Abstract
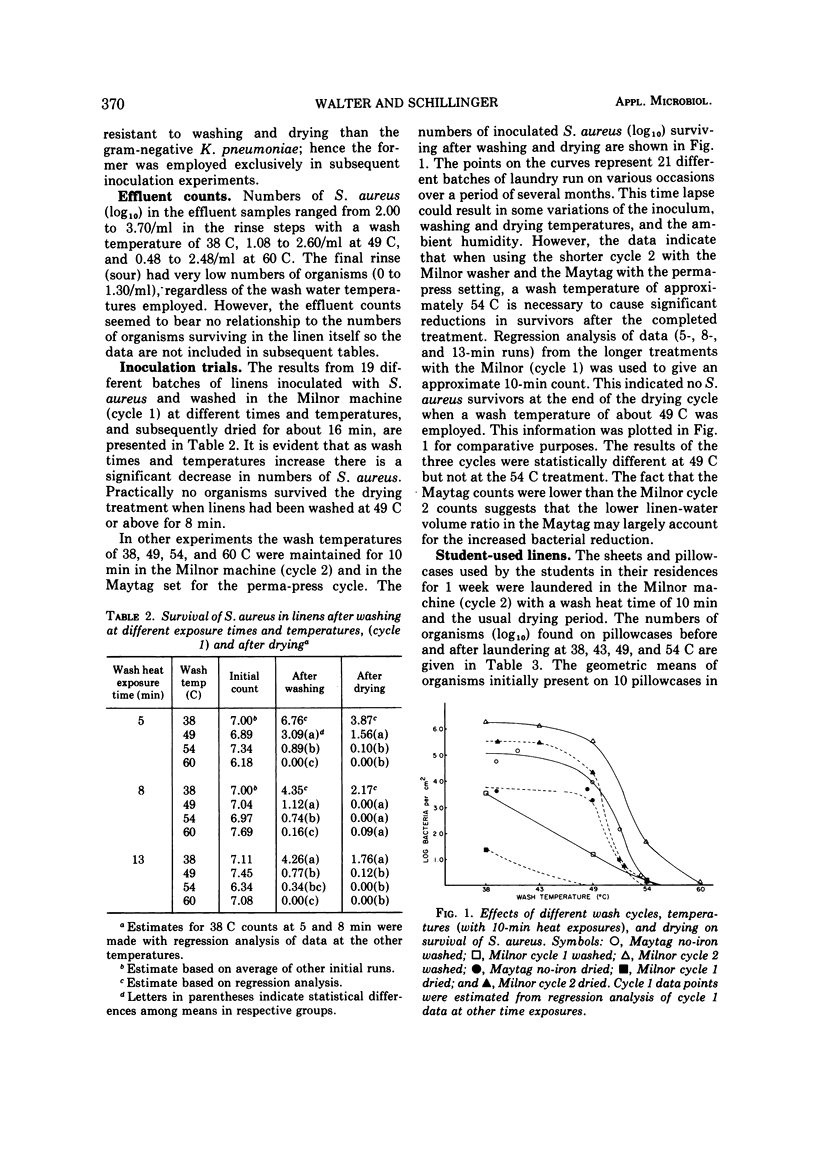
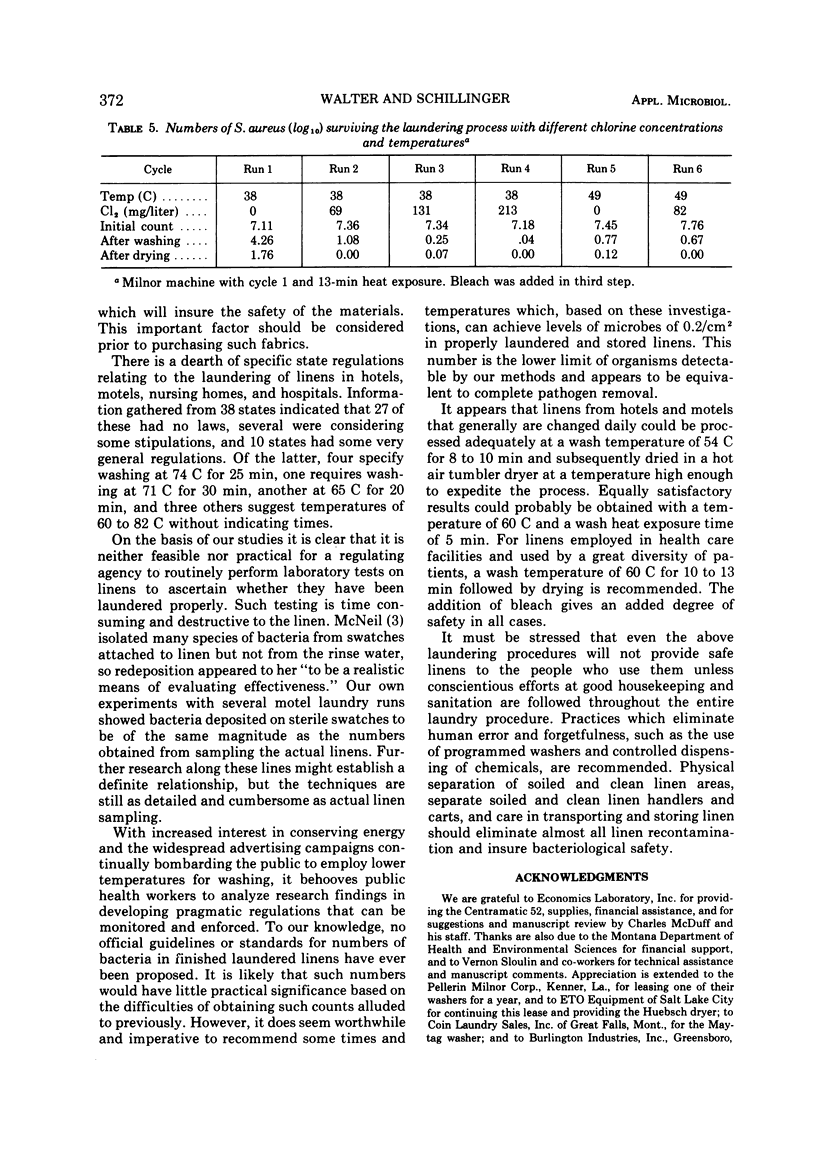
Bacterial survival was determined in linens (i) inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus (ii), taken from hospital isolation patients' beds, and (iii) used by students in their homes. Two different washers using temperatures of 38, 49, 54 and 60 C, respectively, for different times were employed along with a commercial tumbler dryer. Findings, after macerating the linens in a Waring blender and enumerating on nonselective media, indicate that acceptable levels of survivors can be achieved in motel and hotel linens by an 8- to 10-min wash cycle at 54 C followed by adequate drying. However, it is recommended that a wash cycle with 60 C for 10 to 13 min be employed for linens in health care factilities. The microbial significance of various laundering practices is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHURCH B. D., LOOSLI C. G. The role of the laundry in the recontamination of washed bedding. J Infect Dis. 1953 Jul-Aug;93(1):65–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/93.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholes P. S. Bacteria in laundered fabrics. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1970 Nov;60(11):2175–2180. doi: 10.2105/ajph.60.11.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPILLARD M. A. LAUNDERING CAN BREAK THE INFECTION CHAIN. Mod Hosp. 1964 Oct;103:102–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzler T. F., Quan T. J., Schatzle K. Critical analysis of the microflora of toweling. Am J Public Health. 1971 Feb;61(2):376–393. doi: 10.2105/ajph.61.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiksell J. C., Pickett M. S., Hartman P. A. Survival of microorganisms in laundered polyester-cotton sheeting. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):431–435. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.431-435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkoff L. J., Dixon G. J., Westbrook L., Happich W. F. Potentially infectious agents associated with shearling bedpads: effect of laundering with detergent-disinfectant combinations on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):647–652. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.647-652.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


