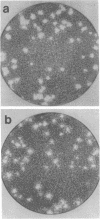
Abstract
A microculture plaque neutralization test is described for California-group arboviruses that is as precise and quantitative as the standard test conducted in 60-mm petri dishes. It was shown that there was no significant between-panel or between-day variation in determinations and that a single pipette could be used for all serum-dilution levels within a titration without inoculum carry-over effect. The experimental protocol and statistical methods used produce 50% neutralization end points that meet the assumptions of parametric statistics. This permits the power and versatility of the analysis of variance to be exploited in testing for treatment effects in serological and immunological studies with viruses.
Full text
PDF

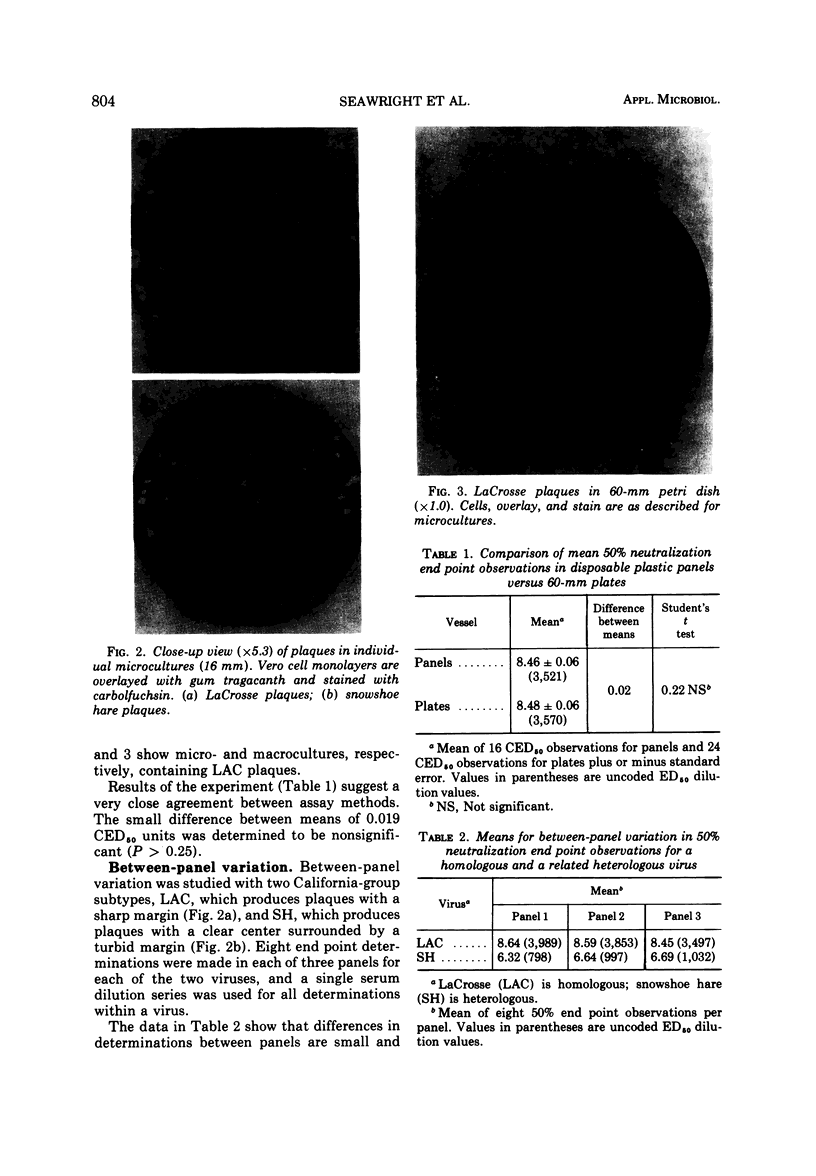

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGDORFER W., NEWHOUSE V. F., THOMAS L. A. Isolation of California encephalitis virus from the blood of a snowshoe hare (Lepus americanus) in western Montana. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:344–349. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Striker R. L., Jr, Benyesh-Melnick M. Microculture plaque assay for human and simian cytomegaloviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):780–783. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.780-783.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley E., Peralta P. H., Johnson K. M. A plaque neutralization method for arboviruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):741–747. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORNEZ R. J. [On statistics of the plaque test]. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1962;12:108–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirchamsy H., Rapp F. A new overlay for plaquing animal viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):13–17. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEHAG S. E., MANDEL B. THE FORMATION AND PROPERTIES OF POLIOVIRUS-NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODY. I. 19S AND 7S ANTIBODY FORMATION: DIFFERENCES IN KINETICS AND ANTIGEN DOSE REQUIREMENT FOR INDUCTION. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:1–19. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON W. H., KALFAYAN B., ANSLOW R. O. ISOLATION OF CALIFORNIA ENCEPHALITIS GROUP VIRUS FROM A FATAL HUMAN ILLNESS. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Mar;81:245–253. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. The neutralization of arboviruses. I. Neutralization homologous virus-serum mixtures with two group B arboviruses. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90313-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway E. G. The neutralization of arboviruses. II. Neutralization in heterologous virus-serum mixtures with four group B arboviruses. Virology. 1965 Aug;26(4):528–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]