Abstract
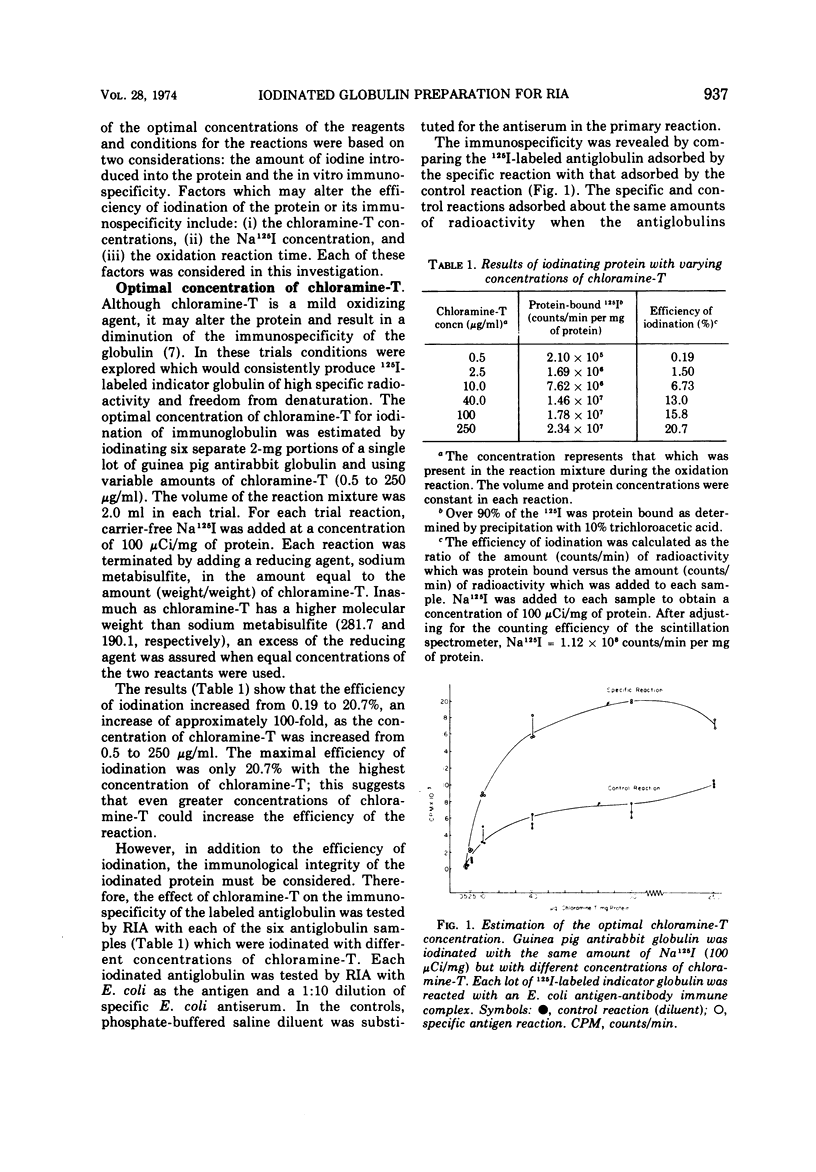
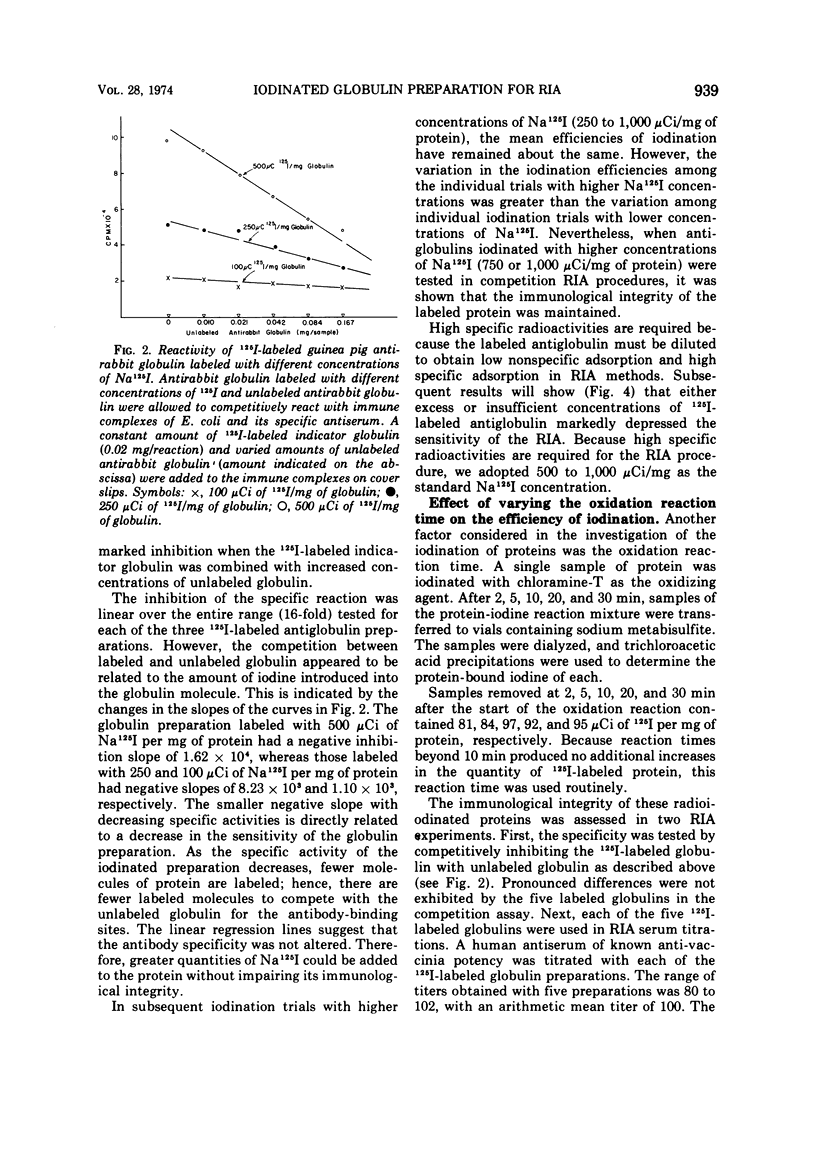
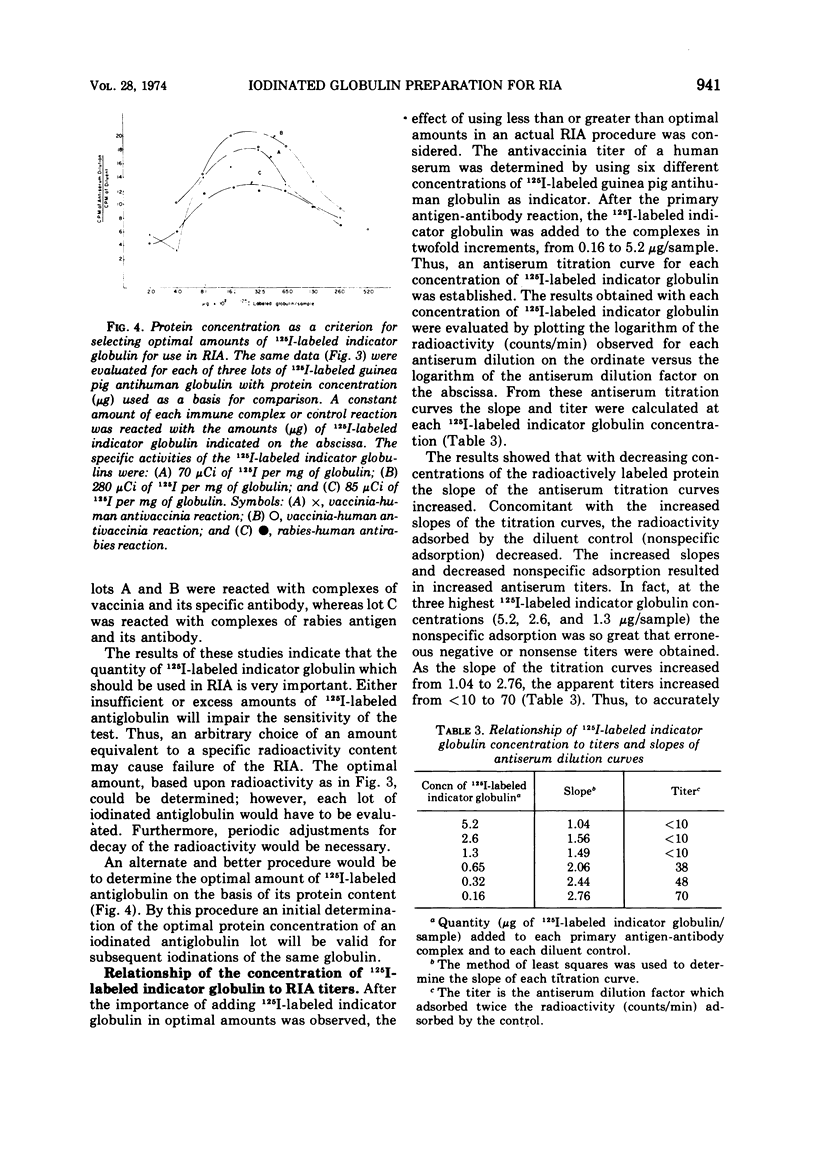
Procedures were examined for labeling immune globulins with radioactive iodine using chloramine-T as the oxidizing agent. The chloramine-T method was critically evaluated to establish the optimal conditions for preparing iodinated globulins with high specific radioactivities without impairing their immunospecificities for use in in vitro radioimmunoassays. The results showed that the use of 100 μg of chloramine-T per ml, 500 to 1,000 μCi of Na 125I per mg of protein, and a 10-min oxidation reaction time produced globulins of both high specific radioactivities and immunospecificities. Criteria were established for evaluating and determining optimal concentrations of iodine-labeled globulin for use in radioimmunoassays. The results of this investigation indicated that the amount of labeled indicator globulin used in radioimmunoassays should be based upon protein concentration rather than radioactivity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bombardieri S., Christian C. L. A technique for immunoassay of human IgG. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Apr;133(4):1366–1369. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K., Tregear G. W. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay in antibody-coated tubes. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S. Quality of radioiodine. Science. 1974 Jun 28;184(4144):1381–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4144.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S. Solid state lactoperoxidase: a highly stable enzyme for simple, gentle iodination of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber J., Wright G. G. Iodine-131 labeling of purified microbial antigens by microdiffusion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):282–284. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Simplified radioimmunoassay for diagnostic serology. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.742-749.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSA U., SCASSELLATI G. A., PENNISI F. LABELLING OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN WITH 131-I BY ELECTROLYTIC IODINATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 8;86:519–526. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal J. D., Hayashi K., Notkins A. L. Rapid micro-radioimmunoassay for the measurement of antiviral antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):171–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


