Abstract
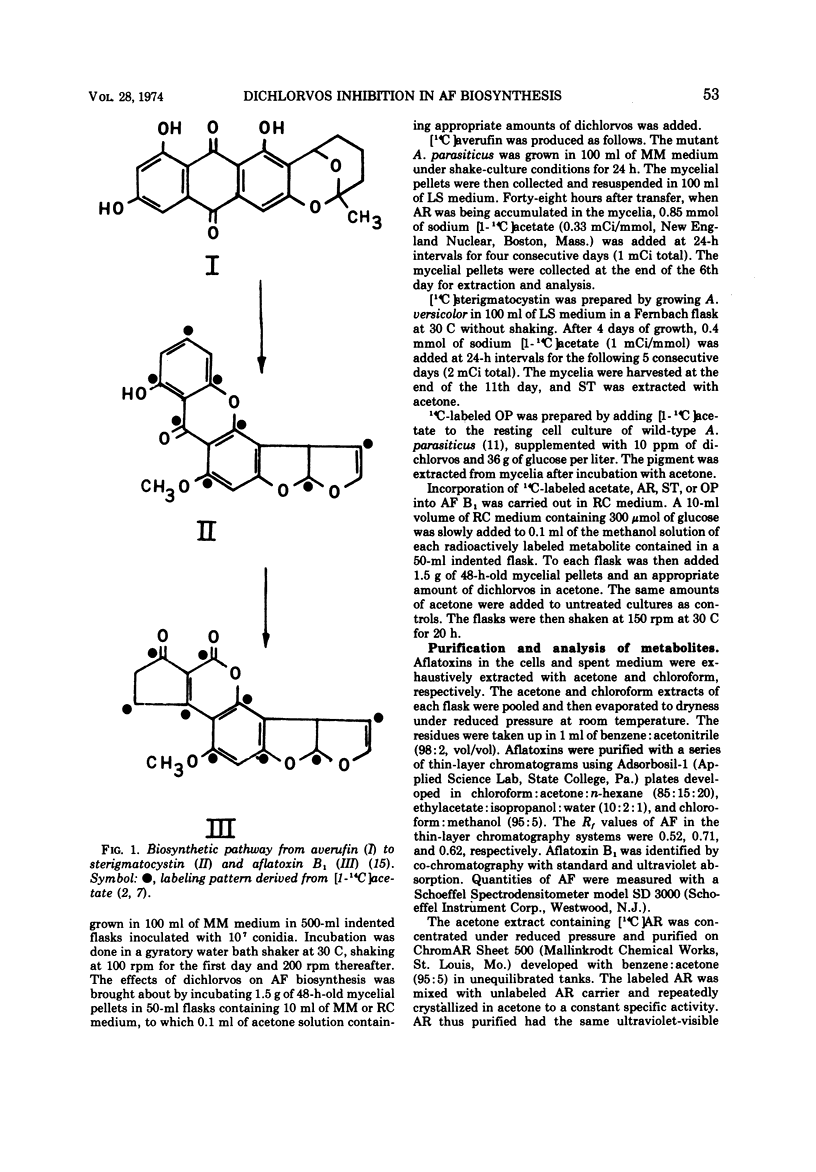
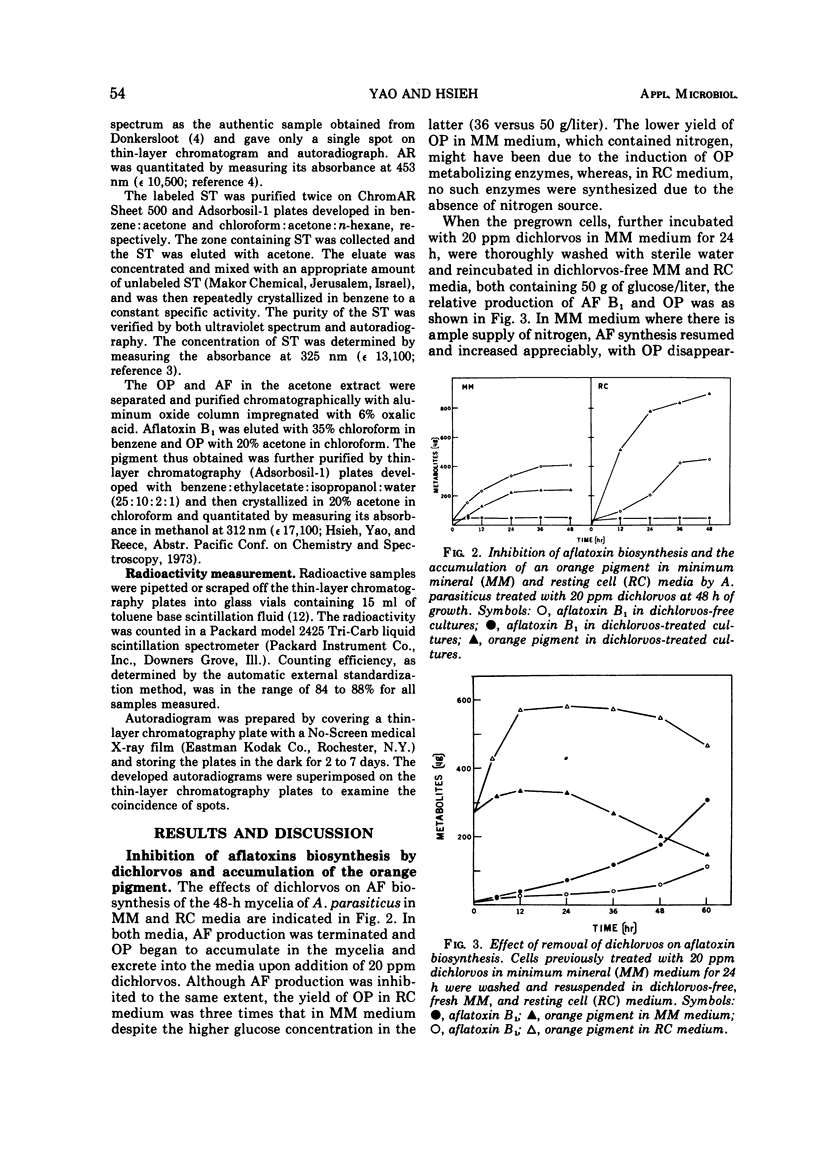
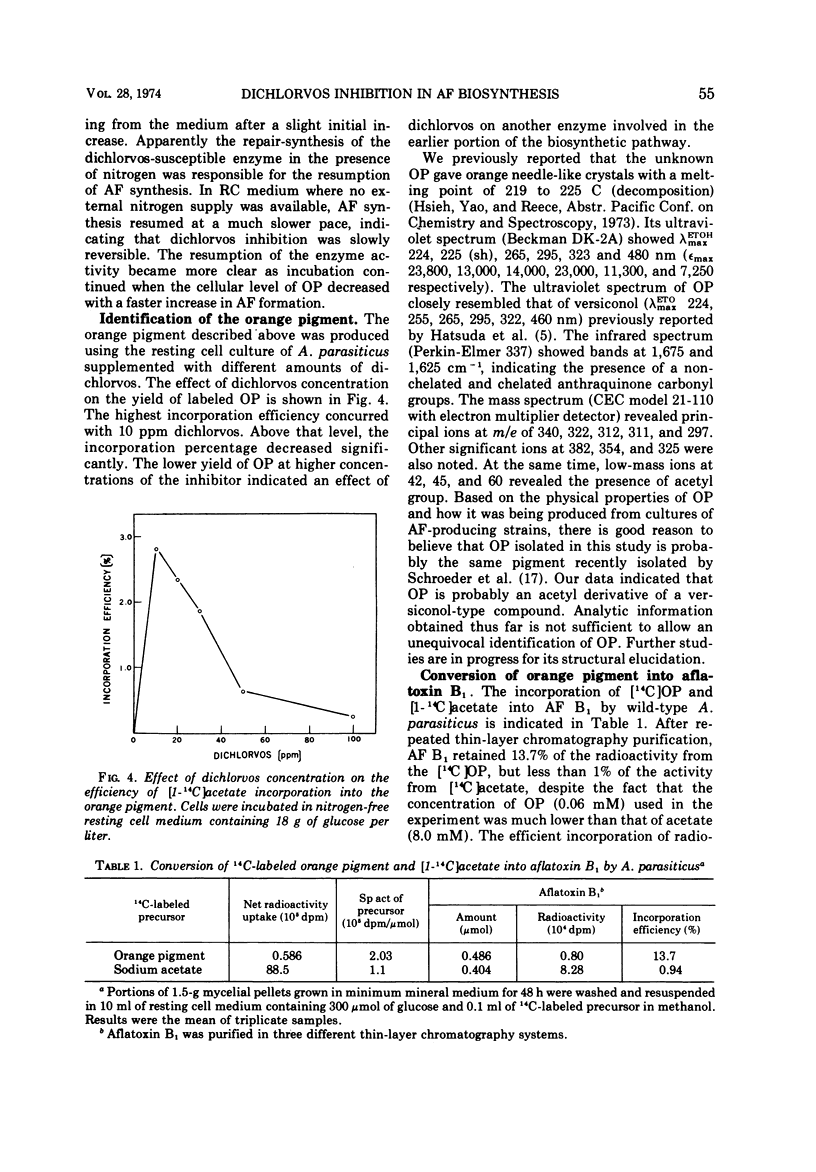
Dichlorvos (dimethyl 2,2-dichlorovinyl phosphate) inhibits the biosynthesis of aflatoxin by Aspergillus parasiticus. Cultures treated with dichlorvos excrete an orange pigment which can be converted into aflatoxin B1 by the untreated mycelia. The orange pigment was partially identified as an acetyl derivative of versiconol-type compound. In the presence of dichlorvos, sterigmatocystin is converted into aflatoxin B1 without being interfered, but averufin is converted into the orange pigment instead of aflatoxin B1. Therefore, dichlorvos appears to block an enzymatic step in the aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway, which lies beyond averufin but before sterigmatocystin, at the formation of the orange pigment.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADYE J., MATELES R. I. INCORPORATION OF LABELLED COMPOUNDS INTO AFLATOXINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:418–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biollaz M., Büchi G., Milne G. The biosynthesis of the aflatoxins. