Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (187.0 KB).
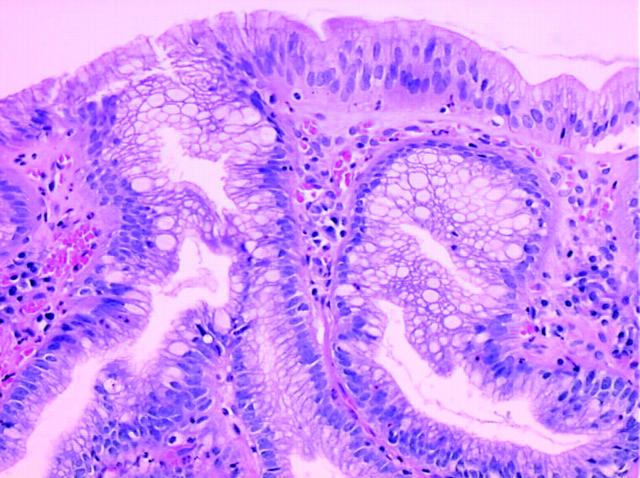
Figure 1.
Barrett's mucosa with incomplete intestinal metaplasia (specialised mucosa). The epithelium is composed of goblet cells interspersed between intermediate mucous cells, both in the surface and glandular epithelium (haematoxylin–eosin, original magnification x400).
Figure 2.
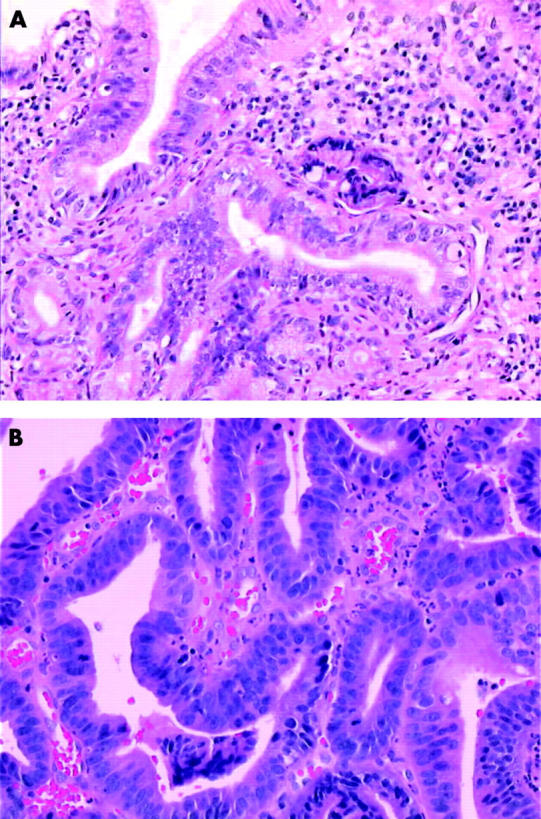
Dysplasia in Barrett's mucosa, with both architectural and cytological abnormalities of low grade (A) and high grade (B) (haematoxylin–eosin, original magnification x400).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alikhan M., Rex D., Khan A., Rahmani E., Cummings O., Ulbright T. M. Variable pathologic interpretation of columnar lined esophagus by general pathologists in community practice. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999 Jul;50(1):23–26. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beilstein Michelle, Silberg Debra. Cellular and molecular mechanisms responsible for progression of Barrett's metaplasia to esophageal carcinoma. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2002 Jun;31(2):461-79, ix. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(02)00013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttar N. S., Wang K. K., Sebo T. J., Riehle D. M., Krishnadath K. K., Lutzke L. S., Anderson M. A., Petterson T. M., Burgart L. J. Extent of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus correlates with risk of adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jun;120(7):1630–1639. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.25111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron A. J., Carpenter H. A. Barrett's esophagus, high-grade dysplasia, and early adenocarcinoma: a pathological study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Apr;92(4):586–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain Denis, Fléjou Jean-François. High-grade dysplasia and superficial adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: histological mapping and expression of p53, p21 and Bcl-2 oncoproteins. Virchows Arch. 2002 Sep 24;442(1):18–24. doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Y., Wang H. H., Antonioli D. A., Spechler S. J., Zeroogian J. M., Goyal R., Shahsafaei A., Odze R. D. Significance of acid-mucin-positive nongoblet columnar cells in the distal esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Hum Pathol. 1999 Dec;30(12):1488–1495. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinyama C. N., Marshall R. E., Owen W. J., Mason R. C., Kothari D., Wilkinson M. L., Sanderson J. D. Expression of MUC1 and MUC2 mucin gene products in Barrett's metaplasia, dysplasia and adenocarcinoma: an immunopathological study with clinical correlation. Histopathology. 1999 Dec;35(6):517–524. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.1999.00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvelard A., Cauvin J. M., Goldfain D., Rotenberg A., Robaszkiewicz M., Fléjou J. F., Groupe d'Etude l'Oesophage de Barrett Cytokeratin immunoreactivity of intestinal metaplasia at normal oesophagogastric junction indicates its aetiology. Gut. 2001 Dec;49(6):761–766. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.6.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dar M. S., Goldblum J. R., Rice T. W., Falk G. W. Can extent of high grade dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus predict the presence of adenocarcinoma at oesophagectomy? Gut. 2003 Apr;52(4):486–489. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester Steven R., Wickramasinghe Kumari S., Lord Reginald V. N., Friedman Adam, Balaji Nagammapudur S., Chandrasoma Parakrama T., Hagen Jeffrey A., Peters Jeffrey H., DeMeester Tom R. Cytokeratin and DAS-1 immunostaining reveal similarities among cardiac mucosa, CIM, and Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002 Oct;97(10):2514–2523. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.06033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Zimaity H. M., Graham D. Y. Cytokeratin subsets for distinguishing Barrett's esophagus from intestinal metaplasia in the cardia using endoscopic biopsy specimens. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 May;96(5):1378–1382. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk G. W., Rice T. W., Goldblum J. R., Richter J. E. Jumbo biopsy forceps protocol still misses unsuspected cancer in Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999 Feb;49(2):170–176. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70482-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller G., Borchard F., Ell C., Seitz G., Stolte M., Walch A., Rüschoff J., Working Group for Gastroenterological Pathology of the German Society for Pathology Histopathological diagnosis of Barrett's mucosa and associated neoplasias: results of a consensus conference of the Working Group for Gastroenterological Pathology of the German Society for Pathology on 22 September 2001 in Erlangen. Virchows Arch. 2003 Sep 24;443(5):597–601. doi: 10.1007/s00428-003-0894-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennerty M. B., Sampliner R. E., Way D., Riddell R., Steinbronn K., Garewal H. S. Discordance between flow cytometric abnormalities and dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1989 Oct;97(4):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. C., Omary M. B., Triadafilopoulos G. Dynamic effects of acid on Barrett's esophagus. An ex vivo proliferation and differentiation model. J Clin Invest. 1996 Nov 1;98(9):2120–2128. doi: 10.1172/JCI119018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geboes K., Van Eyken P. The diagnosis of dysplasia and malignancy in Barrett's oesophagus. Histopathology. 2000 Aug;37(2):99–107. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2000.00960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Huberman R. M., Graham D. Y. The gastric cardia in Helicobacter pylori infection. Hum Pathol. 1994 Sep;25(9):915–919. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman J. N., Wang H., Das K. M., Goyal R. K., Spechler S. J., Antonioli D., Odze R. D. Phenotype of Barrett's esophagus and intestinal metaplasia of the distal esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: an immunohistochemical study of cytokeratins 7 and 20, Das-1 and 45 MI. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001 Jan;25(1):87–94. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200101000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum John R., Lauwers Gregory Y. Dysplasia arising in barrett's esophagus: diagnostic pitfalls and natural history. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2002 Feb;19(1):12–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillem P., Billeret V., Buisine M. P., Flejou J. F., Lecomte-Houcke M., Degand P., Aubert J. P., Triboulet J. P., Porchet N. Mucin gene expression and cell differentiation in human normal, premalignant and malignant esophagus. Int J Cancer. 2000 Dec 15;88(6):856–861. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20001215)88:6<856::aid-ijc3>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggitt R. C. Adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus: a new epidemic? Hum Pathol. 1992 May;23(5):475–476. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90121-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R. A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000 Jan 7;100(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassall E. Columnar-lined esophagus in children. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1997 Sep;26(3):533–548. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitmiller R. F., Redmond M., Hamilton S. R. Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. An indication for prophylactic esophagectomy. Ann Surg. 1996 Jul;224(1):66–71. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199607000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong M. K., Laskin W. B., Herman B. E., Johnston M. H., Vargo J. J., Steinberg S. M., Allegra C. J., Johnston P. G. Expansion of the Ki-67 proliferative compartment correlates with degree of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Cancer. 1995 Jan 15;75(2):423–429. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950115)75:2<423::aid-cncr2820750202>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski J. A., Wright N. A., Meltzer S. J., Triadafilopoulos G., Geboes K., Casson A. G., Kerr D., Young L. S. Molecular evolution of the metaplasia-dysplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence in the esophagus. Am J Pathol. 1999 Apr;154(4):965–973. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65346-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R., Clarke M. R., Melhem M. F., Young M. A., Vanbibber M. M., Safatle-Ribeiro A. V., Ribeiro U., Jr, Reynolds J. C. Expression of p53, PCNA, and C-erbB-2 in Barrett's metaplasia and adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Dec;42(12):2453–2462. doi: 10.1023/a:1018891923998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. S., Haggitt R. C., Blount P. L., Rabinovitch P. S., Rusch V. W., Reid B. J. An endoscopic biopsy protocol can differentiate high-grade dysplasia from early adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1993 Jul;105(1):40–50. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90008-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed I. A., Streutker C. J., Riddell R. H. Utilization of cytokeratins 7 and 20 does not differentiate between Barrett's esophagus and gastric cardiac intestinal metaplasia. Mod Pathol. 2002 Jun;15(6):611–616. