGF alpha in transgenic mice: induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, and carcinoma of the breast. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1121–1135. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90075-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Luetteke N. C., Qiu T. H., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Lee D. C. Transforming growth factor alpha dramatically enhances oncogene-induced carcinogenesis in transgenic mouse pancreas and liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):320–330. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Quaife C. J., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Oncogene-induced liver neoplasia in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):715–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent L. M., Sanderson N. D., Thorgeirsson S. S. Ploidy and karyotypic alterations associated with early events in the development of hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice harboring c-myc and transforming growth factor alpha transgenes. Cancer Res. 1996 May 1;56(9):2137–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmacher P., Held W. A., Yang D., Biempica L., Rogler C. E. Selective amplification of periportal transitional cells precedes formation of hepatocellular carcinoma in SV40 large tag transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sepulveda A. R., Finegold M. J., Smith B., Slagle B. L., DeMayo J. L., Shen R. F., Woo S. L., Butel J. S. Development of a transgenic mouse system for the analysis of stages in liver carcinogenesis using tissue-specific expression of SV40 large T-antigen controlled by regulatory elements of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 1;49(21):6108–6117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheikh M. S., Rochefort H., Garcia M. Overexpression of p21WAF1/CIP1 induces growth arrest, giant cell formation and apoptosis in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1995 Nov 2;11(9):1899–1905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom S. C., Faust J. B., Cappelluti E., Harris R. B., Lalwani N. D. Characterization of liver epithelial cells transfected with myc and/or ras oncogenes. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 May;36(5):642–652. doi: 10.1007/BF01297033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Farshid M., Di Bisceglie A., Hsia C. C. Increased expression of transforming growth factor alpha after transfection of a human hepatoblastoma cell line with the hepatitis B virus. J Med Virol. 1992 Aug;37(4):271–273. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E. Tumor suppressor genes, growth factor genes, and oncogenes in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol. 1994 Apr;42(4):357–365. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890420406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Sharp R., Hammermeister C., Goodrow T., Bradley M. O., Fausto N., Merlino G. Molecular and genetic analysis of liver oncogenesis in transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5171–5177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi H., Sharp R., Takayama H., Anver M. R., Ward J. M., Merlino G. Collaboration between growth factors and diverse chemical carcinogens in hepatocarcinogenesis of transforming growth factor alpha transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 15;53(18):4329–4336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa J. E., Quigley J. P. The role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in aggressive tumor cell behavior. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Dec;9(4):353–367. doi: 10.1007/BF00049524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshkov I., Chisari F. V., Bannasch P. Hepatic preneoplasia in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Hepatology. 1994 Nov;20(5):1162–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tönjes R. R., Löhler J., O'Sullivan J. F., Kay G. F., Schmidt G. H., Dalemans W., Pavirani A., Paul D. Autocrine mitogen IgEGF cooperates with c-myc or with the Hcs locus during hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):765–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Pepper M. S. Tumour biology. Membrane proteases in focus. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):14–15. doi: 10.1038/370014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada K., Kondo F., Kondo Y. Large regenerative nodules and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic livers: a histopathologic study. Hepatology. 1988 Nov-Dec;8(6):1684–1688. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Okita K., Harada T., Kodama T., Numa Y., Takemoto T., Takahashi T. Morphologic studies of the liver cell dysplasia. Cancer. 1983 Jun 15;51(12):2197–2205. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830615)51:12<2197::aid-cncr2820511208>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber E. M., Wu J. C., Wang L., Merlino G., Fausto N. Overexpression of transforming growth factor-alpha causes liver enlargement and increased hepatocyte proliferation in transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):398–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Merlino G., Cveklova K., Mosinger B., Jr, Fausto N. Autonomous growth in serum-free medium and production of hepatocellular carcinomas by differentiated hepatocyte lines that overexpress transforming growth factor alpha 1. Cancer Res. 1994 Nov 15;54(22):5964–5973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Huang D. P., Chiu D. K., Chiu J. F. The expression of oncogenes in human developing liver and hepatomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):932–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]