Abstract
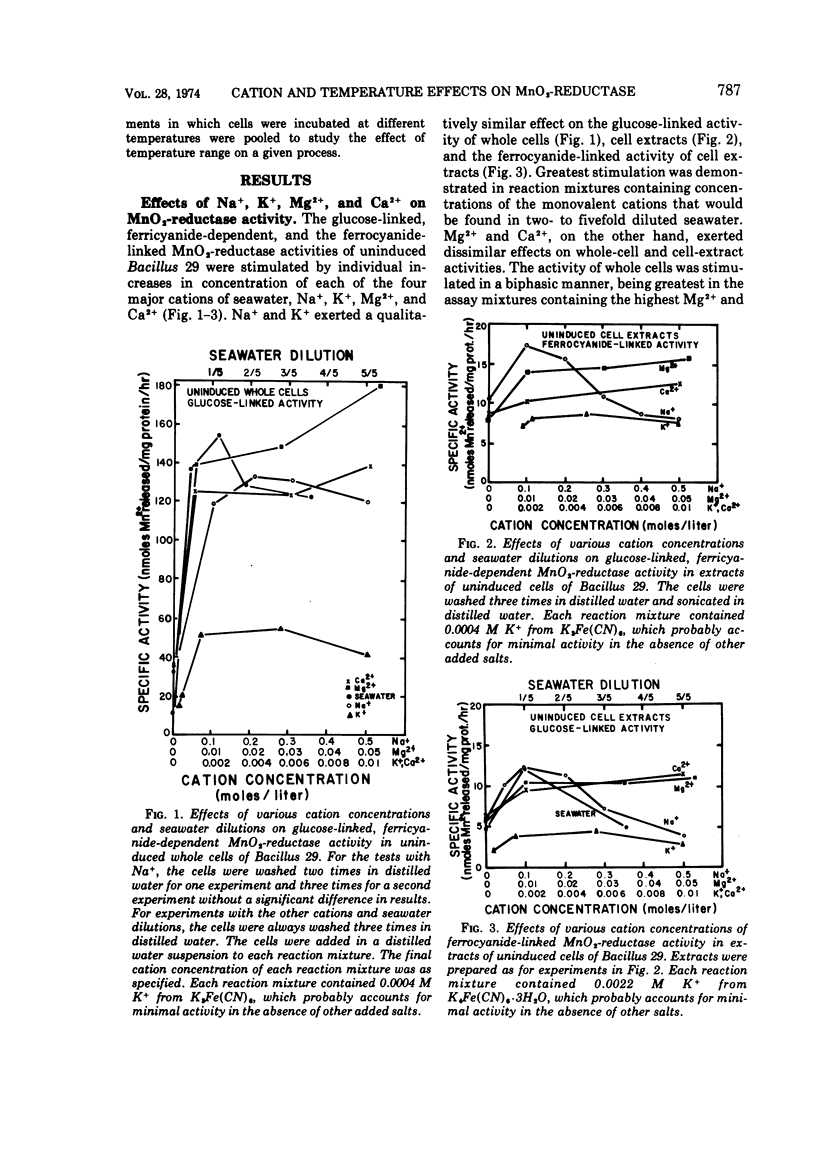
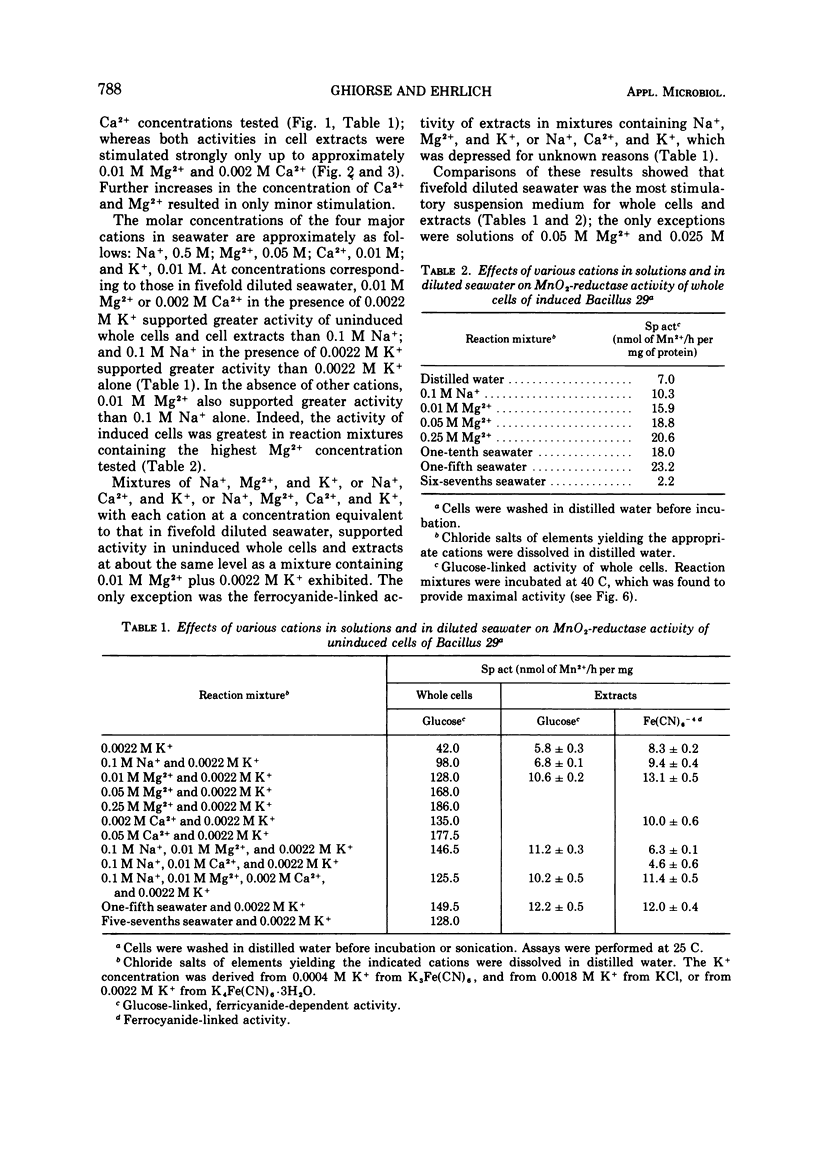
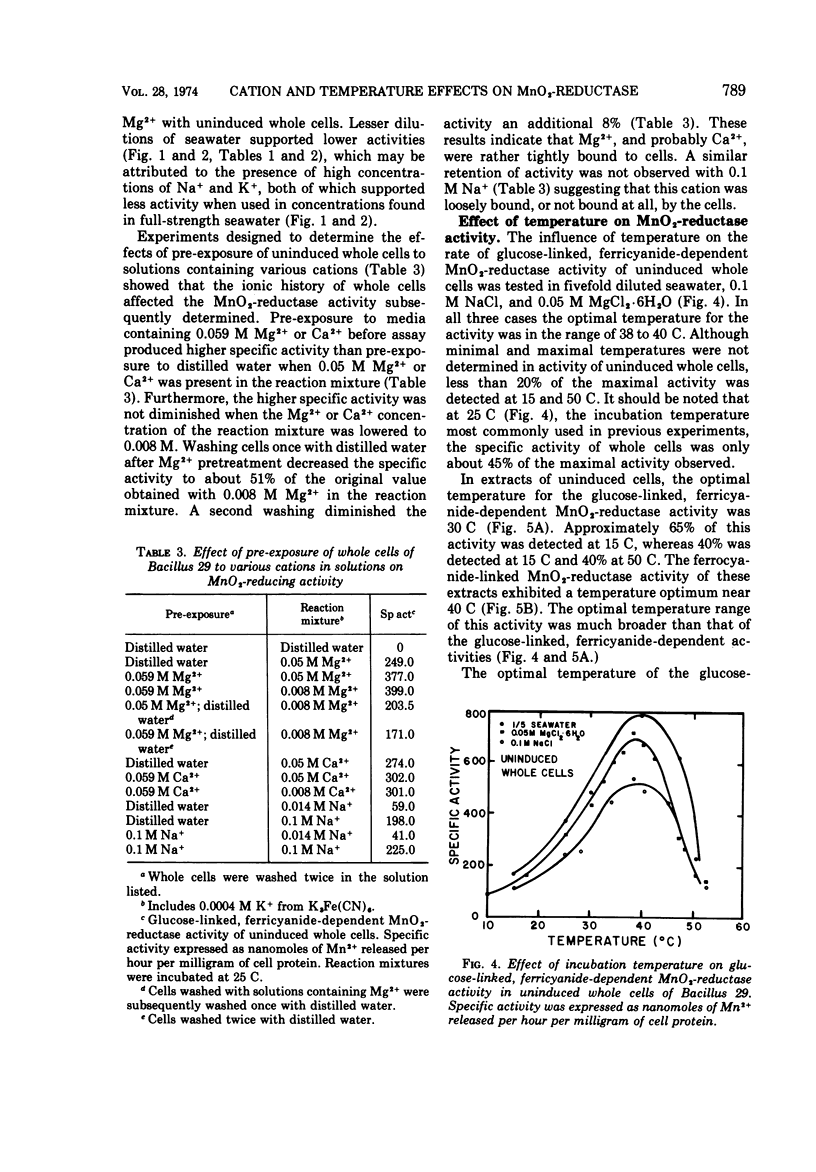
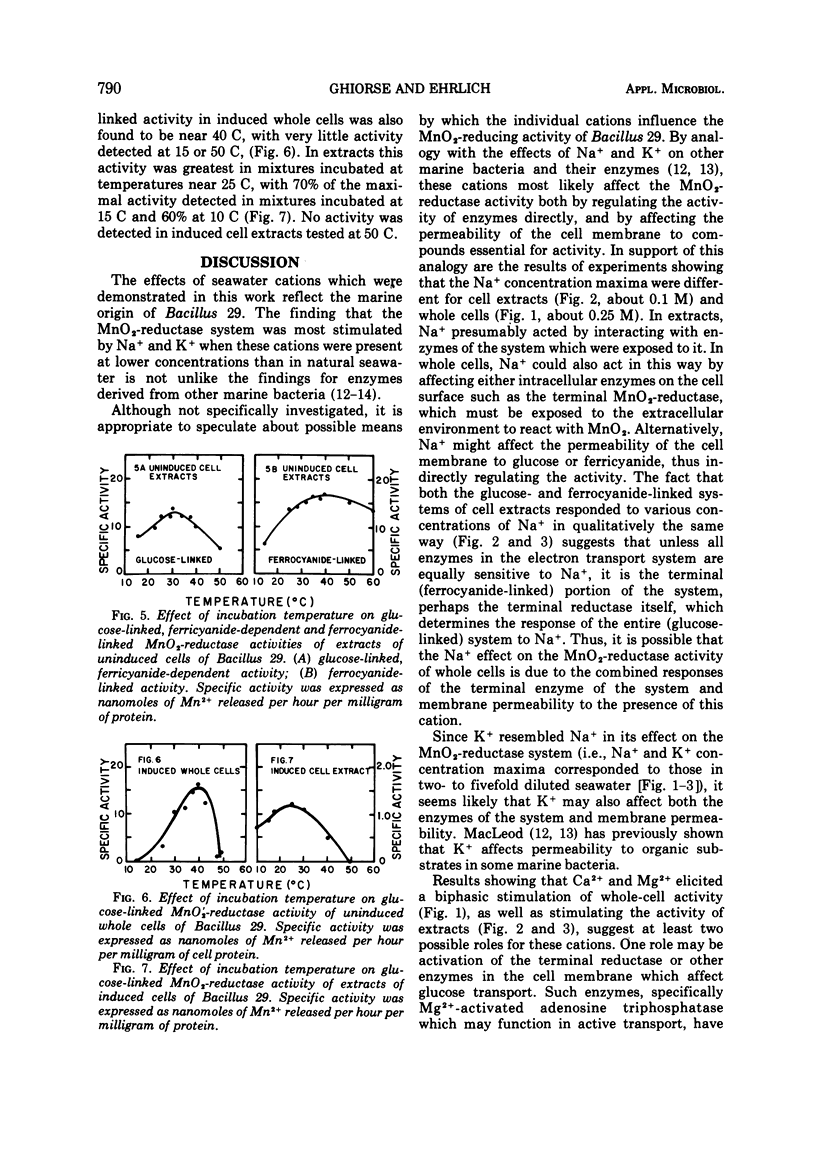
The seawater cations, Na+, K+, Mg2+, and Ca2+, each stimulated MnO2-reductase activity of whole cells and cell extracts of Bacillus 29. Concentrations of Na+ and K+ which stimulated whole cells and cell extracts maximally were equivalent to those in two- to fivefold diluted seawater. Cell-extract activity was strongly stimulated by Ca2+ and Mg2+ up to a concentration of 0.01 M Mg2+ and 0.002 M Ca2+, with little additional stimulation above these concentrations. Whole-cell activity was stimulated biphasically with increasing concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+. Comparison of the effects of individual cations or mixtures of them at concentrations equivalent to their concentration in fivefold diluted seawater showed that more activity was obtained with 0.01 M Mg2+ or 0.002 M Ca2+ than with 0.1 M Na+, and more with 0.1 M Na+ than with 0.0022 M K+. Fivefold diluted seawater permitted as much or more activity as solutions of individual or synthetic mixtures of the cations. Pre-exposure experiments showed that the ionic history of whole cells was important to their ultimate activity. The MnO2-reductase activity of induced whole