Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (172.2 KB).
Figure 1 .
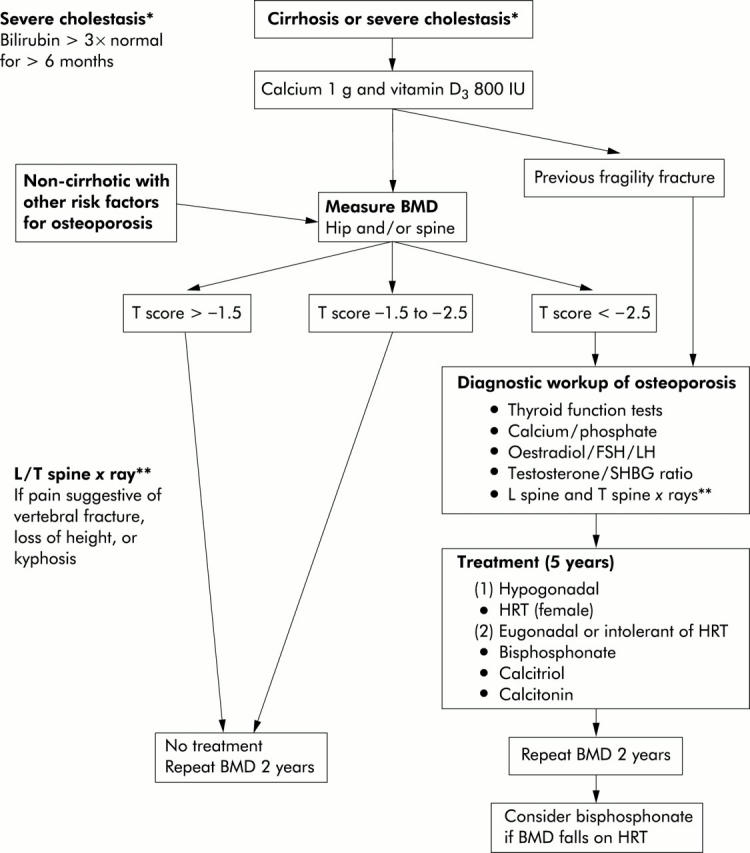
Summary of the strategy for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. BMD, bone mineral density measured by dual energy x ray absorptiometry; HRT, hormone replacement therapy; SHBG, sex hormone binding globulin; FH, follicle stimulating hormone; LH, luteinising hormone.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson F. H., Francis R. M., Peaston R. T., Wastell H. J. Androgen supplementation in eugonadal men with osteoporosis: effects of six months' treatment on markers of bone formation and resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 1997 Mar;12(3):472–478. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angulo P., Therneau T. M., Jorgensen A., DeSotel C. K., Egan K. S., Dickson E. R., Hay J. E., Lindor K. D. Bone disease in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis: prevalence, severity and prediction of progression. J Hepatol. 1998 Nov;29(5):729–735. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behre H. M., von Eckardstein S., Kliesch S., Nieschlag E. Long-term substitution therapy of hypogonadal men with transscrotal testosterone over 7-10 years. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999 May;50(5):629–635. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1999.00705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkovsky H. L., Hawkins M., Steinberg K., Hersh T., Galambos J. T., Henderson J. M., Millikan W. J., Galloway J. R. Prevalence and prediction of osteopenia in chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1990 Aug;12(2):273–280. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840120214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camisasca M., Crosignani A., Battezzati P. M., Albisetti W., Grandinetti G., Pietrogrande L., Biffi A., Zuin M., Podda M. Parenteral calcitonin for metabolic bone disease associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1994 Sep;20(3):633–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Wang S. S., Jeng F. S., Lee S. D. Metabolic bone disease of liver cirrhosis: is it parallel to the clinical severity of cirrhosis? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 May;11(5):417–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1996.tb00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston J. E., Crowe J. P., Horton L. W. Treatment of osteomalacia associated with primary biliary cirrhosis with oral 1-alpha-hydroxy vitamin D3. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 4;2(6185):309–309. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6185.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crippin J. S., Jorgensen R. A., Dickson E. R., Lindor K. D. Hepatic osteodystrophy in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of medical treatment. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jan;89(1):47–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosbie O. M., Freaney R., McKenna M. J., Hegarty J. E. Bone density, vitamin D status, and disordered bone remodeling in end-stage chronic liver disease. Calcif Tissue Int. 1999 Apr;64(4):295–300. doi: 10.1007/s002239900622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Lunzer M., Wilkinson M., Posen S. Ethanol reduces bone formation and may cause osteoporosis. Am J Med. 1989 Mar;86(3):282–288. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Lunzer M., Wilkinson M., Roche J., Posen S. Osteoporosis and skeletal fractures in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1990 Jan;31(1):82–87. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Lunzer M., Wilkinson M., Roche J., Posen S. Osteoporosis and skeletal fractures in chronic liver disease. Gut. 1990 Jan;31(1):82–87. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Mason R., Lissner D., Bikle D., Wilson S., Posen S. Serum vitamin D metabolites are not responsible for low turnover osteoporosis in chronic liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec;69(6):1234–1239. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-6-1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Posen S. Effects of testosterone and venesection on spinal and peripheral bone mineral in six hypogonadal men with hemochromatosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1991 Jan;6(1):39–43. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650060108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond T., Stiel D., Posen S. Osteoporosis in hemochromatosis: iron excess, gonadal deficiency, or other factors? Ann Intern Med. 1989 Mar 15;110(6):430–436. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-6-430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastell R., Boyle I. T., Compston J., Cooper C., Fogelman I., Francis R. M., Hosking D. J., Purdie D. W., Ralston S., Reeve J. Management of male osteoporosis: report of the UK Consensus Group. QJM. 1998 Feb;91(2):71–92. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/91.2.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastell R., Dickson E. R., Hodgson S. F., Wiesner R. H., Porayko M. K., Wahner H. W., Cedel S. L., Riggs B. L., Krom R. A. Rates of vertebral bone loss before and after liver transplantation in women with primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1991 Aug;14(2):296–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastell R., Reid D. M., Compston J., Cooper C., Fogelman I., Francis R. M., Hosking D. J., Purdie D. W., Ralston S. H., Reeve J. A UK Consensus Group on management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: an update. J Intern Med. 1998 Oct;244(4):271–292. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1998.00408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein O., Kato Y., Dick R., Sherlock S. Vitamin D, hydroxyapatite, and calcium gluconate in treatment of cortical bone thinning in postmenopausal women with primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Sep;36(3):426–430. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/36.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feitelberg S., Epstein S., Ismail F., D'Amanda C. Deranged bone mineral metabolism in chronic alcoholism. Metabolism. 1987 Apr;36(4):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floreani A., Zappala F., Fries W., Naccarato R., Plebani M., D'Angelo A., Chiaramonte M. A 3-year pilot study with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, calcium, and calcitonin for severe osteodystrophy in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997 Jun;24(4):239–244. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199706000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego-Rojo F. J., Gonzalez-Calvin J. L., Muñoz-Torres M., Mundi J. L., Fernandez-Perez R., Rodrigo-Moreno D. Bone mineral density, serum insulin-like growth factor I, and bone turnover markers in viral cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998 Sep;28(3):695–699. doi: 10.1002/hep.510280315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Calvín J. L., Garcia-Sanchez A., Bellot V., Muñoz-Torres M., Raya-Alvarez E., Salvatierra-Rios D. Mineral metabolism, osteoblastic function and bone mass in chronic alcoholism. Alcohol Alcohol. 1993 Sep;28(5):571–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guañabens N., Parés A., Mariñoso L., Brancós M. A., Piera C., Serrano S., Rivera F., Rodés J. Factors influencing the development of metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990 Oct;85(10):1356–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guañabens N., Parés A., Monegal A., Peris P., Pons F., Alvarez L., de Osaba M. J., Roca M., Torra M., Rodés J. Etidronate versus fluoride for treatment of osteopenia in primary biliary cirrhosis: preliminary results after 2 years. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jul;113(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris S. T., Watts N. B., Genant H. K., McKeever C. D., Hangartner T., Keller M., Chesnut C. H., 3rd, Brown J., Eriksen E. F., Hoseyni M. S. Effects of risedronate treatment on vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized controlled trial. Vertebral Efficacy With Risedronate Therapy (VERT) Study Group. JAMA. 1999 Oct 13;282(14):1344–1352. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.14.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlong H. F., Recker R. R., Maddrey W. C. Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: histologic features and response to 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 1):103–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorge-Hernandez J. A., Gonzalez-Reimers C. E., Torres-Ramirez A., Santolaria-Fernandez F., Gonzalez-Garcia C., Batista-Lopez J. N., Pestana-Pestana M., Hernandez-Nieto L. Bone changes in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. A histomorphometrical analysis of 52 cases. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Sep;33(9):1089–1095. doi: 10.1007/BF01535783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komulainen M. H., Kröger H., Tuppurainen M. T., Heikkinen A. M., Alhava E., Honkanen R., Saarikoski S. HRT and Vit D in prevention of non-vertebral fractures in postmenopausal women; a 5 year randomized trial. Maturitas. 1998 Nov 30;31(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5122(98)00085-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen K., Kärkkäinen M., Lalla M., Lamberg-Allardt C., Tunninen R., Tähtelä R., Välimäki M. Is alcohol an osteoporosis-inducing agent for young and middle-aged women? Metabolism. 1993 Jul;42(7):875–881. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90063-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalor B. C., France M. W., Powell D., Adams P. H., Counihan T. B. Bone and mineral metabolism and chronic alcohol abuse. Q J Med. 1986 May;59(229):497–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberman U. A., Weiss S. R., Bröll J., Minne H. W., Quan H., Bell N. H., Rodriguez-Portales J., Downs R. W., Jr, Dequeker J., Favus M. Effect of oral alendronate on bone mineral density and the incidence of fractures in postmenopausal osteoporosis. The Alendronate Phase III Osteoporosis Treatment Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 30;333(22):1437–1443. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511303332201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindor K. D., Janes C. H., Crippin J. S., Jorgensen R. A., Dickson E. R. Bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis: does ursodeoxycholic acid make a difference? Hepatology. 1995 Feb;21(2):389–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R., Hart D. M., Forrest C., Baird C. Prevention of spinal osteoporosis in oophorectomised women. Lancet. 1980 Nov 29;2(8205):1151–1154. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin E. G., Wahner H. W., O'Fallon W. M., Hodgson S. F., Kotowicz M. A., Lane A. W., Judd H. L., Caplan R. H., Riggs B. L. Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis with transdermal estrogen. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Jul 1;117(1):1–9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall D., Johnell O., Wedel H. Meta-analysis of how well measures of bone mineral density predict occurrence of osteoporotic fractures. BMJ. 1996 May 18;312(7041):1254–1259. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7041.