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E., Bronner M. P., Goldblum J. R., Greenson J. K., Haber M. M., Hart J., Lamps L. W., Lauwers G. Y., Lazenby A. J., Lewin D. N. Reproducibility of the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett esophagus: a reaffirmation. Hum Pathol. 2001 Apr;32(4):368–378. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2001.23510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery E., Goldblum J. R., Greenson J. K., Haber M. M., Lamps L. W., Lauwers G. Y., Lazenby A. J., Lewin D. N., Robert M. E., Washington K. Dysplasia as a predictive marker for invasive carcinoma in Barrett esophagus: a follow-up study based on 138 cases from a diagnostic variability study. Hum Pathol. 2001 Apr;32(4):379–388. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2001.23511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales Carmela P., Souza Rhonda F., Spechler Stuart J. Hallmarks of cancer progression in Barrett's oesophagus. Lancet. 2002 Nov 16;360(9345):1587–1589. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11569-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg S., DeMeester T. R., Peters J. H., Hagen J. A., Nigro J. J., DeMeester S. R., Theisen J., Campos G. M., Crookes P. F. The extent of Barrett's esophagus depends on the status of the lower esophageal sphincter and the degree of esophageal acid exposure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999 Mar;117(3):572–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5223(99)70337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsby A. H., Goldblum J. R., Rice T. W., Richter J. E., Falk G. W., Vaezi M. F., Gramlich T. L. Cytokeratin subsets can reliably distinguish Barrett's esophagus from intestinal metaplasia of the stomach. Hum Pathol. 1999 Mar;30(3):288–294. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsby A. H., Petras R. E., Henricks W. H., Rice T. W., Rybicki L. A., Richter J. E., Goldblum J. R. Observer variation in the diagnosis of superficial oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut. 2002 Nov;51(5):671–676. doi: 10.1136/gut.51.5.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsby A. H., Vaezi M. F., Richter J. E., Goldblum J. R., Rice T. W., Falk G. W., Gramlich T. L. Cytokeratin immunoreactivity patterns in the diagnosis of short-segment Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2000 Sep;119(3):683–690. doi: 10.1053/gast.2000.16482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull A., Trier J. S., Dalton M. D., Camp R. C., Loeb P., Goyal R. K. The histologic spectrum of Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 26;295(9):476–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608262950904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters F. T., Ganesh S., Kuipers E. J., Sluiter W. J., Karrenbeld A., de Jager-Krikken A., Klinkenberg-Knol E. C., Lamers C. B., Kleibeuker J. H. Effect of elimination of acid reflux on epithelial cell proliferative activity of Barrett esophagus. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2000 Dec;35(12):1238–1244. doi: 10.1080/003655200453557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peuchmaur M., Potet F., Goldfain D. Mucin histochemistry of the columnar epithelium of the oesophagus (Barrett's oesophagus): a prospective biopsy study. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):607–610. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Blount P. L., Rubin C. E., Levine D. S., Haggitt R. C., Rabinovitch P. S. Flow-cytometric and histological progression to malignancy in Barrett's esophagus: prospective endoscopic surveillance of a cohort. Gastroenterology. 1992 Apr;102(4 Pt 1):1212–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Rubin C. E., Roth G., Surawicz C. M., Van Belle G., Lewin K., Weinstein W. M., Antonioli D. A., Goldman H. Observer variation in the diagnosis of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Hum Pathol. 1988 Feb;19(2):166–178. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80344-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid B. J., Levine D. S., Longton G., Blount P. L., Rabinovitch P. S. Predictors of progression to cancer in Barrett's esophagus: baseline histology and flow cytometry identify low- and high-risk patient subsets. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Jul;95(7):1669–1676. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell R. H., Goldman H., Ransohoff D. F., Appelman H. D., Fenoglio C. M., Haggitt R. C., Ahren C., Correa P., Hamilton S. R., Morson B. C. Dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: standardized classification with provisional clinical applications. Hum Pathol. 1983 Nov;14(11):931–968. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothery G. A., Patterson J. E., Stoddard C. J., Day D. W. Histological and histochemical changes in the columnar lined (Barrett's) oesophagus. Gut. 1986 Sep;27(9):1062–1068. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.9.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K. Biomarkers for malignancy in the columnar-lined esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1997 Sep;26(3):599–606. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampliner R. E. Practice guidelines on the diagnosis, surveillance, and therapy of Barrett's esophagus. The Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jul;93(7):1028–1032. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlemper R. J., Riddell R. H., Kato Y., Borchard F., Cooper H. S., Dawsey S. M., Dixon M. F., Fenoglio-Preiser C. M., Fléjou J. F., Geboes K. The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia. Gut. 2000 Aug;47(2):251–255. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. G., Riddell R. H., Walther B., Skinner D. B., Riemann J. F. Dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1985;110(2):145–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00402729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell T. G., Sontag S. J., Chejfec G., Aranha G., Metz A., O'Connell S., Seidel U. J., Sonnenberg A. Long-term nonsurgical management of Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jun;120(7):1607–1619. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.25065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selaru F. M., Zou T., Xu Y., Shustova V., Yin J., Mori Y., Sato F., Wang S., Olaru A., Shibata D. Global gene expression profiling in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer: a comparative analysis using cDNA microarrays. Oncogene. 2002 Jan 17;21(3):475–478. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma P., Morales T. G., Sampliner R. E. Short segment Barrett's esophagus--the need for standardization of the definition and of endoscopic criteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jul;93(7):1033–1036. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skacel M., Petras R. E., Gramlich T. L., Sigel J. E., Richter J. E., Goldblum J. R. The diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus and its implications for disease progression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Dec;95(12):3383–3387. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K. The columnar-lined esophagus, intestinal metaplasia, and Norman Barrett. Gastroenterology. 1996 Feb;110(2):614–621. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.agast960614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teodori L., Göhde W., Persiani M., Ferrario F., Tirindelli Danesi D., Scarpignato C., Di Tondo U., Alò P., Capurso L. DNA/protein flow cytometry as a predictive marker of malignancy in dysplasia-free Barrett's esophagus: thirteen-year follow-up study on a cohort of patients. Cytometry. 1998 Dec 15;34(6):257–263. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0320(19981215)34:6<257::aid-cyto3>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurberg B. L., Duray P. H., Odze R. D. Polypoid dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular study of five cases. Hum Pathol. 1999 Jul;30(7):745–752. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Mueller J., Walch A., Höfler H. The molecular pathology of Barrett's esophagus. Histol Histopathol. 1999 Apr;14(2):553–559. doi: 10.14670/HH-14.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Banerjee S. K., Sharma P., Tran T. M., Richards R., Cherian R. p53 protein overexpression in low grade dysplasia (LGD) in Barrett's esophagus: immunohistochemical marker predictive of progression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 May;96(5):1355–1362. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03851.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Sharma P., Topalovski M., Richards R., Cherian R., Dixon A. Long-term follow-up of Barrett's high-grade dysplasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Aug;95(8):1888–1893. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnhoven B. P., Tilanus H. W., Dinjens W. N. Molecular biology of Barrett's adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. 2001 Mar;233(3):322–337. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200103000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younes M., Ertan A., Lechago L. V., Somoano J. R., Lechago J. p53 Protein accumulation is a specific marker of malignant potential in Barrett's metaplasia. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Apr;42(4):697–701. doi: 10.1023/a:1018828207371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwas F., Shields H. M., Doos W. G., Antonioli D. A., Goldman H., Ransil B. J., Spechler S. J. Scanning electron microscopy of Barrett's epithelium and its correlation with light microscopy and mucin stains. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jun;90(6):1932–1941. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]