cells exhibited a temperature optimum near 40 C. Cell extracts had different temperature optima (Topt), depending on whether induced glucose-linked activity (Topt = 25 C), uninduced glucose-linked, ferricyanide-dependent activity (Topt = 30 C), or uninduced ferrocyanide-linked activity (Topt = 40 C) were being measured. Some of these optima are higher than previously reported.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cutinelli C., Galdiero F. Ion-binding properties of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):2022–2023. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.2022-2023.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of Manganese Nodules: I. Bacterial Action on Manganese in Nodule Enrichments. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jan;11(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/am.11.1.15-19.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules. II. Manganese oxidation by cell-free extract from a manganese nodule bacterium. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Feb;16(2):197–202. doi: 10.1128/am.16.2.197-202.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules. V. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on bacterial oxidation of MnII and reduction of MnO2. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Feb;21(2):306–310. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L., Yang S. H., Mainwaring J. D., Jr Bacteriology of manganese nodules. VI. Fate of copper, nickel, cobalt, and iron during bacterial and chemical reduction of the manganese (IV). Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Lembo M., Tufano M. A. Affinity of various cations for Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall. Experientia. 1968 Jan 15;24(1):34–36. doi: 10.1007/BF02136776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., HORI A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. VIII. Tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in a marine bacterium and their response to inorganic salts. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:464–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.464-471.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules. IV. Induction of an MnO2-reductase system in a marine bacillus. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):966–972. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.966-972.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules: III. Reduction of MnO(2) by two strains of nodule bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 May;16(5):695–702. doi: 10.1128/am.16.5.695-702.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


