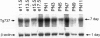Abstract
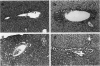
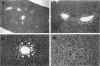
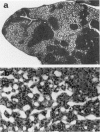
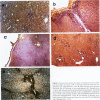
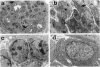
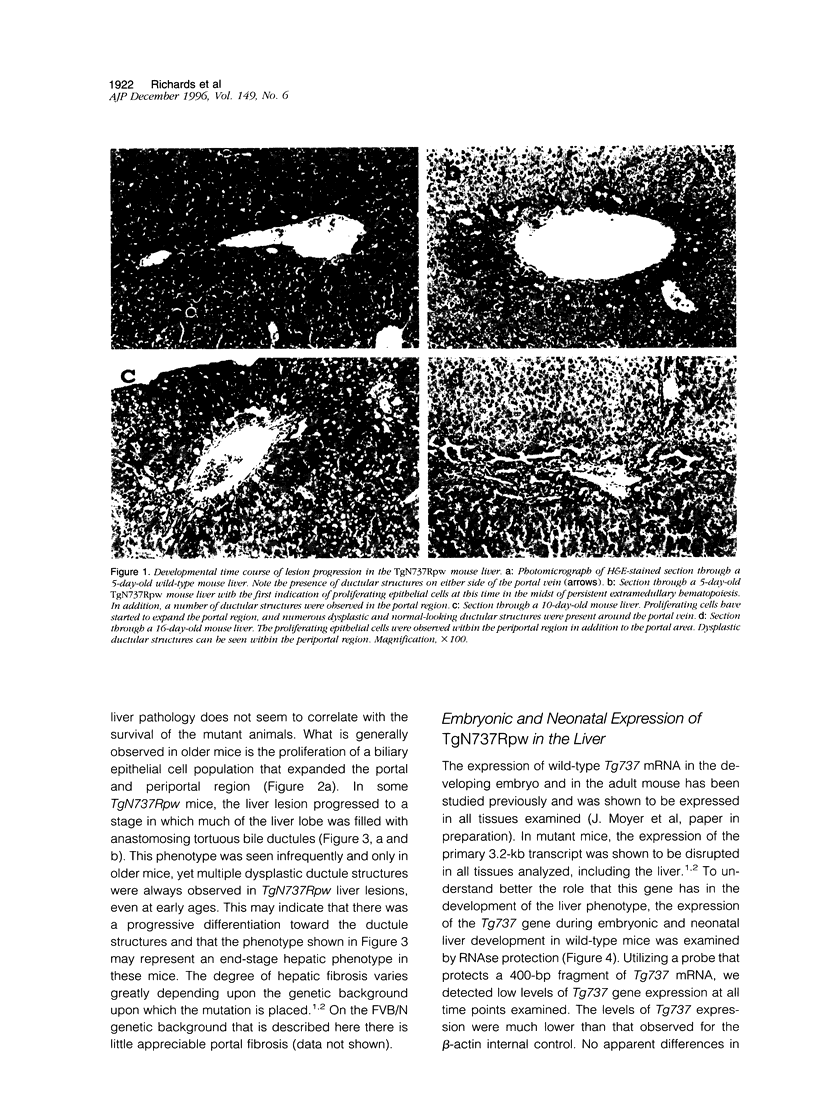
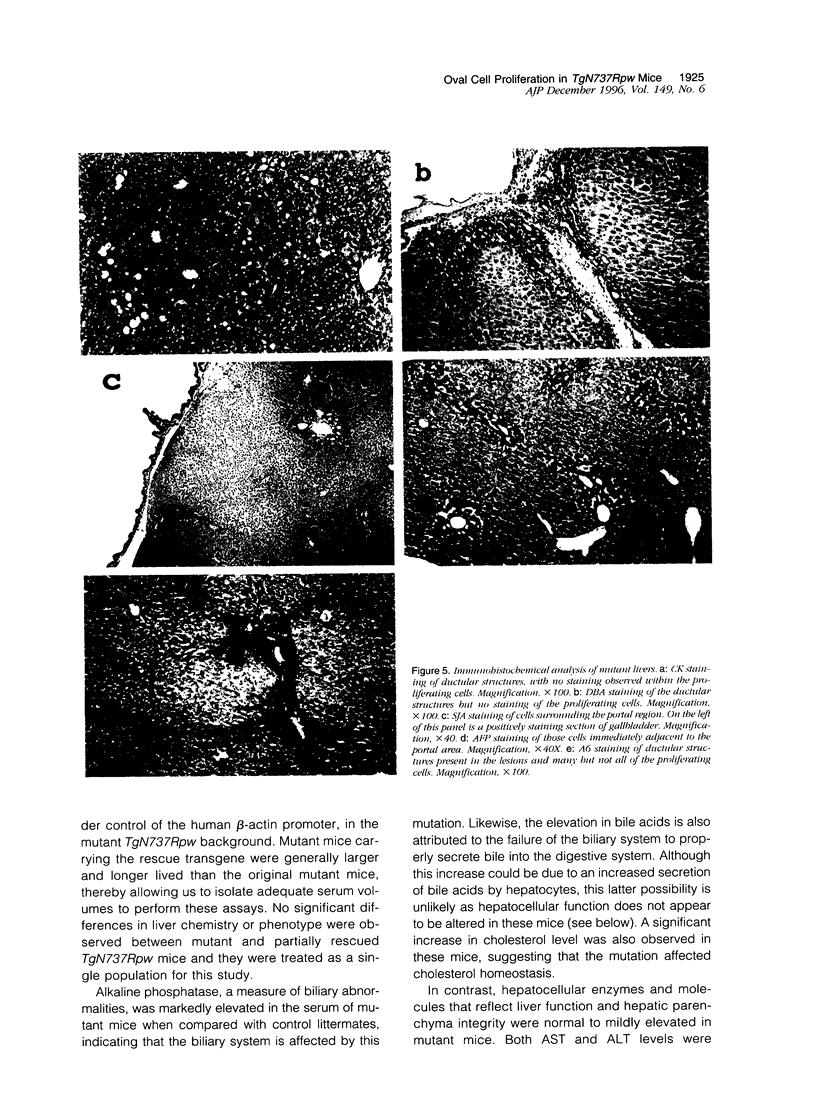
The Tg737 gene was identified by its direct association with a transgene-induced insertion mutation in the mouse. This mutation causes pleiotropic phenotypes including a syndrome similar to autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in humans. This syndrome, in addition to renal cyst formation, includes the presence of an invariably associated liver abnormality. The liver pathology in TgN737Rpw mice is characterized by a biliary hyperplasia that includes the proliferation of cells that morphologically and immunologically resemble oval cells, a liver progenitor cell. This abnormality is first observed at approximately 5 days of age in the portal region and then progresses into the periportal regions. Additionally, the formation and proliferation of dysplastic ductular structures are observed from the onset of the phenotype. Serum chemistry indicated that the primary defect is likely to be of biliary origin, and hepatic function appears normal in the mutant mice. Therefore, this mutation is unlike other causes of oval cell proliferation in that the hepatic parenchyma is relatively unaffected. The identification of the Tg737 gene associated with this mutation suggests that it functions in regulating the proliferation/differentiation of oval cells within the liver, which further indicates that this gene may function in pathological conditions that include oval cell proliferation, such as hepatocellular carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF




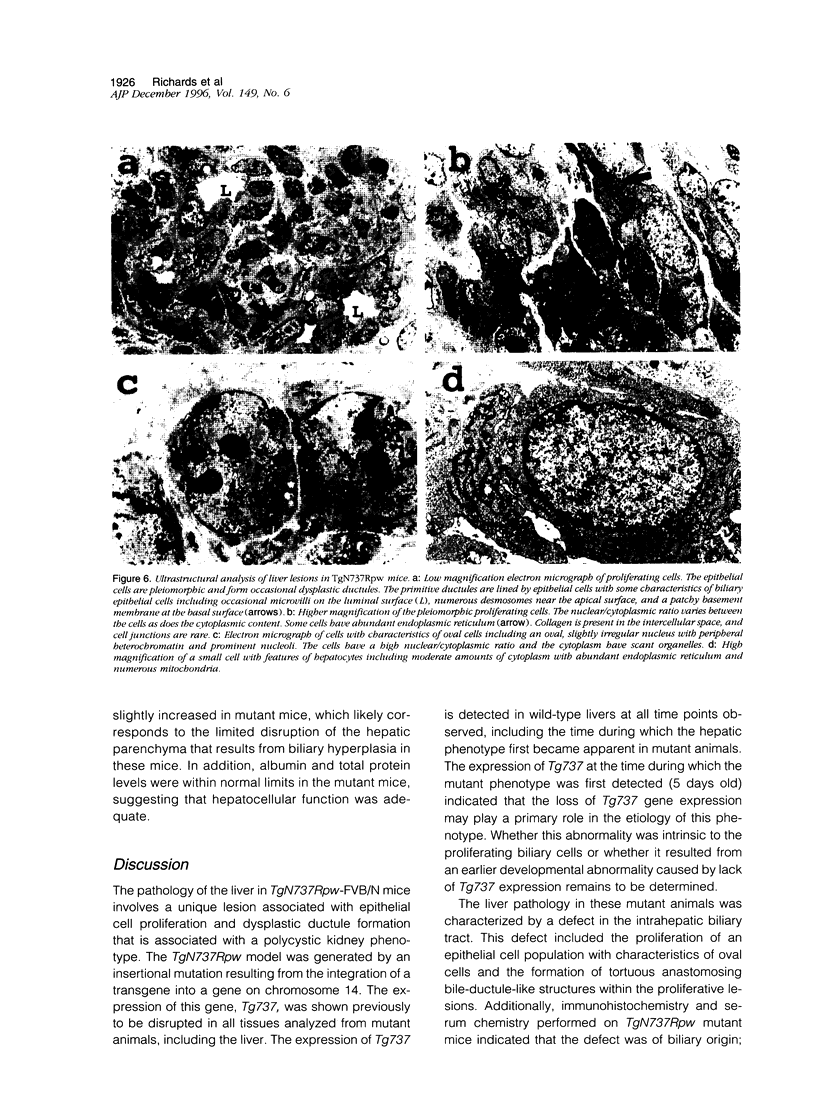
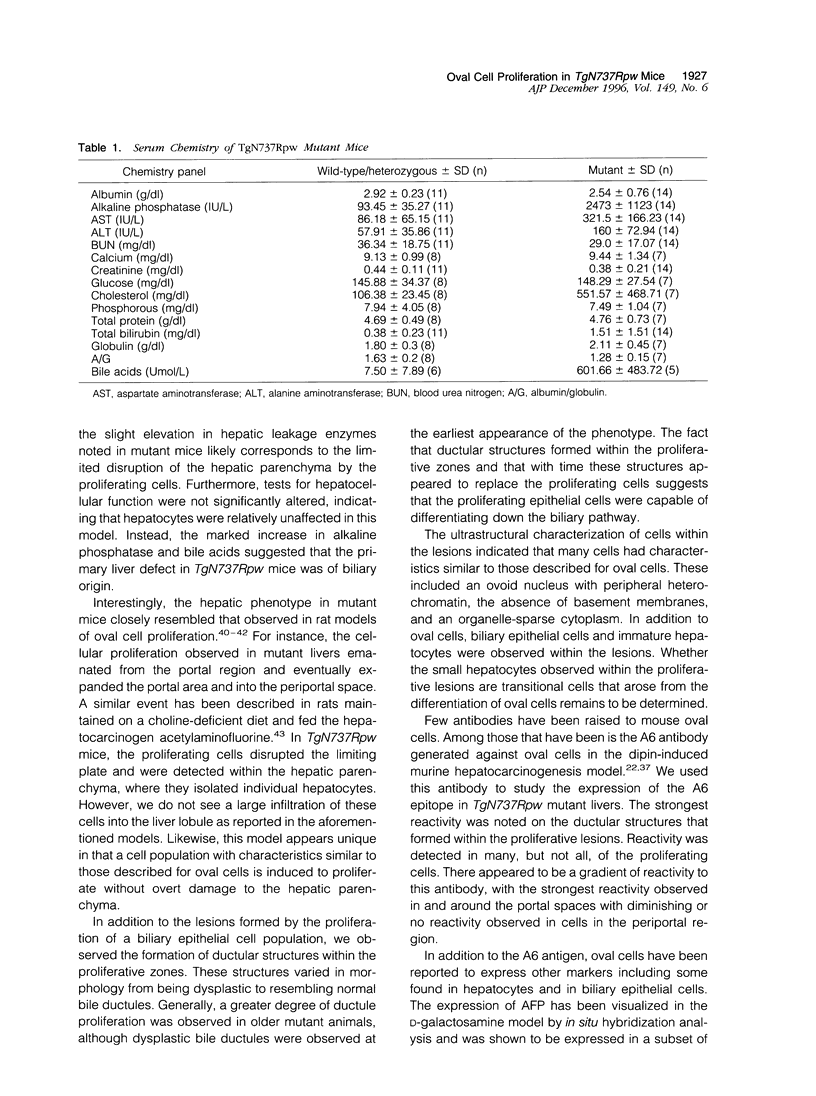



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arber N., Zajicek G., Ariel I. The streaming liver. II. Hepatocyte life history. Liver. 1988 Apr;8(2):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1988.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atala A., Freeman M. R., Mandell J., Beier D. R. Juvenile cystic kidneys (jck): a new mouse mutation which causes polycystic kidneys. Kidney Int. 1993 May;43(5):1081–1085. doi: 10.1038/ki.1993.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J., Chandra M., Creswell J., Kahn E., Malouf N. N., McVicar M., Weinberg A. G., Wybel R. E. Renal-hepatic-pancreatic dysplasia: a syndrome reconsidered. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Feb;26(2):391–403. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein J., Stickler G. B., Neel I. V. Congenital hepatic fibrosis: evolving morphology. APMIS Suppl. 1988;4:17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenberg T. A., Ruebner B. H., Ellis W. G., Bernstein J., Dimmick J. E. Pathology of renal and hepatic anomalies in Meckel syndrome. Am J Med Genet Suppl. 1987;3:395–410. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth H., Ockenden B. G. Polycystic disease of kidney and liver presenting in childhood. J Med Genet. 1971 Sep;8(3):257–284. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.3.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. B., Wennerberg A. E., Smith G. J., Grisham J. W. Regulation of the differentiation of diploid and some aneuploid rat liver epithelial (stemlike) cells by the hepatic microenvironment. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1373–1382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agata I. D., Jonas M. M., Perez-Atayde A. R., Guay-Woodford L. M. Combined cystic disease of the liver and kidney. Semin Liver Dis. 1994 Aug;14(3):215–228. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Shafritz D. A. Activation, proliferation, and differentiation of progenitor cells into hepatocytes in the D-galactosamine model of liver regeneration. Am J Pathol. 1993 Dec;143(6):1606–1620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davisson M. T., Guay-Woodford L. M., Harris H. W., D'Eustachio P. The mouse polycystic kidney disease mutation (cpk) is located on proximal chromosome 12. Genomics. 1991 Apr;9(4):778–781. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90376-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsford H. A., Karnasuta C., Hunt J. M., Sell S. Different lineages of chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats defined by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4894–4900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt N. V., Factor V. M., Medvinsky A. L., Baranov V. N., Lazareva M. N., Poltoranina V. S. Common antigen of oval and biliary epithelial cells (A6) is a differentiation marker of epithelial and erythroid cell lineages in early development of the mouse. Differentiation. 1993 Dec;55(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1993.tb00029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt N. V., Factor V. M., Yasova A. K., Poltoranina V. S., Baranov V. N., Lasareva M. N. Common antigens of mouse oval and biliary epithelial cells. Expression on newly formed hepatocytes. Differentiation. 1990 Oct;45(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts R. P., Marsden E., Hanna P., Wirth P. J., Thorgeirsson S. S. Isolation of preneoplastic rat liver cells by centrifugal elutriation and binding to asialofetuin. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5718–5724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts R. P., Nagy P., Nakatsukasa H., Marsden E., Thorgeirsson S. S. In vivo differentiation of rat liver oval cells into hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1541–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor V. M., Radaeva S. A., Thorgeirsson S. S. Origin and fate of oval cells in dipin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in the mouse. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):409–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausto N., Lemire J. M., Shiojiri N. Cell lineages in hepatic development and the identification of progenitor cells in normal and injured liver. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 Dec;204(3):237–241. doi: 10.3181/00379727-204-43659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty L., Bryda E. C., Collins D., Rudofsky U., Montogomery J. C. New mouse model for polycystic kidney disease with both recessive and dominant gene effects. Kidney Int. 1995 Feb;47(2):552–558. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Thung S. N. Liver stem cells and development. Lab Invest. 1993 Mar;68(3):253–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain L., Noël M., Gourdeau H., Marceau N. Promotion of growth and differentiation of rat ductular oval cells in primary culture. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 15;48(2):368–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M., Yanagida M. The TPR snap helix: a novel protein repeat motif from mitosis to transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90070-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Faris R., Braun L., Hixson D., Fausto N. Expression of hepatocyte and oval cell antigens in hepatocellular carcinomas produced by oncogene-transfected liver epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4809–4817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham J. J. Polycystic kidney disease: hereditary and acquired. Adv Intern Med. 1993;38:409–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham J. W., Coleman W. B., Smith G. J. Isolation, culture, and transplantation of rat hepatocytic precursor (stem-like) cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 Dec;204(3):270–279. doi: 10.3181/00379727-204-43663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Shiojiri N., Fausto N. Oval cell proliferation and the origin of small hepatocytes in liver injury induced by D-galactosamine. Am J Pathol. 1991 Sep;139(3):535–552. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer J. H., Lee-Tischler M. J., Kwon H. Y., Schrick J. J., Avner E. D., Sweeney W. E., Godfrey V. L., Cacheiro N. L., Wilkinson J. E., Woychik R. P. Candidate gene associated with a mutation causing recessive polycystic kidney disease in mice. Science. 1994 May 27;264(5163):1329–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.8191288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Takahashi H. Linkage analysis of two murine polycystic kidney disease genes, pcy and cpk. Jikken Dobutsu. 1991 Oct;40(4):557–560. doi: 10.1538/expanim1978.40.4_557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauta J., Ozawa Y., Sweeney W. E., Jr, Rutledge J. C., Avner E. D. Renal and biliary abnormalities in a new murine model of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993 Apr;7(2):163–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00864387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama T., Fullerton F., Reznik G., Bucci T. J., Ward J. M. Mouse hepatoblastomas: a histologic, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical study. Vet Pathol. 1988 Jul;25(4):286–296. doi: 10.1177/030098588802500407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Martin A. A., Thung S. N., Gerber M. A. Morphometric and immunohistochemical characterization of human liver regeneration. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):397–404. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrick J. J., Onuchic L. F., Reeders S. T., Korenberg J., Chen X. N., Moyer J. H., Wilkinson J. E., Woychik R. P. Characterization of the human homologue of the mouse Tg737 candidate polycystic kidney disease gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Apr;4(4):559–567. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.4.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Hunt J. M., Knoll B. J., Dunsford H. A. Cellular events during hepatocarcinogenesis in rats and the question of premalignancy. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;48:37–111. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. Liver stem cells. Mod Pathol. 1994 Jan;7(1):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Salman J. Light- and electron-microscopic autoradiographic analysis of proliferating cells during the early stages of chemical hepatocarcinogenesis in the rat induced by feeding N-2-fluorenylacetamide in a choline-deficient diet. Am J Pathol. 1984 Feb;114(2):287–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal S. H., Brill S., Fiorino A. S., Reid L. M. The liver as a stem cell and lineage system. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):G139–G148. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.2.G139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirica A. E., Mathis G. A., Sano N., Elmore L. W. Isolation, culture, and transplantation of intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells and oval cells. Pathobiology. 1990;58(1):44–64. doi: 10.1159/000163564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Calvet J. P., Dittemore-Hoover D., Yoshida K., Grantham J. J., Gattone V. H., 2nd A hereditary model of slowly progressive polycystic kidney disease in the mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Jan;1(7):980–989. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V17980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada T., Nakanuma Y. Development of human intrahepatic peribiliary glands. Histological, keratin immunohistochemical, and mucus histochemical analyses. Lab Invest. 1993 Mar;68(3):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson S. S. Hepatic stem cells. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1331–1333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J. The search for liver stem cells picks up. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1829–1829. doi: 10.1126/science.8456311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao M. S., Grisham J. W. Hepatocarcinomas, cholangiocarcinomas, and hepatoblastomas produced by chemically transformed cultured rat liver epithelial cells. A light- and electron-microscopic analysis. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):168–181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. K., Richards W. G., Sommardahl C., Sweeney W. E., Michaud E. J., Wilkinson J. E., Avner E. D., Woychik R. P. Functional correction of renal defects in a mouse model for ARPKD through expression of the cloned wild-type Tg737 cDNA. Kidney Int. 1996 Oct;50(4):1240–1248. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder B. K., Richards W. G., Sweeney W. E., Wilkinson J. E., Avener E. D., Woychik R. P. Insertional mutagenesis and molecular analysis of a new gene associated with polycystic kidney disease. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1995 Oct;107(3):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajicek G., Oren R., Weinreb M., Jr The streaming liver. Liver. 1985 Dec;5(6):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1985.tb00252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerres K., Mücher G., Bachner L., Deschennes G., Eggermann T., Käriäinen H., Knapp M., Lennert T., Misselwitz J., von Mühlendahl K. E. Mapping of the gene for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) to chromosome 6p21-cen. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):429–432. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]