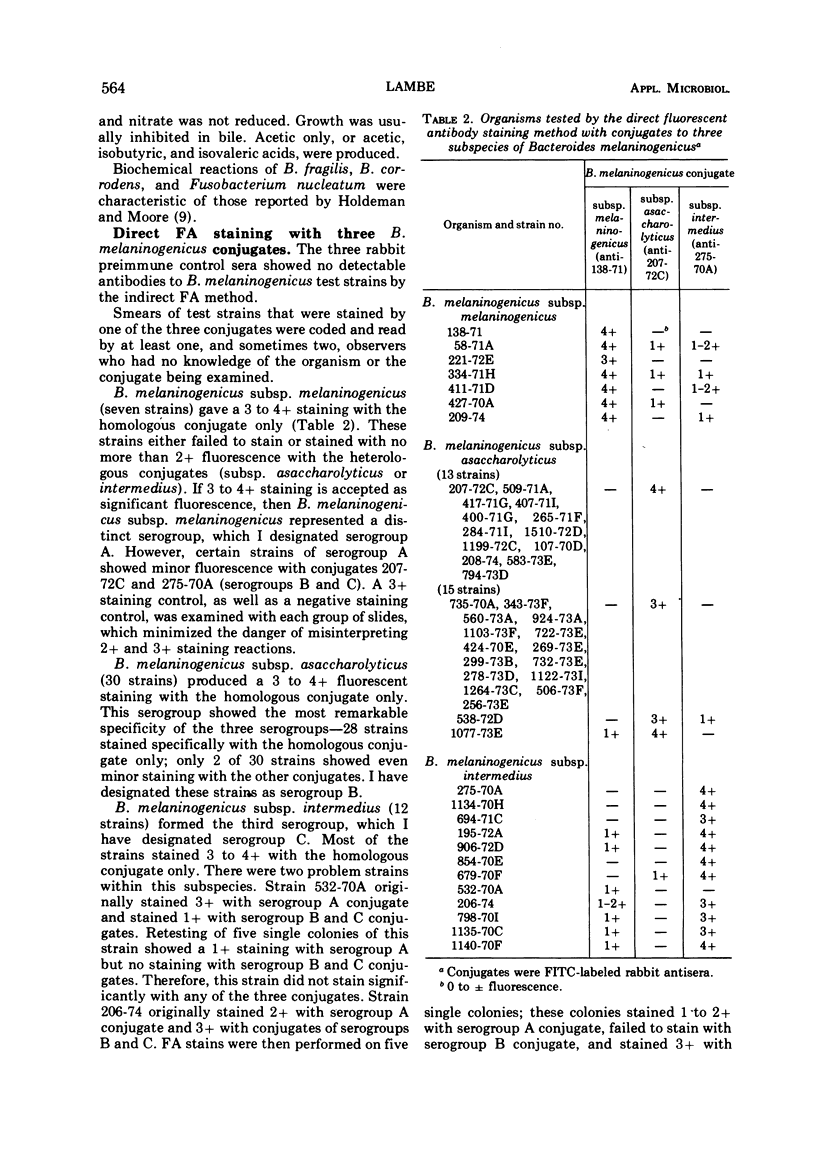
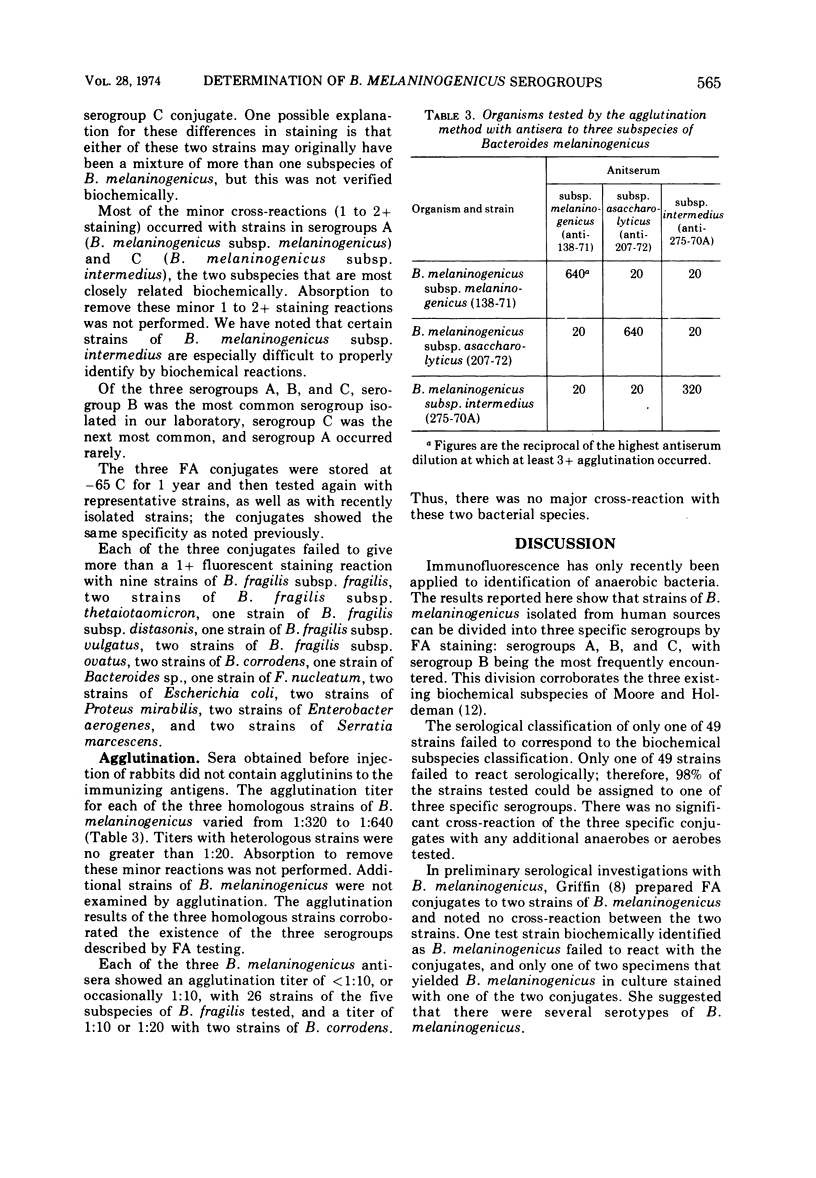
Abstract
Fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled antibody reagents (conjugates) were prepared to one strain of each of the three subspecies of Bacteroides melaninogenicus: B. melaninogenicus subsp. melaninogenicus, B. melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus, and B. melaninogenicus subsp. intermedius. These three conjugates were specific; thus, they provided a new serological classification of B. melaninogenicus. The three serogroups were designated A, B, and C. Most test strains (98%) isolated from human clinical specimens were assigned to a specific serogroup by immunofluorescence, and the serogroup of these test strains corroborated the biochemical characterization of the three subspecies of B. melaninogenicus. The conjugates failed to cross-react with other anaerobes or aerobes tested. This fluorescent antibody technique provided a more rapid classification of the three subspecies of B. melaninogenicus than did conventional biochemical methods.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A. THE BACTERIAL FLORA OF ACUTE PERFORATED APPENDICITIS WITH PERITONITIS: A BACTERIOLOGIC STUDY BASED UPON ONE HUNDRED CASES. Ann Surg. 1938 Apr;107(4):517–528. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193804000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courant P. R., Gibbons R. J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1605–1613. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felner J. M., Dowell V. R., Jr "Bacteroides" bacteremia. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., SOCRANSKY S. S., SAWYER S., KAPSIMALIS B., MACDONALD J. B. The microbiota of the gingival crevice area of man. II. The predominant cultivable organisms. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 May-Jun;8:281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin M. H. Fluorescent antibody techniques in the identification of the gram-negative nonsporeforming anaerobes. Health Lab Sci. 1970 Apr;7(2):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerèbel B., Sedallian A. Action de Bacteroides melaninogenicus sur la dentine in vitro. SSO Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnheilkd. 1972 Jul;82(7):731–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobles E. R., Jr Bacteroides infections. Ann Surg. 1973 May;177(5):601–606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosan B. Antigens of Streptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):205–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.205-211.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER S. J., MACDONALD J. B., GIBBONS R. J. Biochemical characteristics of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. A study of thirty-one strains. Arch Oral Biol. 1962 Nov-Dec;7:685–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(62)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S. S., GIBBONS R. J., DALE A. C., BORTNICK L., ROSENTHAL E., MACDONALD J. B. The microbiota of the gingival crevice area of man. I. Total microscopic and viable counts and counts of specific organisms. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 May-Jun;8:275–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbaj J., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Anaerobic pyogenic liver abscess. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Oct;77(4):627–638. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-4-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Sebald M. Etude sérologique d'anaérobies gram-Bégatifs aspourlés, et particulièrement de Bacteroides convexus et Bacteriodes melaninogenicu. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Sep;115(3):350–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


