Abstract
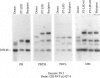
Recent clinical, pathological, and molecular studies have increased our understanding of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders (PT-LPDs). Studies have shown that the majority of PT-LPDs arising in bone marrow transplant recipients are of donor origin; however, the source (host or donor) of the lymphoid cells that make up PT-LPDs arising in solid organ transplant recipients has not been systemically investigated. In this study, 18 PT-LPDs occurring in 16 organ transplant recipients (13 heart, 2 kidney, 1 lung), 9 donor tissues (for 10 recipients), and 14 uninvolved recipient tissues (from 12 patients) were examined employing restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis to determine their host or donor origin. The PstI-digested DNAs were analyzed by Southern blot hybridization using two highly informative polymorphic probes that map to chromosome 21 (CRI-PAT-pL427-4) and chromosome 7 (CRI-PAT-pS194). All solid organ PT-LPDs with corresponding uninvolved recipient DNA showed identical hybridization patterns; none of the PT-LPDs exhibited a hybridization pattern that matched donor DNA. These findings suggest that the vast majority of PT-LPDs arising in solid organ transplant recipients, in contrast to those arising in bone marrow transplant recipients, are of recipient origin.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Farsakh H., Cagle P. T., Buffone G. J., Bruner J. M., Weilbaecher D., Greenberg S. D. Heart allograft involvement with Epstein-Barr virus-associated posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Jan;116(1):93–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfrey E. J., Friedman A. L., Grossman R. A., Perloff L. J., Naji A., Barker C. F., Montone K. T., Tomaszewski J. E., Chmielewski C., Holland T. A recent decrease in the time to development of monomorphous and polymorphous posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Transplantation. 1992 Aug;54(2):250–253. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199208000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armes J. E., Angus P., Southey M. C., Battaglia S. E., Ross B. C., Jones R. M., Venter D. J. Lymphoproliferative disease of donor origin arising in patients after orthotopic liver transplantation. Cancer. 1994 Nov 1;74(9):2436–2441. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19941101)74:9<2436::aid-cncr2820740908>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Green P., Knowlton R., Schumm J., Lander E., Oliphant A., Willard H., Akots G., Brown V., Gravius T. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 7 with 63 DNA markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8006–8010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L. C., Copenhaver C. M., Morrison V. A., Gruber S. A., Dunn D. L., Gajl-Peczalska K., Strickler J. G. B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in solid-organ transplant patients: detection of Epstein-Barr virus by in situ hybridization. Hum Pathol. 1992 Feb;23(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90237-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadburn A., Cesarman E., Liu Y. F., Addonizio L., Hsu D., Michler R. E., Knowles D. M. Molecular genetic analysis demonstrates that multiple posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in one anatomic site in a single patient represent distinct primary lymphoid neoplasms. Cancer. 1995 Jun 1;75(11):2747–2756. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19950601)75:11<2747::aid-cncr2820751119>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. M., Barr M. L., Chadburn A., Frizzera G., Schenkel F. A., Sciacca R. R., Reison D. S., Addonizio L. J., Rose E. A., Knowles D. M. Management of lymphoproliferative disorders after cardiac transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993 Sep;56(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(93)90893-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui D., Duvoux C., Plassa F., Gaulard P., Julien M., Fagniez P. L., Dhumeaux D., Goossens M., Farcet J. P. Lymphoproliferative disorder of donor origin in a liver transplant recipient: complete remission after drastic reduction of immunosuppression without graft loss. Transplantation. 1993 Oct;56(4):1023–1026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockfield S. M., Preiksaitis J. K., Jewell L. D., Parfrey N. A. Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in renal allograft recipients. Clinical experience and risk factor analysis in a single center. Transplantation. 1993 Jul;56(1):88–96. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199307000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. H., Sweny P., Edwards J. M., Janossy G., Hoffbrand A. V. Long-term T-cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in renal-allograft recipients receiving cyclosporin A. Lancet. 1981 Jan 3;1(8210):10–12. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzera G., Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Rosai J., McKenna R. W., Sibley R. K., Holahan K. P., Lindquist L. L. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasias and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4262–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett T. J., Chadburn A., Barr M. L., Drusin R. E., Chen J. M., Schulman L. L., Smith C. R., Reison D. S., Rose E. A., Michler R. E. Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders treated with cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine-prednisone chemotherapy. Cancer. 1993 Nov 1;72(9):2782–2785. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19931101)72:9<2782::aid-cncr2820720941>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston J. S., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Epstein-Barr-virus-specific T-cell memory in renal-allograft recipients under long-term immunosuppression. Lancet. 1982 Apr 24;1(8278):923–925. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91930-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godyn J. J., Hicks D. G., Hsu S. H., Kant J., Montone K. T., Zmijewski C. M., Tomaszewski J. E. Demonstration of passenger leukocytes in a case of Epstein-Barr virus posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1992 Mar;116(3):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett T. C., Gale R. P., Fleischman H., Austin G. E., Sparkes R. S., Taylor C. R. Immunoblastic sarcoma in donor cells after bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 19;300(16):904–907. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904193001606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Frizzera G., Purtilo D. T., Sakamoto K., Sullivan J. L., Saemundsen A. K., Klein G., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Clinical spectrum of lymphoproliferative disorders in renal transplant recipients and evidence for the role of Epstein-Barr virus. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4253–4261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Frizzera G., Arthur D. C., Balfour H. H., Jr, McClain K., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induced polyclonal and monoclonal B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases occurring after renal transplantation. Clinical, pathologic, and virologic findings and implications for therapy. Ann Surg. 1983 Sep;198(3):356–369. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198309000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegele R. G., Bicknell S. G., Bailey D. J., Cameron R. G. In situ hybridization for the Y chromosome reveals a donor origin for a posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder in a sex-mismatched hepatic allograft. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994 Aug;118(8):795–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelle B., Evans-Holm M., Yen T. S., Garovoy M., Guis M., Edman J. C. A poorly differentiated lymphoma of donor origin in a renal allograft recipient. Transplantation. 1989 Jun;47(6):945–948. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198906000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban R. H., Long P. P., Perlman E. J., Hutchins G. M., Baumgartner W. A., Baughman K. L., Griffin C. A. Fluorescence in situ hybridization for the Y-chromosome can be used to detect cells of recipient origin in allografted hearts following cardiac transplantation. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):975–980. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. A., Ferry J. A., Harris N. L., Jacobson J. O. Clonal analysis of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders, using both episomal Epstein-Barr virus and immunoglobulin genes as markers. Am J Clin Pathol. 1994 May;101(5):590–596. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/101.5.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor N., Jung L. K., Engelhard D., Filler J., Shalit I., Landreth K. S., Good R. A. Lymphoma in a patient with severe combined immunodeficiency with adenosine deaminase deficiency, following unsustained engraftment of histoincompatible T cell-depleted bone marrow. J Pediatr. 1986 Mar;108(3):435–438. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80892-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Cesarman E., Chadburn A., Frizzera G., Chen J., Rose E. A., Michler R. E. Correlative morphologic and molecular genetic analysis demonstrates three distinct categories of posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):552–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Shulman H. M., Schubach W. H., Hansen J. A., Fefer A., Miller G., Thomas E. D. Fatal Epstein-Barr-virus-associated proliferation of donor B cells after treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease with a murine anti-T-cell antibody. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Sep;101(3):310–315. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-3-310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meduri G., Fromentin L., Vieillefond A., Fries D. Donor-related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in a renal allograft recipient. Transplant Proc. 1991 Oct;23(5):2649–2649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison V. A., Dunn D. L., Manivel J. C., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Peterson B. A. Clinical characteristics of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Am J Med. 1994 Jul;97(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalesnik M. A., Jaffe R., Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Porter K., Burnham J. A., Makowka L., Ho M., Locker J. The pathology of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):173–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Latt S. A., Pesando J. M., Gustashaw K., Powers M., Chaganti R. S., O'Reilly R. J. Leukemia relapse in donor cells after allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1981 Mar 19;304(12):712–714. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198103193041206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordan J. M., Molloy K., O'Briain D. S., Corbally N., Devaney D., McShane D., Considine N., McCann S. R. Localized, late-onset, high-grade lymphoma following bone marrow transplantation: response to combination chemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 1994 Jan;86(1):183–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb03272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos E. B., Ladanyi M., Emanuel D., Mackinnon S., Boulad F., Carabasi M. H., Castro-Malaspina H., Childs B. H., Gillio A. P., Small T. N. Infusions of donor leukocytes to treat Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1994 Apr 28;330(17):1185–1191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199404283301703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci P. G., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Dalla Favera R. Lymphoid tumors displaying rearrangements of both immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):1015–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn I. Host origin of lymphomas in organ transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1979 Mar;27(3):214–214. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197903000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa P. S., Yousem S. A. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease in a heart-lung allograft. Demonstration of host origin by restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis. Transplantation. 1990 Jan;49(1):126–130. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199001000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa P. S., Yousem S. A., Paradis I. L., Dauber J. A., Griffith B. P., Locker J. The clinical spectrum, pathology, and clonal analysis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in heart-lung transplant recipients. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Aug;92(2):177–185. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddler S. A., Breinig M. C., McKnight J. L. Increased levels of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected lymphocytes and decreased EBV nuclear antigen antibody responses are associated with the development of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease in solid-organ transplant recipients. Blood. 1994 Aug 1;84(3):972–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Hackman R., Neiman P. E., Miller G., Thomas E. D. A monoclonal immunoblastic sarcoma in donor cells bearing Epstein-Barr virus genomes following allogeneic marrow grafting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):180–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütt G., Engemann R., Gassel H. J., Elfeldt R., Leimenstoll G., Westphal E., Schroeder P. Donor-transmitted non-Hodgkin's lymphoma after renal transplantation--a case report. Transplant Proc. 1993 Apr;25(2):2131–2132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. S., McClain K., Frizzera G., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Kersey J. H., Blazar B. R., Arthur D. C., Patton D. F., Greenberg J. S., Burke B. Epstein-Barr virus associated B cell lymphoproliferative disorders following bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1234–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer W. T., Ritz J., Finegold M. J., Guerra I. C., Rosenblatt H. M., Lewis D. E., Pollack M. S., Taber L. H., Sumaya C. V., Grumet F. C. Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell proliferations of diverse clonal origins after bone marrow transplantation in a 12-year-old patient with severe combined immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 2;312(18):1151–1159. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505023121804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Bartram C. R., Friedrich W., Arnold R., Schmeiser T., Hampl W., Müller-Hermelink H. K., Heymer B. Fatal B-cell lymphoproliferative syndrome in allogeneic marrow graft recipients. A clinical, immunobiological and pathological study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1991;60(5):307–319. doi: 10.1007/BF02899562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro I. J., Yandell D. W., Li C., Saini S., Ferry J., Powelson J., Katkov W. N., Cosimi A. B. Brief report: lymphoma of donor origin occurring in the porta hepatis of a transplanted liver. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 1;329(1):27–29. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307013290105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Nalesnik M. A., Porter K. A., Ho M., Iwatsuki S., Griffith B. P., Rosenthal J. T., Hakala T. R., Shaw B. W., Jr, Hardesty R. L. Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporin-steroid therapy. Lancet. 1984 Mar 17;1(8377):583–587. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90994-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinnen L. J., Costanzo-Nordin M. R., Fisher S. G., O'Sullivan E. J., Johnson M. R., Heroux A. L., Dizikes G. J., Pifarre R., Fisher R. I. Increased incidence of lymphoproliferative disorder after immunosuppression with the monoclonal antibody OKT3 in cardiac-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 20;323(25):1723–1728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012203232502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann D. J., Ferry J. A., Harris N. L., Louis D. N., Delmonico F., Spiro I. Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in solid organ recipients are predominantly aggressive tumors of host origin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995 Jun;103(6):748–755. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.6.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson A. H., Smith J. L., Hunsicker L. G., Tobacman J., Kapelanski D. P., Johnson M., Wright F. H., Behrendt D. M., Corry R. J. Increased frequency of posttransplant lymphomas in patients treated with cyclosporine, azathioprine, and prednisone. Transplantation. 1989 Feb;47(2):293–296. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198902000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousem S. A., Randhawa P., Locker J., Paradis I. L., Dauber J. A., Griffith B. P., Nalesnik M. A. Posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders in heart-lung transplant recipients: primary presentation in the allograft. Hum Pathol. 1989 Apr;20(4):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zutter M. M., Martin P. J., Sale G. E., Shulman H. M., Fisher L., Thomas E. D., Durnam D. M. Epstein-Barr virus lymphoproliferation after bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):520–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Amore E. S., Manivel J. C., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Litz C. E., Copenhaver C. M., Shapiro R. S., Strickler J. G. B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders after bone marrow transplant. An analysis of ten cases with emphasis on Epstein-Barr virus detection by in situ hybridization. Cancer. 1991 Sep 15;68(6):1285–1295. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910915)68:6<1285::aid-cncr2820680618>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]