Abstract
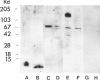
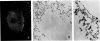
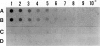
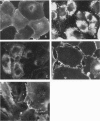
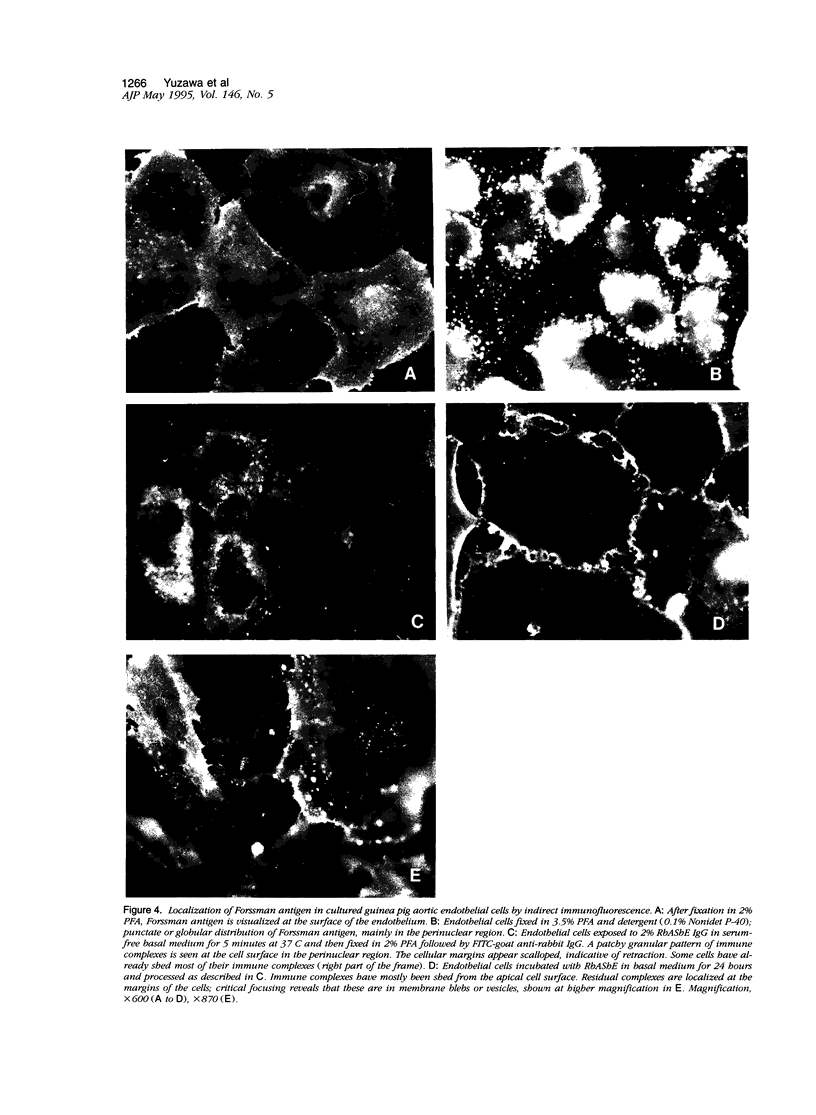
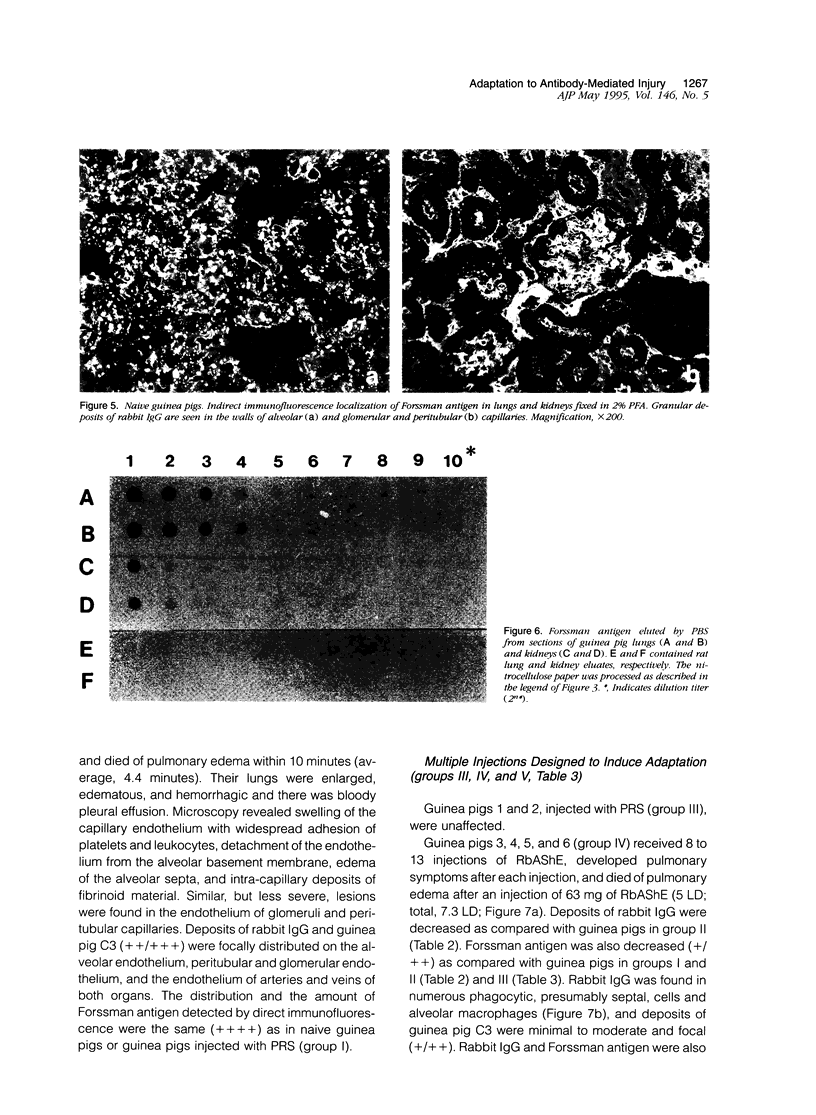
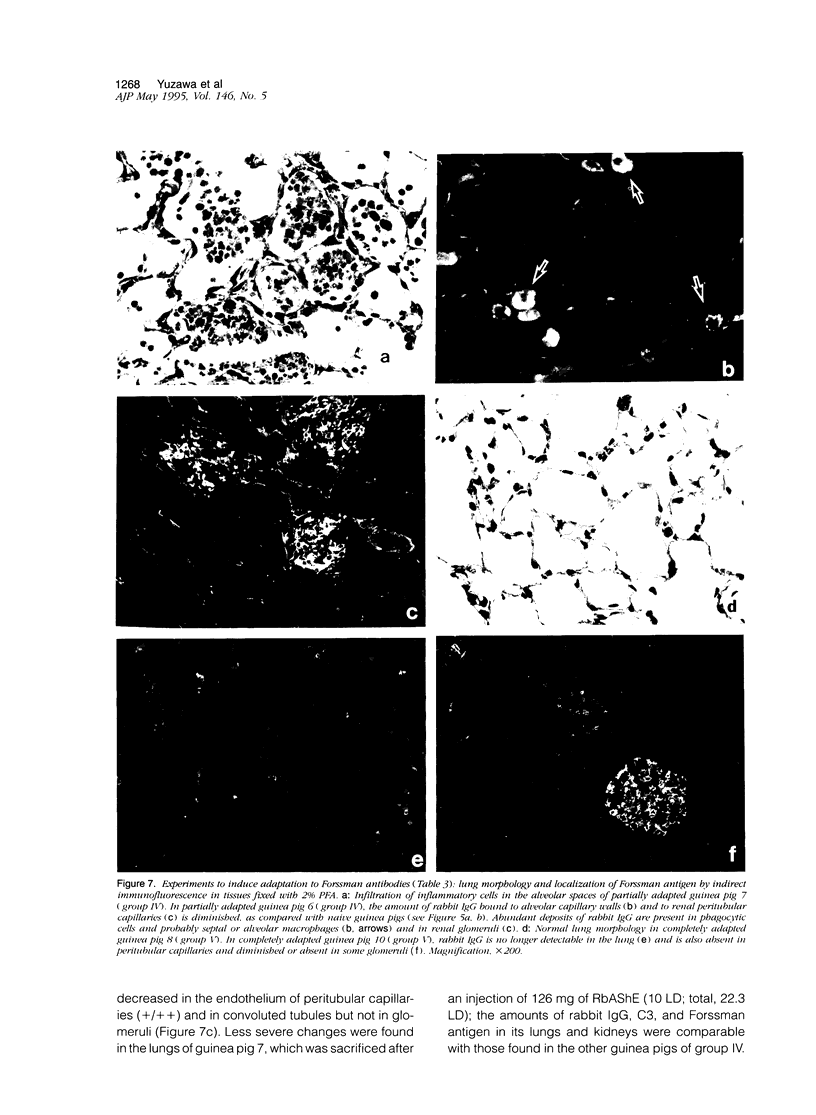
Forssman antigen is a glycosphingolipid with antigenic specificity determined by extra-membrane haptenic sugars similar to blood group antigens and antigens that are the main barrier to xenogeneic organ transplantation. Herein, we describe the localization of Forssman antigen in guinea pig lungs and kidneys and the consequences of its interaction with antibodies in vitro and in vivo (Forssman reaction). Exposure of cultured guinea pig aortic endothelial cells to Forssman antibodies induced rapid redistribution of antigen-antibody complexes at the cell surface, followed by shedding that occurred by blebbing of plasma membrane as vesicles or fragments, and was associated with disappearance of antigen from the cell surface (antigenic modulation). Guinea pigs surviving frequent intravenous infections of increasing amounts of antibodies, for a total of 20 to 40 lethal doses, developed a partial or complete adaptation to generalized Forssman reaction, and adaptation was associated with partial or complete modulation of Forssman antigen at the surface of the pulmonary and, in minor degree, renal endothelial and epithelial cells. These findings support the hypothesis that modulation of endothelial carbohydrate antigens contributes to adaptation of highly vascularized organs exposed to tolerable levels of allo- or xenoantibodies.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G., Brentjens J. R., Caldwell P. R., Camussi G., Matsuo S. Formation of immune deposits and disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):510–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auchincloss H., Jr Xenogeneic transplantation. A review. Transplantation. 1988 Jul;46(1):1–20. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198807000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannett A. D., McAlack R. F., Raja R., Baquero A., Morris M. Experiences with known ABO-mismatched renal transplants. Transplant Proc. 1987 Dec;19(6):4543–4546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barba L. M., Caldwell P. R., Downie G. H., Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. I. In the rabbit a repeated interaction of heterologous anti-angiotensin-converting enzyme antibodies with alveolar endothelium results in resistance to immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2141–2158. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta M., Kirshbom P., Frank M. M., Fries L. F. Mechanism of therapeutic effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Attenuation of acute, complement-dependent immune damage in a guinea pig model. