Abstract
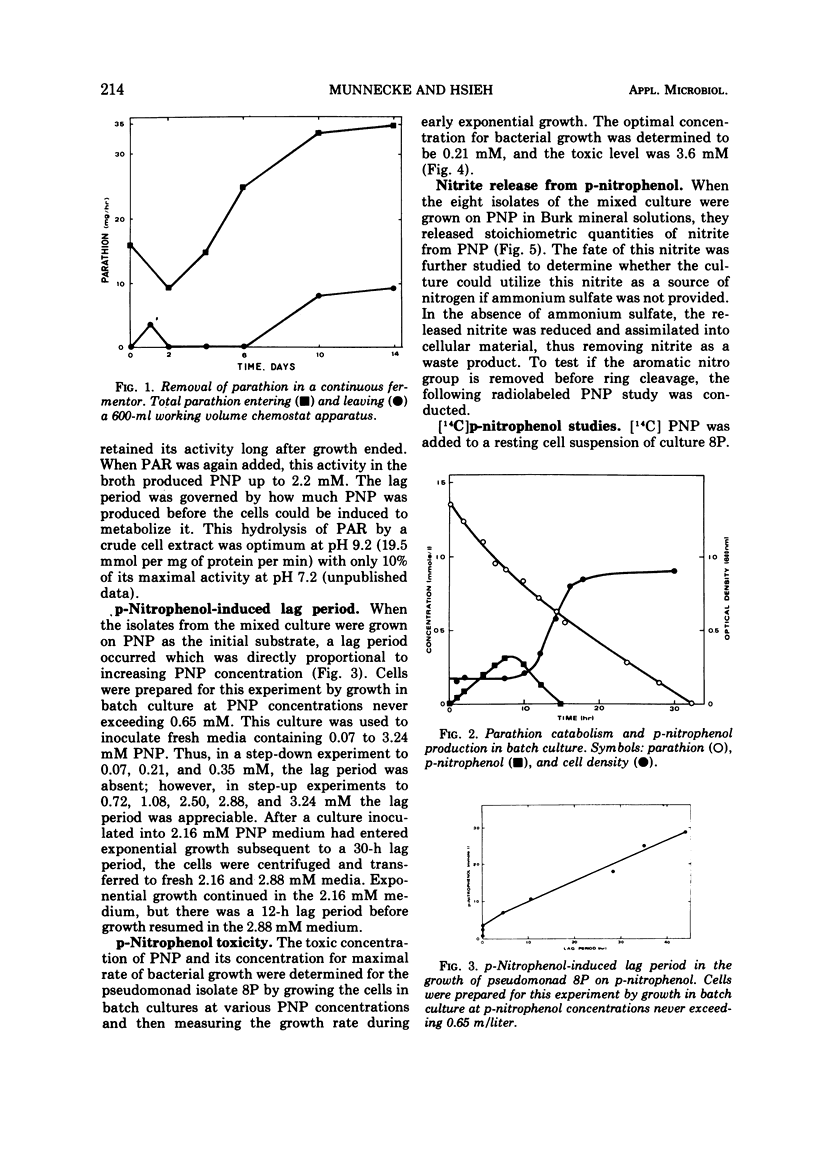
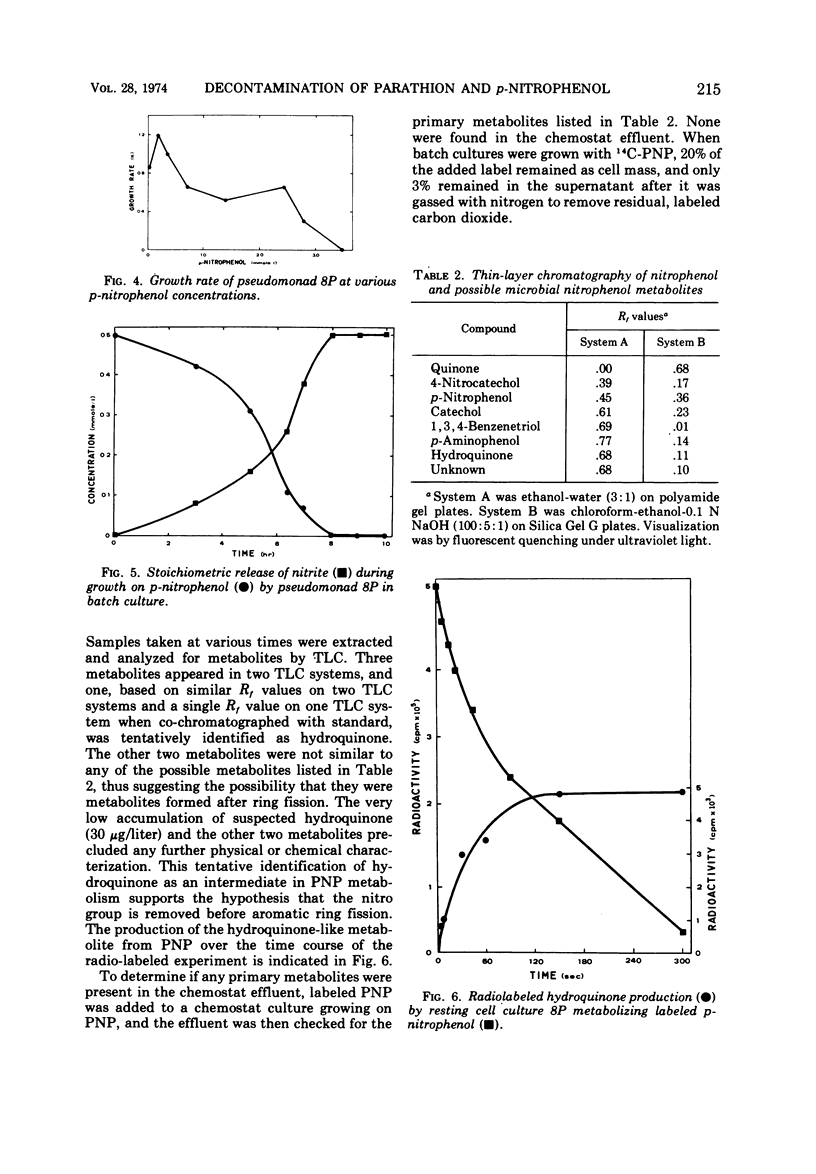
A mixed microbial culture was adapted to growth on parathion to determine the feasibility of using microorganisms to detoxify concentrated parathion in agricultural wastes. In a 600-ml chemostat, the culture was able to degrade 50 mg of parathion per liter per h. Para-nitrophenol, produced by enzymatic hydrolysis of parathion, caused delays in exponential growth which were directly proportional to its concentration. A pseudomonad, isolated from the mixed culture, exhibited optimal growth at 0.21 mM p-nitrophenol and grew in concentrations up to 3.5 mM. In metabolic studies using [14C]p-nitrophenol, the nitro group was removed in stoichiometric quantities as nitrite and hydroquinone was tentatively identified as a metabolite.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain E. M., Dagley S. The metabolism of thymol by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):755–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1100755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust S. D. Chemical hydrolysis of some organic phosphorus and carbamate pesticides in aquatic environments. Environ Lett. 1972;3(3):171–201. doi: 10.1080/00139307209435465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMANIER R., WUHRMANN K. UBER DEN AEROBEN MIKROBIELLEN ABBAU AROMATISCHER NITROVERBINDUNGEN. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1963;26:569–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N. Degradation of parathion in flooded acid soils. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Jul-Aug;21(4):602–604. doi: 10.1021/jf60188a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddaramappa R., Rajaram K. P., Sethunathan N. Degradation of parathion by bacteria isolated from flooded soil. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):846–849. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.846-849.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


