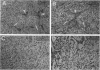
Abstract
In vivo and in vitro experimental models have suggested a major role for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) in tumor cell invasion and metastasis. The uPA proteolytic activity of tumor cells has been shown to be largely determined by the extent of the expression and saturation of the uPA receptor. We have analyzed the expression and cellular localization of both uPA and uPA receptor at the protein and mRNA levels in 33 paired samples of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and non-tumorous kidney tissue. In comparison with adjacent normal non-tumorous kidney tissues RCC tumor cells modestly overexpressed uPA-receptor mRNA and showed significantly decreased uPA mRNA expression. However, the immunoreactive uPA content of tumor cells was comparable to that of the surrounding normal non-tumorous kidney tissue. Assuming constancy of the uPA-receptor affinity for uPA this indicates that a proportion of the RCC-associated uPA may be derived from an exogenous source and subsequently concentrated at the tumor cell surface via uPA receptor expression. The modest increase in uPA receptor expression may lead to a normalization of uPA antigen content in RCC; however, it is not sufficient to substantially increase tumor tissue-uPA content over the level of normal non-tumorous kidney tissue.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. S., Bleakley P., Woodrow G. C., Doe W. F. Inhibition of cancer cell urokinase plasminogen activator by its specific inhibitor PAI-2 and subsequent effects on extracellular matrix degradation. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4676–4684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi E., Cohen R. L., Thor A. T., Todd R. F., 3rd, Mizukami I. F., Lawrence D. A., Ljung B. M., Shuman M. A., Smith H. S. The urokinase receptor is expressed in invasive breast cancer but not in normal breast tissue. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):861–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busso N., Masur S. K., Lazega D., Waxman S., Ossowski L. Induction of cell migration by pro-urokinase binding to its receptor: possible mechanism for signal transduction in human epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):259–270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cajot J. F., Bamat J., Bergonzelli G. E., Kruithof E. K., Medcalf R. L., Testuz J., Sordat B. Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 is a potent natural inhibitor of extracellular matrix degradation by fibrosarcoma and colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casslén B., Gustavsson B., Astedt B. Cell membrane receptors for urokinase plasminogen activator are increased in malignant ovarian tumours. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(11):1445–1448. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90028-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clairmont A., Ebert T., Weber H., Zoidl C., Eickelmann P., Schulz W. A., Sies H., Ryffel G. U. Lowered amounts of the tissue-specific transcription factor LFB1 (HNF1) correlate with decreased levels of glutathione S-transferase alpha messenger RNA in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1319–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C. W., Cohen R. L., Lucas B. K., Liu G., Shuman M. A., Levinson A. D. Prevention of metastasis by inhibition of the urokinase receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eker R., Nesland J. M., Andersen A., Johannessen J. V. Prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 1986 Jul;1(3):255–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. The biology of renal cancer metastasis. Semin Urol. 1992 Feb;10(1):3–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Di Fiore P., Locatelli E. K., Falco J., Blasi F. Modulation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression during the transition from quiescent to proliferative state in normal mouse cells. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Kirkeby L. T., Kristensen P., Lund L. R., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HE C. S., Wilhelm S. M., Pentland A. P., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. A., Rehemtulla A., Babins E. M. Species differences in the detection of high molecular weight urinary plasminogen activators. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1986;84(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(86)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata M. [The study of plasminogen activator in renal cell carcinoma with special remarks on urokinase type plasminogen activator]. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 1989 Nov;80(11):1558–1565. doi: 10.5980/jpnjurol1989.80.1558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing V. J., Law L. W., Corti A., Appella E., Blasi F. Modulation of metastatic potential by cell surface urokinase of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1270–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B. R., Tansey W. P., Phillips S. M., Ramshaw I. A., Kefford R. F. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional activation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression in metastatic tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1992 May 1;52(9):2489–2496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoefler H., Childers H., Montminy M. R., Lechan R. M., Goodman R. H., Wolfe H. J. In situ hybridization methods for the detection of somatostatin mRNA in tissue sections using antisense RNA probes. Histochem J. 1986 Nov-Dec;18(11-12):597–604. doi: 10.1007/BF01675295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollas W., Blasi F., Boyd D. Role of the urokinase receptor in facilitating extracellular matrix invasion by cultured colon cancer. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3690–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber K., Kirchheimer J., Binder B. R. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight urokinase from native human urine. Thromb Haemost. 1982 Jun 28;47(3):197–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. H., Christensen E. I., Ebbesen P., Gliemann J., Andreasen P. A. Lysosomal degradation of receptor-bound urokinase-type plasminogen activator is enhanced by its inhibitors in human trophoblastic choriocarcinoma cells. Cell Regul. 1990 Dec;1(13):1043–1056. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.13.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Pflüger H., Hienert G., Binder B. R. Increased urokinase activity to antigen ratio in human renal-cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jun 15;35(6):737–741. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klöne A., Weidner U., Hussnätter R., Harris J., Meyer D., Peter S., Ketterer B., Sies H. Decreased expression of the glutathione S-transferases alpha and pi genes in human renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2179–2183. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Two alternatively spliced mouse urokinase receptor mRNAs with different histological localization in the gastrointestinal tract. