Abstract
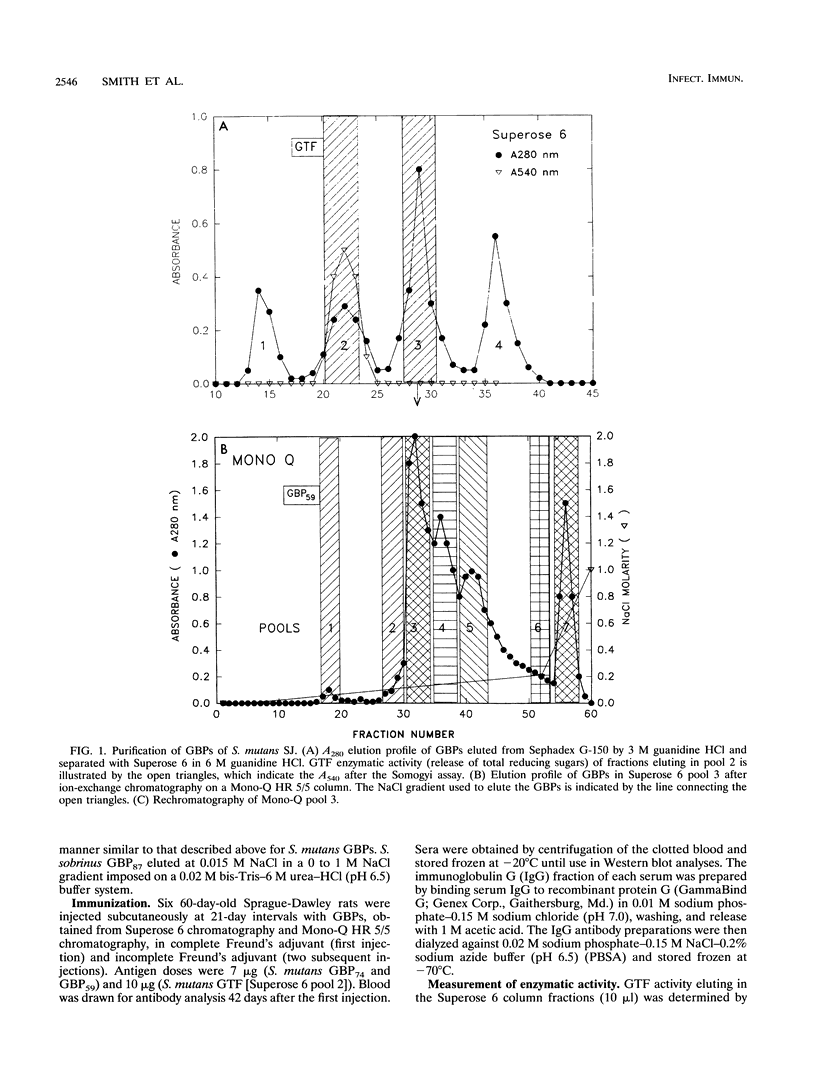
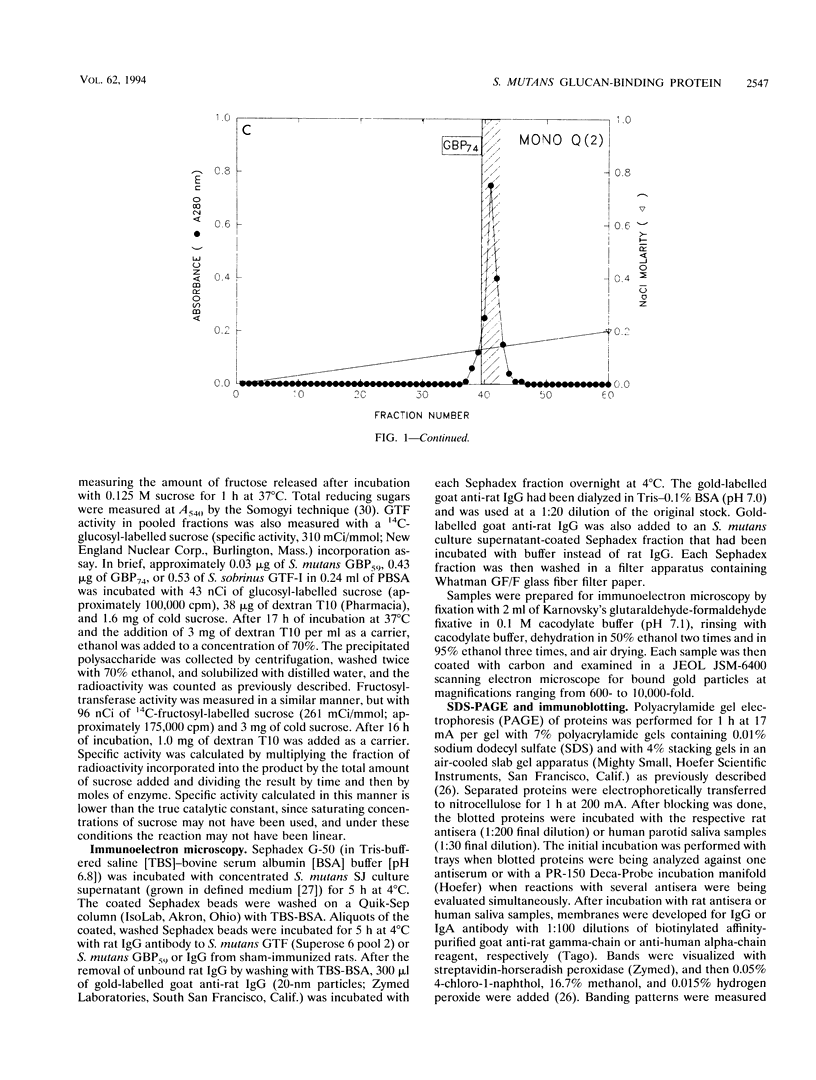
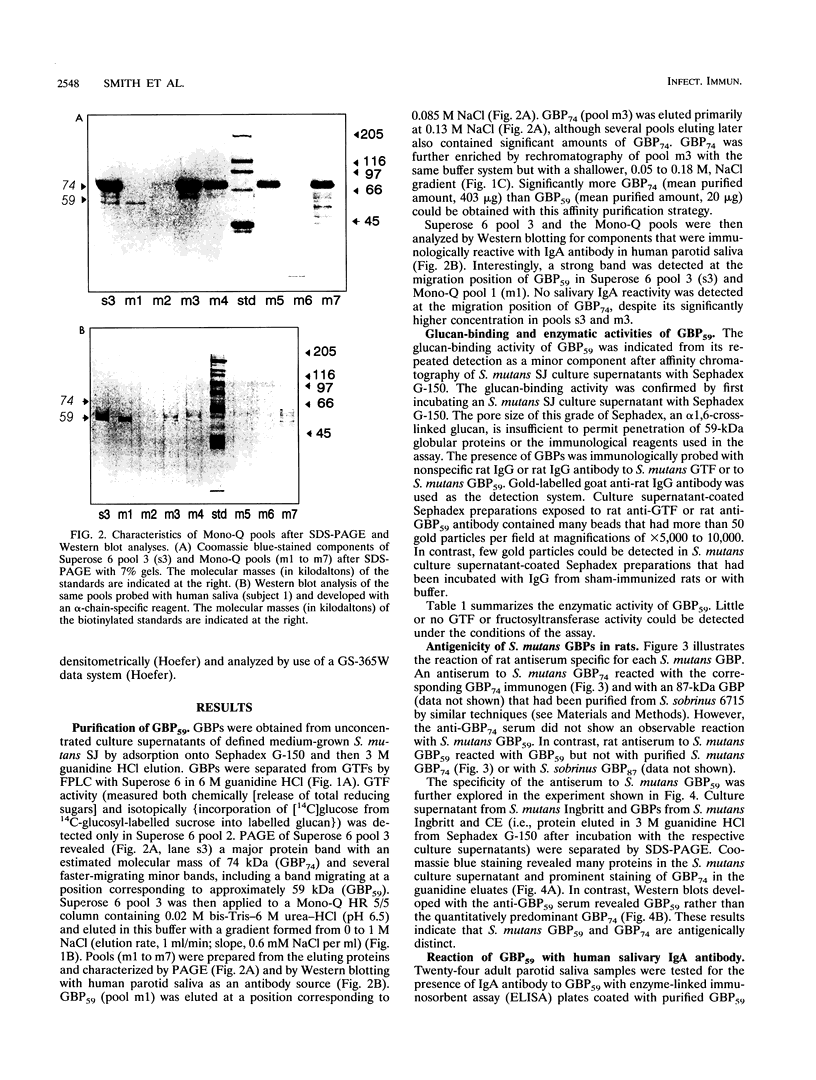
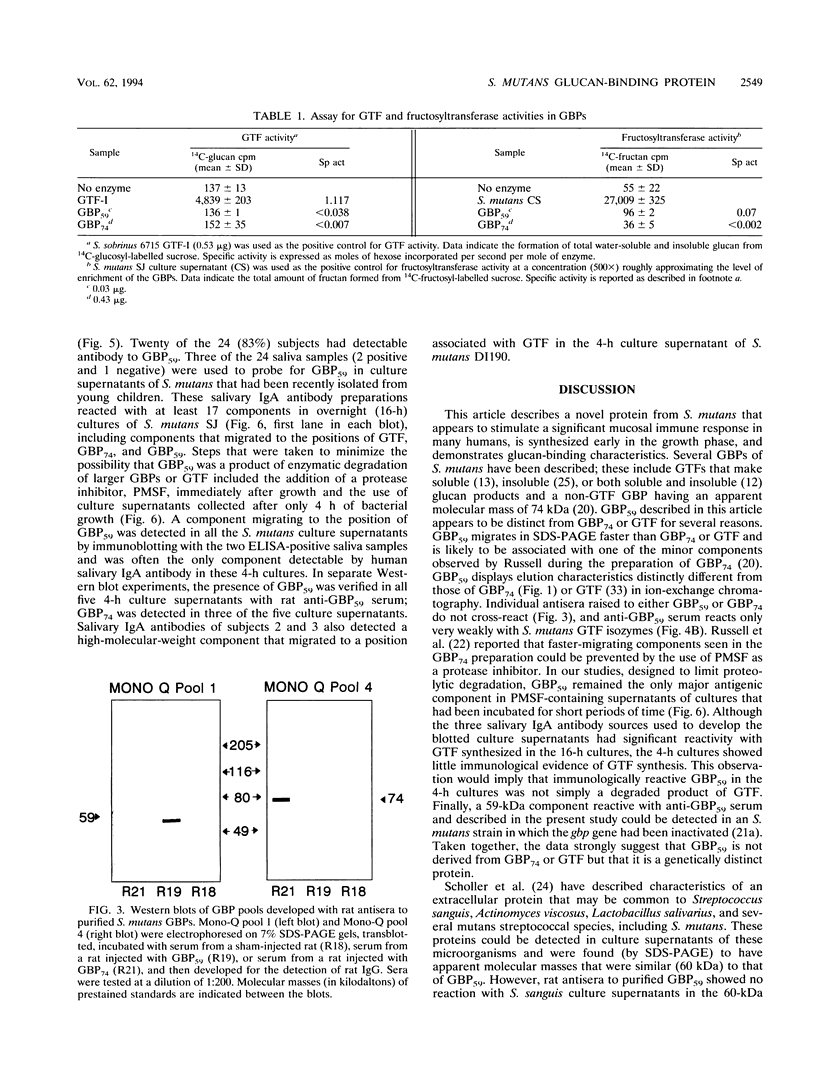
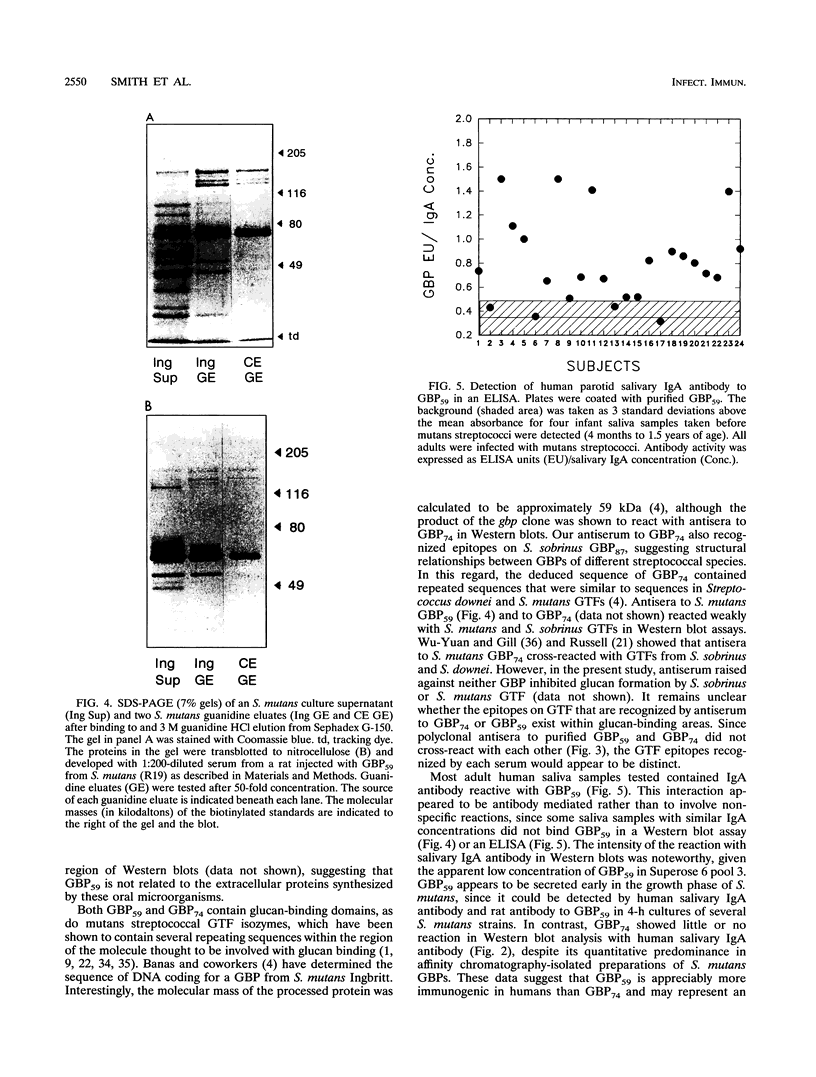
A novel glucan-binding protein (GBP) having an apparent molecular mass of 59 kDa (GBP59) has been purified from Streptococcus mutans SJ by a combination of affinity chromatography on alpha-1,6-linked glucan, gel filtration chromatography, and ion-exchange chromatography. GBP59 was distinct from the quantitatively predominant S. mutans GBP (GBP74) on the basis of size, elution position in a salt gradient, and antigenicity. Rat antisera to purified GBP59 and GBP74 did not cross-react. GBP59 is apparently immunogenic in humans, since immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody in 20 of 24 adult parotid saliva samples was shown to react with GBP59 in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The glucan-binding activity of GBP59 was confirmed by anti-GBP59 immunogold labelling of Sephadex G-50 that had been preincubated with S. mutans culture supernatant. GBP59 could be detected in culture supernatants of all laboratory strains of S. mutans (e.g., Ingbritt), as well as all strains of S. mutans that had been recently isolated from young children. GBP59 was often the only component in protease inhibitor-containing 4-h S. mutans culture supernatants that reacted with human parotid salivary IgA antibody in Western blot (immunoblot) analyses. These studies suggest that GBP59 is a structurally and antigenically distinct S. mutans GBP that can elicit significant levels of salivary IgA antibody in humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo H., Matsumura T., Kodama T., Ohta H., Fukui K., Kato K., Kagawa H. Peptide sequences for sucrose splitting and glucan binding within Streptococcus sobrinus glucosyltransferase (water-insoluble glucan synthetase). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):989–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.989-996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aduse-Opoku J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Genetic and antigenic comparison of Streptococcus mutans fructosyltransferase and glucan-binding protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jun;50(3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90432-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banas J. A., Russell R. R., Ferretti J. J. Sequence analysis of the gene for the glucan-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):667–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.667-673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Taylor K. G., Bleiweis A. S., Doyle R. J. Specificity of the glucan-binding lectin of Streptococcus cricetus. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1864–1872. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1864-1872.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Huang T. T., Russell R. R. Sequence analysis of the glucosyltransferase A gene (gtfA) from Streptococcus mutans Ingbritt. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1585-1588.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffard P. M., Simpson C. L., Milward C. P., Jacques N. A. Molecular characterization of a cluster of at least two glucosyltransferase genes in Streptococcus salivarius ATCC 25975. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Nov;137(11):2577–2593. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-11-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore K. S., Russell R. R., Ferretti J. J. Analysis of the Streptococcus downei gtfS gene, which specifies a glucosyltransferase that synthesizes soluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2452–2458. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2452-2458.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfC gene, coding for synthesis of both soluble and insoluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1999–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1999-2005.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfD gene, coding for primer-dependent soluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2079–2085. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2079-2085.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial adhesions of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):321–340. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Asakawa H., Okahashi N., Hamada S. Sucrose-dependent cell adherence and cariogenicity of serotype c Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Oct;132(10):2873–2883. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-10-2873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landale E. C., McCabe M. M. Characterization by affinity electrophoresis of an alpha-1,6-glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3011–3016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3011-3016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Alberts M., Stein J. Monoclonal antibodies to the extracellular glucosyltransferases from Streptococcus sobrinus 6715. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1900–1905. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1900-1905.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M., Hamelik R. M., Smith E. E. Purification of dextran-binding protein from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe M. M. Purification and characterization of a primer-independent glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans 6715-13 mutant 27. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.771-777.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser G., Wong C. Isolation of a glucan-binding domain of glucosyltransferase (1,6-alpha-glucan synthase) from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):880–884. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.880-884.