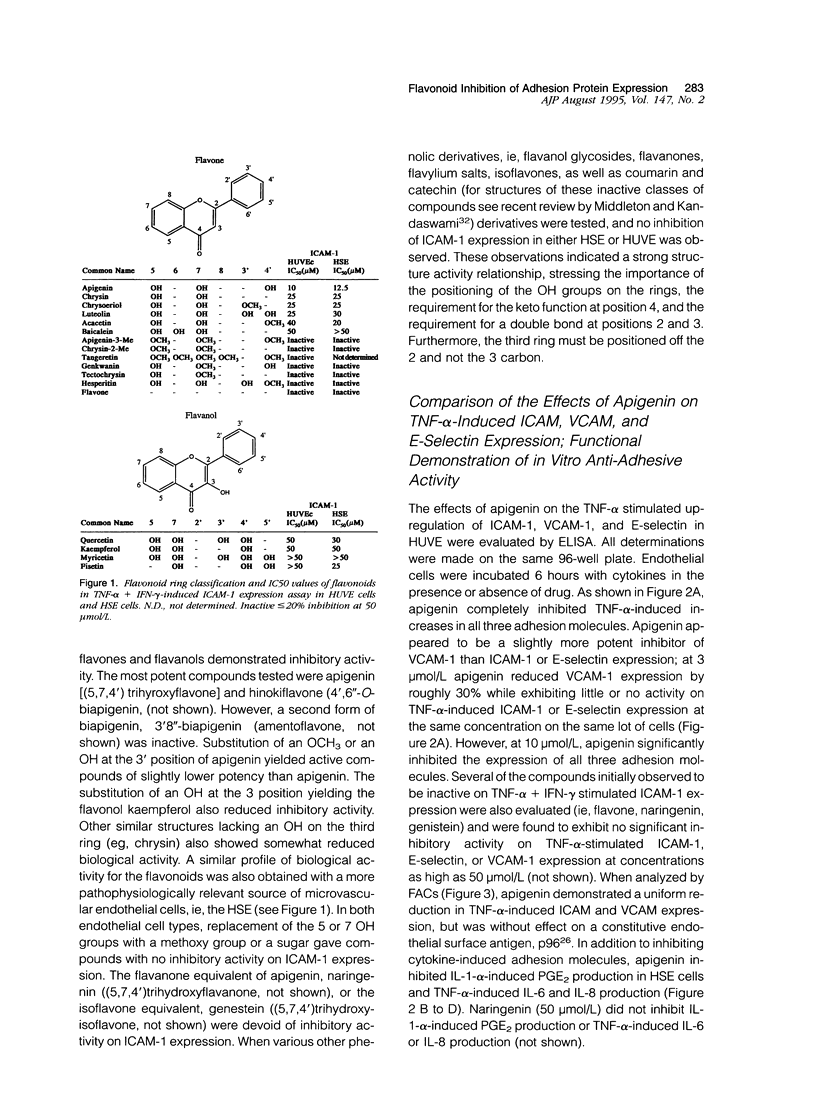
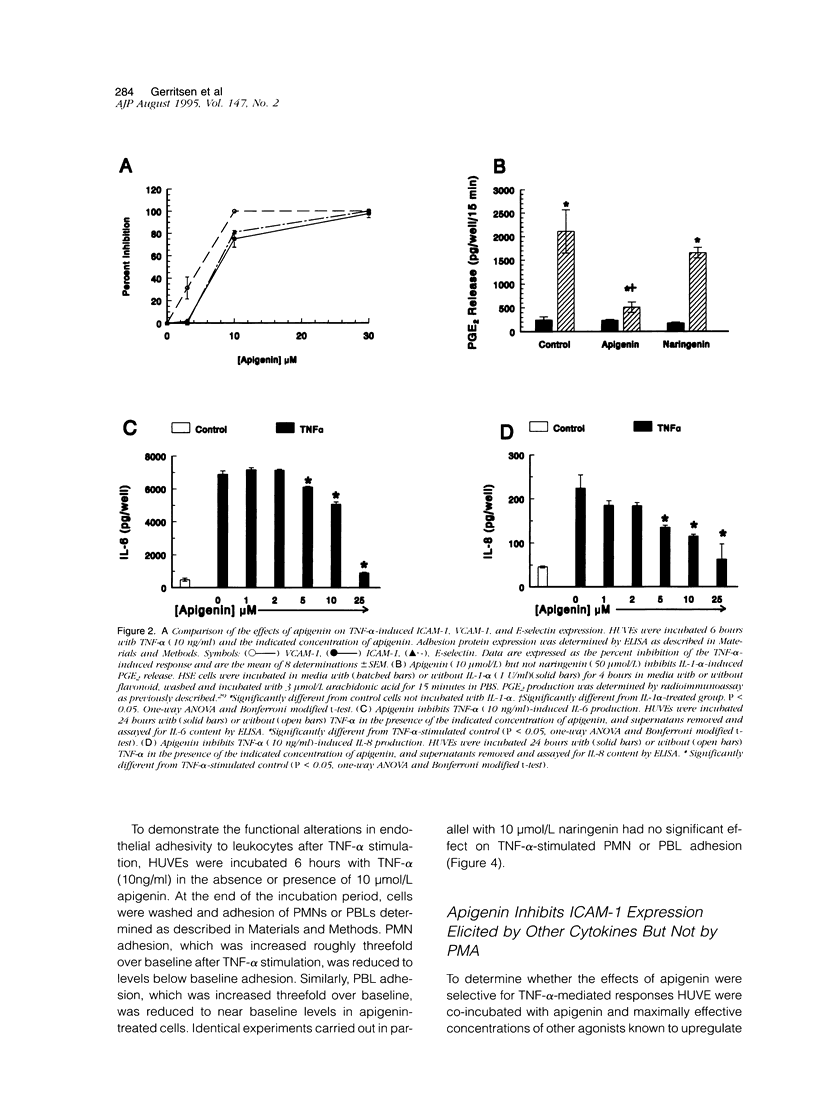
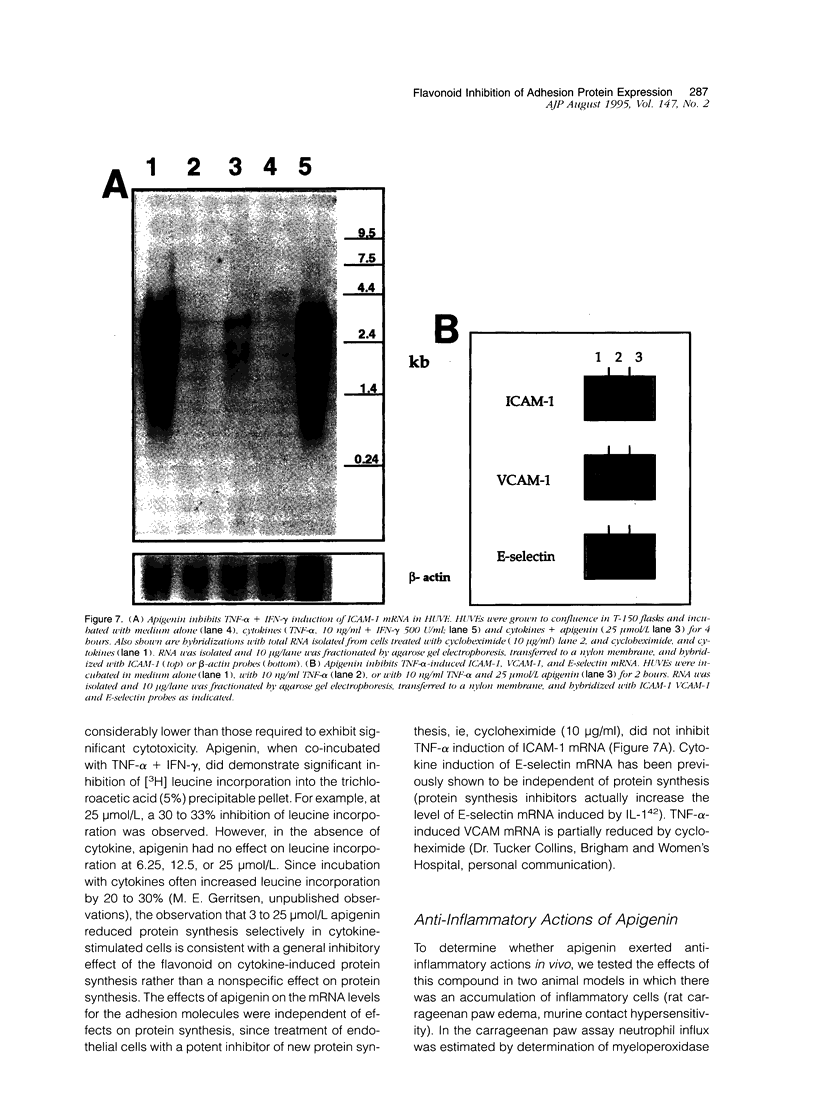
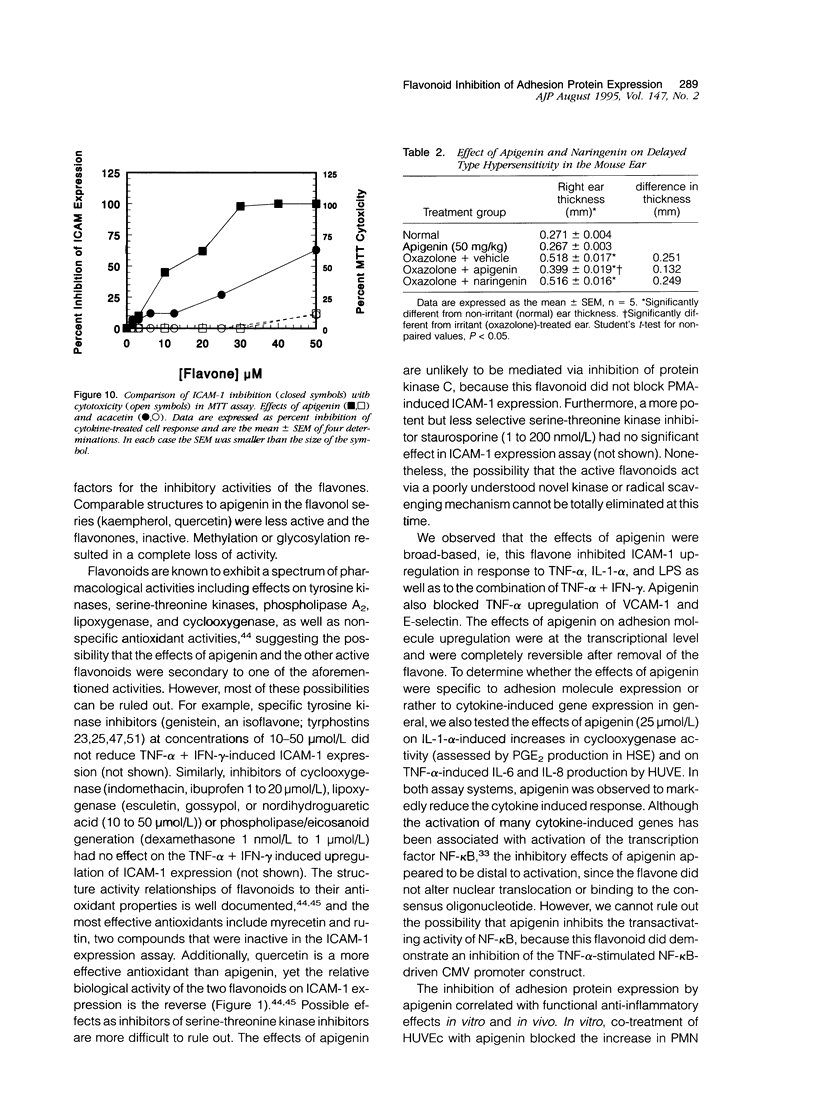
Abstract
Treatment of human endothelial cells with cytokines such as interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interferon-gamma induces the expression of specific leukocyte adhesion molecules on the endothelial cell surface. Interfering with either leukocyte adhesion or adhesion protein upregulation is an important therapeutic target as evidenced by the potent anti-inflammatory actions of neutralizing antibodies to these ligands in various animal models and in patients. In the present study we report that cotreatment of human endothelial cells with certain hydroxyflavones and flavanols blocks cytokine-induced ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and E-selectin expression on human endothelial cells. One of the most potent flavones, apigenin, exhibited a dose- and time-dependent, reversible effect on adhesion protein expression as well as inhibiting adhesion protein upregulation at the transcriptional level. Apigenin also inhibited IL-1 alpha-induced prostaglandin synthesis and TNF-alpha-induced IL-6 and IL-8 production, suggesting that the hydroxyflavones may act as general inhibitors of cytokine-induced gene expression. Although apigenin did not inhibit TNF-alpha-induced nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B(p50(NFKB1)/p65(RelA)) we found this flavonoid did inhibit TNF-alpha induced beta-galactosidase activity in SW480 cells stably transfected with a beta-galactosidase reporter construct driven by four NF-kappa B elements, suggesting an action on NF-kappa B transcriptional activation. Adhesion of leukocytes to cytokine-treated endothelial cells was blocked in endothelial cells cotreated with apigenin. Finally, apigenin demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory activity in carrageenan induced rat paw edema and delayed type hypersensitivity in the mouse. We conclude that flavonoids offer important therapeutic potential for the treatment of a variety of inflammatory diseases involving an increase in leukocyte adhesion and trafficking.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal O. P. The anti-inflammatory action of nepitrin, a flavonoid. Agents Actions. 1982 Jul;12(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01965393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann J., von Bruchhausen F., Wurm G. Flavonoids and related compounds as inhibition of arachidonic acid peroxidation. Prostaglandins. 