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Feb 25;92(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1021/ja00707a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donkersloot J. A., Mateles R. I., Yang S. S. Isolation of averufin from a mutant of Aspergillus parasiticus impaired in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90939-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P. Inhibition of aflatoxin biosynthesis of dichlorvos. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 May-Jun;21(3):468–470. doi: 10.1021/jf60187a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Lin M. T., Yao R. C. Conversion of sterigmatocystin to aflatoxin B 1 by Aspergillus parasiticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):992–997. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Mateles R. I. Preparation of labeled aflatoxins with high specific activities. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jul;22(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/am.22.1.79-83.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Mateles R. I. The relative contribution of acetate and glucose to aflatoxin biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun;208(3):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. T., Hsieh D. P., Yao R. C., Donkersloot J. A. Conversion of averufin into aflatoxins by Aspergillus parasiticus. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5167–5171. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao H. R., Harein P. K. Inhibition of aflatoxin and zearalenone biosynthesis with dichlorvos. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1973 Aug;10(2):112–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01685882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy T. V., Viswanathan L., Venkitasubramanian T. A. High aflatoxin production on a chemically defined medium. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):393–396. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.393-396.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Cole R. J., Grigsby R. D., Hein H., Jr Inhibition of aflatoxin production and tentative identification of an aflatoxin intermediate "versiconal acetate" from treatment with dichlorvos. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):394–399. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.394-399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