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda S., Okano T., Osawa K., Shinjo M., Suematsu T., Kobayashi T. Concentrations of vitamin D-binding protein and vitamin D metabolites in plasma of patients with liver cirrhosis. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 1989 Aug;35(4):225–234. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.35.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matloff D. S., Kaplan M. M., Neer R. M., Goldberg M. J., Bitman W., Wolfe H. J. Osteoporosis in primary biliary cirrhosis: effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 treatment. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jul;83(1 Pt 1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison H. C., Malcolm A. J., Bassendine M. F., James O. F. Metabolic bone disease in primary biliary cirrhosis at presentation. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):463–470. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90438-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobarhan S. A., Russell R. M., Recker R. R., Posner D. B., Iber F. L., Miller P. Metabolic bone disease in alcoholic cirrhosis: a comparison of the effect of vitamin D2, 25-hydroxyvitamin D, or supportive treatment. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):266–273. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monegal A., Navasa M., Guañabens N., Peris P., Pons F., Martinez de Osaba M. J., Rimola A., Rodés J., Muñoz-Gómez J. Osteoporosis and bone mineral metabolism disorders in cirrhotic patients referred for orthotopic liver transplantation. Calcif Tissue Int. 1997 Feb;60(2):148–154. doi: 10.1007/s002239900205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachtigall L. E., Nachtigall R. H., Nachtigall R. D., Beckman E. M. Estrogen replacement therapy I: a 10-year prospective study in the relationship to osteoporosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Mar;53(3):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naessén T., Persson I., Adami H. O., Bergström R., Bergkvist L. Hormone replacement therapy and the risk for first hip fracture. A prospective, population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jul 15;113(2):95–103. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-2-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninkovic M., Skingle S. J., Bearcroft P. W., Bishop N., Alexander G. J., Compston J. E. Incidence of vertebral fractures in the first three months after orthotopic liver transplantation. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000 Aug;12(8):931–935. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200012080-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donohue J., Williams R. Hormone replacement therapy in women with liver disease. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997 Jan;104(1):1–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1997.tb10638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R., Mattsson L. A., Obrant K., Mellström D. Estrogen-progestogen therapy for low bone mineral density in primary biliary cirrhosis. Liver. 1999 Jun;19(3):188–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.1999.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peris P., Guañabens N., Monegal A., Suris X., Alvarez L., Martinez de Osaba M. J., Hernandez M. V., Muñoz-Gomez J. Aetiology and presenting symptoms in male osteoporosis. Br J Rheumatol. 1995 Oct;34(10):936–941. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/34.10.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid I. R., Wattie D. J., Evans M. C., Stapleton J. P. Testosterone therapy in glucocorticoid-treated men. Arch Intern Med. 1996 Jun 10;156(11):1173–1177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby P. L., Peacock M. The effect of transdermal oestrogen on bone, calcium-regulating hormones and liver in postmenopausal women. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1986 Nov;25(5):543–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1986.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi S., Masaki K., Habu D., Takeda T., Nishiguchi S., Kuroki T., Tanaka T., Ochi H. Calcitriol for bone disease in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999 Jun;14(6):547–552. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1746.1999.01913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinigaglia L., Fargion S., Fracanzani A. L., Binelli L., Battafarano N., Varenna M., Piperno A., Fiorelli G. Bone and joint involvement in genetic hemochromatosis: role of cirrhosis and iron overload. J Rheumatol. 1997 Sep;24(9):1809–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer H., Rubio N., Rubio E., Indreika M., Seitam A. Chronic alcoholism. Frequently overlooked cause of osteoporosis in men. Am J Med. 1986 Mar;80(3):393–397. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90712-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellon A. J., Davies A., Compston J., Williams R. Osteoporosis in chronic cholestatic liver disease. Q J Med. 1985 Nov;57(223):783–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Berkum F. N., Beukers R., Birkenhäger J. C., Kooij P. P., Schalm S. W., Pols H. A. Bone mass in women with primary biliary cirrhosis: the relation with histological stage and use of glucocorticoids. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1134–1139. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90635-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfhagen F. H., van Buuren H. R., den Ouden J. W., Hop W. C., van Leeuwen J. P., Schalm S. W., Pols H. A. Cyclical etidronate in the prevention of bone loss in corticosteroid-treated primary biliary cirrhosis. A prospective, controlled pilot study. J Hepatol. 1997 Feb;26(2):325–330. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(97)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