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1763–1771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):341–349. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1899685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2533–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer D. J., Kuo A., Kariko K., Ahuja M., Klugherz B. D., Ivanics K. M., Hoxie J. A., Williams W. V., Liang B. T., Cines D. B. Regulation of the endothelial cell urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor. Evidence for cyclic AMP-dependent and protein kinase C-dependent pathways. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):330–340. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Rømer J., Rønne E., Ellis V., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-receptor biosynthesis, mRNA level and gene transcription are increased by transforming growth factor beta 1 in human A549 lung carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3399–3407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04904.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menoud P. A., Matthies R., Hofsteenge J., Nagamine Y. Purification and cDNA cloning of a transcription factor which functionally cooperates within a cAMP regulatory unit in the porcine uPA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1845–1852. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignatti P., Robbins E., Rifkin D. B. Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. J., Jensen P. J., Dzubow L. M., Lazarus G. S. Urokinase plasminogen activator is immunocytochemically detectable in squamous cell but not basal cell carcinomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Mar;98(3):351–358. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12499803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nekarda H., Schmitt M., Ulm K., Wenninger A., Vogelsang H., Becker K., Roder J. D., Fink U., Siewert J. R. Prognostic impact of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor PAI-1 in completely resected gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Jun 1;54(11):2900–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D., Pöllänen J., Høyer-Hansen G., Rønne E., Sakaguchi K., Wun T. C., Appella E., Danø K., Blasi F. Internalization of the urokinase-plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex is mediated by the urokinase receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9129–9133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Clunie G., Masucci M. T., Blasi F. In vivo paracrine interaction between urokinase and its receptor: effect on tumor cell invasion. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1107–1112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L. In vivo invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2437–2445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen L. C., Lund L. R., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Skriver L. One-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator from human sarcoma cells is a proenzyme with little or no intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11189–11195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrides P. E., Bock S., Bovens J., Hofmann R., Jakse G. Modulation of pro-epidermal growth factor, pro-transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in human renal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 1;50(13):3934–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Ralfkiaer E., Rønne E., Høyer-Hansen G., Kirkeby L., Danø K. Immunohistochemical detection of the receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in human colon cancer. Histopathology. 1994 Feb;24(2):131–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1994.tb01291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Saksela O., Salonen E. M., Andreasen P., Nielsen L., Danø K., Vaheri A. Distinct localizations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type 1 inhibitor under cultured human fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1085–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., Pedersen N., Masucci M. T., Weening-Verhoeff E. J., Danø K., Verheijen J. H., Blasi F. Complementation between urokinase-producing and receptor-producing cells in extracellular matrix degradation. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):793–803. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter L. S., Kruithof E. K., Cajot J. F., Sordat B. The role of the urokinase receptor in extracellular matrix degradation by HT29 human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 Feb 1;53(3):444–450. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910530316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A. L., Cubellis M. V., Masucci M. T., Behrendt N., Lund L. R., Danø K., Appella E., Blasi F. Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):467–474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Belin D., Huarte J., Hirschel-Scholz S., Saurat J. H., Vassalli J. D. Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1073–1079. doi: 10.1172/JCI115406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M., Chucholowski N., Busch E., Hellmann D., Wagner B., Goretzki L., Jänicke F., Günzler W. A., Graeff H. Fluorescent probes as tools to assess the receptor for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator on tumor cells. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):291–302. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Tacchetti C., Cubellis M. V., Corti A., Hearing V. J., Cassani G., Appella E., Blasi F. Autocrine saturation of pro-urokinase receptors on human A431 cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Verde P., Grimaldi G., Locatelli E. K., Blasi F. Increase in urokinase plasminogen activator mRNA synthesis in human carcinoma cells is a primary effect of the potent tumor promoter, phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1235–1241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde P., Stoppelli M. P., Galeffi P., Di Nocera P., Blasi F. Identification and primary sequence of an unspliced human urokinase poly(A)+ RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner U., Peter S., Strohmeyer T., Hussnätter R., Ackermann R., Sies H. Inverse relationship of epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2/neu gene expression in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Sawaya R., Mohanam S., Bindal A. K., Bruner J. M., Oka K., Rao V. H., Tomonaga M., Nicolson G. L., Rao J. S. Expression and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human astrocytomas in vivo. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 15;54(14):3656–3661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneda J., Saiki I., Fujii H., Abe F., Kojima Y., Azuma I. Inhibition of tumor invasion and extracellular matrix degradation by ubenimex (bestatin). Clin Exp Metastasis. 1992 Jan;10(1):49–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00163576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]