1980 Oct;20(4):627–639. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. P., Priebat D. A., Christensen R. D., Rothstein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Mar;78(3):206–209. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. T., Zheng R. L., Jia Z. J., Ju Y. Flavonoids as superoxide scavengers and antioxidants. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;9(1):19–21. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90045-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung-Welch N., Patton W. F., Yen-Patton G. P., Hechtman H. B., Shepro D. Phenotypic comparison between mesothelial and microvascular endothelial cell lineages using conventional endothelial cell markers, cytoskeletal protein markers and in vitro assays of angiogenic potential. Differentiation. 1989 Oct;42(1):44–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Williams A., Johnston G. I., Kim J., Eddy R., Shows T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Bevilacqua M. P. Structure and chromosomal location of the gene for endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2466–2473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Fries J. W., Williams A. J., Sultan P., Eddy R., Byers M., Shows T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Collins T. Gene structure, chromosomal location, and basis for alternative mRNA splicing of the human VCAM1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7859–7863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degitz K., Li L. J., Caughman S. W. Cloning and characterization of the 5'-transcriptional regulatory region of the human intercellular adhesion molecule 1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14024–14030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Loggia R., Ragazzi E., Tubaro A., Fassina G., Vertua R. Anti-inflammatory activity of benzopyrones that are inhibitors of cyclo- and lipo-oxygenase. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1988 Dec;20 (Suppl 5):91–94. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(88)80849-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denizot F., Lang R. Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods. 1986 May 22;89(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90368-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferriola P. C., Cody V., Middleton E., Jr Protein kinase C inhibition by plant flavonoids. Kinetic mechanisms and structure-activity relationships. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1617–1624. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway C. J., Madanat M. S., Sarr T., Espevik T., Dumas M. L., Mitra G., Ranges G. E. Anti-tumor necrosis factor receptor and tumor necrosis factor agonist activity by an anti-idiotypic antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):3045–3048. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdin B., Svensjö E. Inhibitory effect of the flavonoid O-(beta-hydroxyethyl)-rutoside on increased microvascular permeability induced by various agents in rat skin. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1983;2(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E., Bloor C. M. Endothelial cell gene expression in response to injury. FASEB J. 1993 Apr 1;7(6):523–532. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.6.8472891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen M. E., Kelley K. A., Ligon G., Perry C. A., Shen C. P., Szczepanski A., Carley W. W. Regulation of the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 in cultured human endothelial cells derived from rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 May;36(5):593–602. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Whelan J., DeLamarter J. F. Labile proteins play a dual role in the control of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) gene regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19226–19232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Virtanen I., Kariniemi A. L., Hormia M., Linder E., Miettinen A. Ulex europaeus I lectin as a marker for vascular endothelium in human tissues. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iigo Y., Takashi T., Tamatani T., Miyasaka M., Higashida T., Yagita H., Okumura K., Tsukada W. ICAM-1-dependent pathway is critically involved in the pathogenesis of adjuvant arthritis in rats. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4167–4171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledebur H. C., Parks T. P. Transcriptional regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-kappa B site and p65 homodimers. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):933–943. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscinskas F. W., Brock A. F., Arnaout M. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule-1-dependent and leukocyte (CD11/CD18)-dependent mechanisms contribute to polymorphonuclear leukocyte adhesion to cytokine-activated human vascular endothelium. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2257–2263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascolo N., Pinto A., Capasso F. Flavonoids, leucocyte migration and eicosanoids. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;40(4):293–295. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton E., Jr, Kandaswami C. Effects of flavonoids on immune and inflammatory cell functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 17;43(6):1167–1179. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90489-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K. F., Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Goff D., Vassallo C., Tarr P. I., Bomsztyk K., Lobb R., Harlan J. M. Activation of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. A., Whitley M. Z., Williams A. J., Collins T. NF-kappa B and I kappa B alpha: an inducible regulatory system in endothelial activation. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):503–512. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robak J., Gryglewski R. J. Flavonoids are scavengers of superoxide anions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar A., Gasco M. A., Alcaraz M. J. Anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer properties of hypolaetin-8-glucoside, a novel plant flavonoid. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;36(12):820–823. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voraberger G., Schäfer R., Stratowa C. Cloning of the human gene for intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and analysis of its 5'-regulatory region. Induction by cytokines and phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyta J. C., Via D. P., Butterfield C. E., Zetter B. R. Identification and isolation of endothelial cells based on their increased uptake of acetylated-low density lipoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2034–2040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Ghersa P., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Gray J., Chandra G., Talabot F., DeLamarter J. F. An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 25;19(10):2645–2653. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.10.2645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