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1974–1981. doi: 10.1172/JCI114387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Biesecker G., Caldwell P. R., Biancone L., Andres G., Brentjens J. R. Role of the membrane attack complex of complement in lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1993;102(3):216–223. doi: 10.1159/000236529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Noble B., Kerjaschki D., Malavasi F., Roholt O. A., Farquhar M. G., Andres G. Antibody-induced redistribution of Heymann antigen on the surface of cultured glomerular visceral epithelial cells: possible role in the pathogenesis of Heymann glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2409–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Caldwell P. R., Andres G., Brentjens J. R. Lung injury mediated by antibodies to endothelium. II. Study of the effect of repeated antigen-antibody interactions in rabbits tolerant to heterologous antibody. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):216–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Kerjaschki D., Gonda M., Nevins T., Rielle J. C., Brentjens J., Andres G. Expression and modulation of surface antigens in cultured rat glomerular visceral epithelial cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Nov;37(11):1675–1687. doi: 10.1177/37.11.2809176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Pawlowski I., Bussolino F., Caldwell P. R., Brentjens J., Andres G. Release of platelet activating factor in rabbits with antibody-mediated injury of the lung: the role of leukocytes and of pulmonary endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1802–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. K., Good A. H., Koren E., Oriol R., Malcolm A. J., Ippolito R. M., Neethling F. A., Ye Y., Romano E., Zuhdi N. Identification of alpha-galactosyl and other carbohydrate epitopes that are bound by human anti-pig antibodies: relevance to discordant xenografting in man. Transpl Immunol. 1993;1(3):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0966-3274(93)90047-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. K., Ye Y., Niekrasz M., Kehoe M., Martin M., Neethling F. A., Kosanke S., DeBault L. E., Worsley G., Zuhdi N. Specific intravenous carbohydrate therapy. A new concept in inhibiting antibody-mediated rejection--experience with ABO-incompatible cardiac allografting in the baboon. Transplantation. 1993 Oct;56(4):769–777. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199310000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Clark M. R., Shohet S. B., Buehler J., Macher B. A. Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-Gal antibody and the Gal alpha 1----3Gal epitope in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U. Interaction of the natural anti-Gal antibody with alpha-galactosyl epitopes: a major obstacle for xenotransplantation in humans. Immunol Today. 1993 Oct;14(10):480–482. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90261-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili U., Rachmilewitz E. A., Peleg A., Flechner I. A unique natural human IgG antibody with anti-alpha-galactosyl specificity. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1519–1531. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles G. R., Boehmig H. J., Lilly J., Amemiya H., Takagi H., Coburg A. J., Hathaway W. E., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J., Starzl T. E. Mechanism and modification of rejection of heterografts between divergent species. Transplant Proc. 1970 Dec;2(4):522–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good A. H., Cooper D. K., Malcolm A. J., Ippolito R. M., Koren E., Neethling F. A., Ye Y., Zuhdi N., Lamontagne L. R. Identification of carbohydrate structures that bind human antiporcine antibodies: implications for discordant xenografting in humans. Transplant Proc. 1992 Apr;24(2):559–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipids. Sci Am. 1986 May;254(5):44–53. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0586-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan R. I., Sriwatanawongsa V., Wallwork J., White D. J. Consistent prolonged "concordant" survival of hamster-to-rat cardiac xenografts by inhibition of anti-species antibodies with methotrexate. Transplant Proc. 1993 Feb;25(1 Pt 1):421–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan R. I., van den Bogaerde J., Forty J., Wright L., Wallwork J., White D. J. Prolonged survival of hamster to rat heart xenografts with cyclophosphamide therapy. Transplant Proc. 1992 Apr;24(2):517–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Yamagata T. A novel glycosphingolipid-degrading enzyme cleaves the linkage between the oligosaccharide and ceramide of neutral and acidic glycosphingolipids. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14278–14282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissmeyer-Nielsen F., Olsen S., Petersen V. P., Fjeldborg O. Hyperacute rejection of kidney allografts, associated with pre-existing humoral antibodies against donor cells. Lancet. 1966 Sep 24;2(7465):662–665. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92829-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klassen J., Milgrom F. Studies on cortical necrosis in rabbit renal homografts. Transplantation. 1971 Jan;11(1):35–44. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197101000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo S., Caldwell P. R., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. In vivo interaction of antibodies with cell surface antigens. A mechanism responsible for in situ formation of immune deposits in the zona pellucida of rabbit oocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1369–1380. doi: 10.1172/JCI111838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo S., Fukatsu A., Taub M. L., Caldwell P. R., Brentjens J. R., Andres G. Glomerulonephritis induced in the rabbit by antiendothelial antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1798–1811. doi: 10.1172/JCI113021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriol R., Ye Y., Koren E., Cooper D. K. Carbohydrate antigens of pig tissues reacting with human natural antibodies as potential targets for hyperacute vascular rejection in pig-to-man organ xenotransplantation. Transplantation. 1993 Dec;56(6):1433–1442. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199312000-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer A., Taube D., Welsh K., Bewick M., Gjorstrup P., Thick M. Removal of anti-HLA antibodies by extracorporeal immunoadsorption to enable renal transplantation. Lancet. 1989 Jan 7;1(8628):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91672-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEMTSMA K., MCCRACKEN B. H., SCHLEGEL J. U., PEARL M. HETEROTRANSPLANTATION OF THE KIDNEY: TWO CLINICAL EXPERIENCES. Science. 1964 Feb 14;143(3607):700–702. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3607.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rone J. D., Goodman A. L. Heterogeneity of rabbit aortic endothelial cells in primary culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1987 Apr;184(4):495–503. doi: 10.3181/00379727-184-42506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEAR G. S. Desensitization of the guinea pig to Forssman antibody. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1955 May;96(5):199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., MARCHIORO T. L., HOLMES J. H., HERMANN G., BRITTAIN R. S., STONINGTON O. H., TALMAGE D. W., WADDELL W. R. RENAL HOMOGRAFTS IN PATIENTS WITH MAJOR DONOR-RECIPIENT BLOOD GROUP INCOMPATIBILITIES. Surgery. 1964 Feb;55:195–200. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., MARCHIORO T. L., PETERS G. N., KIRKPATRICK C. H., WILSON W. E., PORTER K. A., RIFKIND D., OGDEN D. A., HITCHCOCK C. R., WADDELL W. R. RENAL HETEROTRANSPLANTATION FROM BABOON TO MAN: EXPERIENCE WITH 6 CASES. Transplantation. 1964 Nov;2:752–776. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196411000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., MARCHIORO T. L., WADDELL W. R. THE REVERSAL OF REJECTION IN HUMAN RENAL HOMOGRAFTS WITH SUBSEQUENT DEVELOPMENT OF HOMOGRAFT TOLERANCE. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Oct;117:385–395. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrin M. S., Vaughan H. A., Dabkowski P. L., McKenzie I. F. Studies on human naturally occurring antibodies to pig xenografts. Transplant Proc. 1993 Oct;25(5):2917–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui B., Hakomori S. A revised structure for the Forssman glycolipid hapten. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5766–5769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Fung J., Tzakis A., Todo S., Demetris A. J., Marino I. R., Doyle H., Zeevi A., Warty V., Michaels M. Baboon-to-human liver transplantation. Lancet. 1993 Jan 9;341(8837):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92553-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Brett J., Harris K., Nawroth P. Participation of endothelial cells in the protein C-protein S anticoagulant pathway: the synthesis and release of protein S. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1971–1978. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taube D. H., Williams D. G., Cameron J. S., Bewick M., Ogg C. S., Rudge C. J., Welsh K. I., Kennedy L. A., Thick M. G. Renal transplantation after removal and prevention of resynthesis of HLA antibodies. Lancet. 1984 Apr 14;1(8381):824–828. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibaudeau K., Anegon I., Lemauff B., Soulillou J. P., Blanchard D. Human natural antibodies to porcine platelets. Transplantation. 1994 Apr 15;57(7):1110–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbrandt R., Tung K. S., Deodhar S. D., Nakamoto S., Kolff W. J. ABO blood group incompatibility in human renal homotransplantation. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Jan;51(1):15–23. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/51.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. M., Hume D. M., Hudson R. P., Jr, Morris P. J., Kano K., Milgrom F. "Hyperacute" renal-homograft rejection in man. N Engl J Med. 1968 Sep 19;279(12):611–618. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196809192791201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuzawa Y., Brentjens J. R., Brett J., Caldwell P. R., Esposito C., Fukatsu A., Godman G., Stern D., Andres G. Antibody-mediated redistribution and shedding of endothelial antigens in the rabbit. J Immunol. 1993 Jun 15;150(12):5633–5646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Genderen I. L., van Meer G., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Voorhout W. F. Subcellular localization of Forssman glycolipid in epithelial MDCK cells by immuno-electronmicroscopy after freeze-substitution. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1009–1019. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]