Abstract
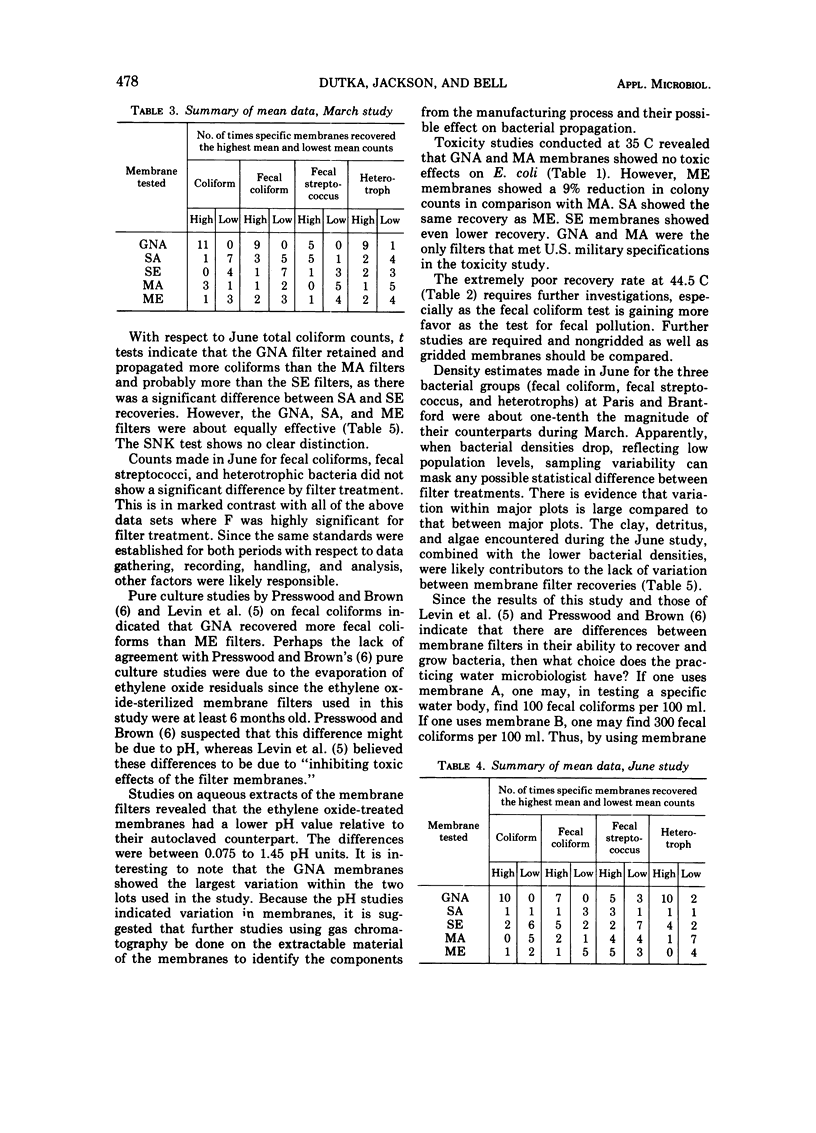
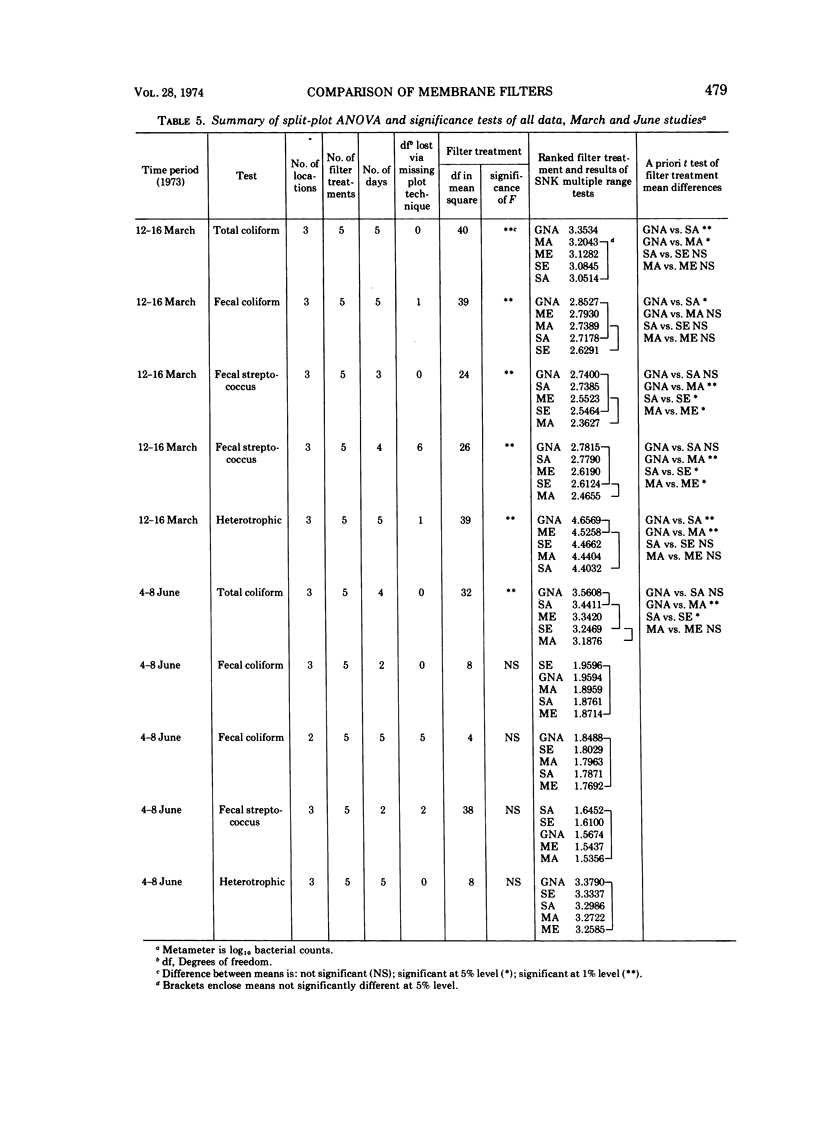
Autoclave and ethylene oxide-sterilized membrane filters manufactured by Gelman, Millipore, and Sartorius were field tested for their recovery of total coliforms, fecal coliforms, fecal streptococci, and heterotrophs. The data were analyzed by using split-plot analysis of variance and significance tests. Membranes were also tested for pH and toxicity using Escherichia coli. The mean data summaries indicated that Gelman membrane filters generally produced the highest counts during the field studies. Statistical analyses of the March data showed that there were significant differences between membrane filters at 1% level; however, statistical analyses of June data revealed no significant differences except in total coliform recoveries. Toxicity tests at 35 C indicated that Gelman and Millipore autoclaved membrane filters were able to recover 92% of the test organisms. Toxicity tests performed at 44.5 C revealed that no membranes were able to recover more than 40% of the test organisms. Since differences were found in the ability of the three brands of membrane filters to recover bacteria from natural and controlled sources, membrane filters from different manufacturers cannot be readily interchanged. There is a need for a standardized procedure for testing bacterial recovery by membrane filters.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Presswood W. G., Brown L. R. Comparison of Gelman and Millipore membrane filters for enumerating fecal coliform bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):332–336. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.332-336.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]