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Donald A. C., Douglas C. W. Fructosyltransferase activity of a glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3243–3250. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Glucan-binding proteins of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 May;112(1):197–201. doi: 10.1099/00221287-112-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Molecular genetics of glucan metabolism in oral streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1990;35 (Suppl):53S–58S. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(90)90131-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K., Ferretti J. J. Homology of glucosyltransferase gene and protein sequences from Streptococcus sobrinus and Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1988 Mar;67(3):543–547. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670030401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöller M., Klein J. P., Sommer P., Frank R. Common antigens of streptococcal and nonstreptococcal oral bacteria: characterization of wall-associated protein and comparison with extracellular protein antigen. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1186–1191. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1186-1191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfB gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4263–4270. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4263-4270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., King W. F., Taubman M. A. Salivary IgA antibody to oral streptococcal antigens in predentate infants. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1990 Apr;5(2):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1990.tb00228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Ebersole J. L. Preparation of glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans by elution from water-insoluble polysaccharide with a dissociating solvent. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):446–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.446-452.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Holmberg C. F., Eastcott J., King W. F., Ali-Salaam P. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of a synthetic peptide derived from a glucan-binding domain of mutans streptococcal glucosyltransferase. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2899–2905. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2899-2905.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland I. W. Microbial exopolysaccharides -- their role in microbial adhesion in aqueous systems. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1983;10(2):173–201. doi: 10.3109/10408418209113562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taubman M. A., Smith D. J., King W. F., Eastcott J. W., Bergey E. J., Levine M. J. Immune properties of glucosyltransferases from S. sobrinus. J Oral Pathol. 1988 Nov;17(9-10):466–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Hefta S. A., Paxton R. J., Shively J. E., Mooser G. Size and subdomain architecture of the glucan-binding domain of sucrose:3-alpha-D-glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2165–2170. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2165-2170.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Yuan C. D., Gill R. E. An 87-kilodalton glucan-binding protein of Streptococcus sobrinus B13. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5291–5293. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5291-5293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Eichel-Streiber C., Sauerborn M., Kuramitsu H. K. Evidence for a modular structure of the homologous repetitive C-terminal carbohydrate-binding sites of Clostridium difficile toxins and Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6707–6710. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6707-6710.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]