Abstract
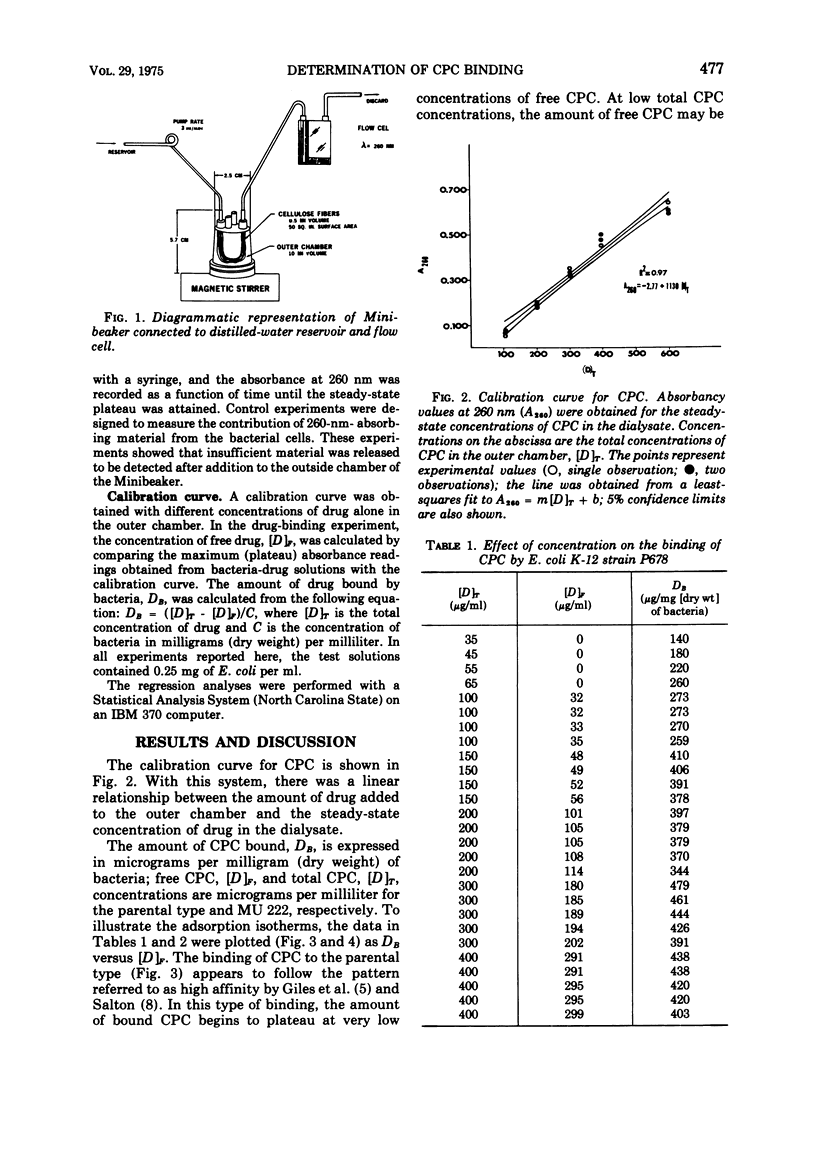
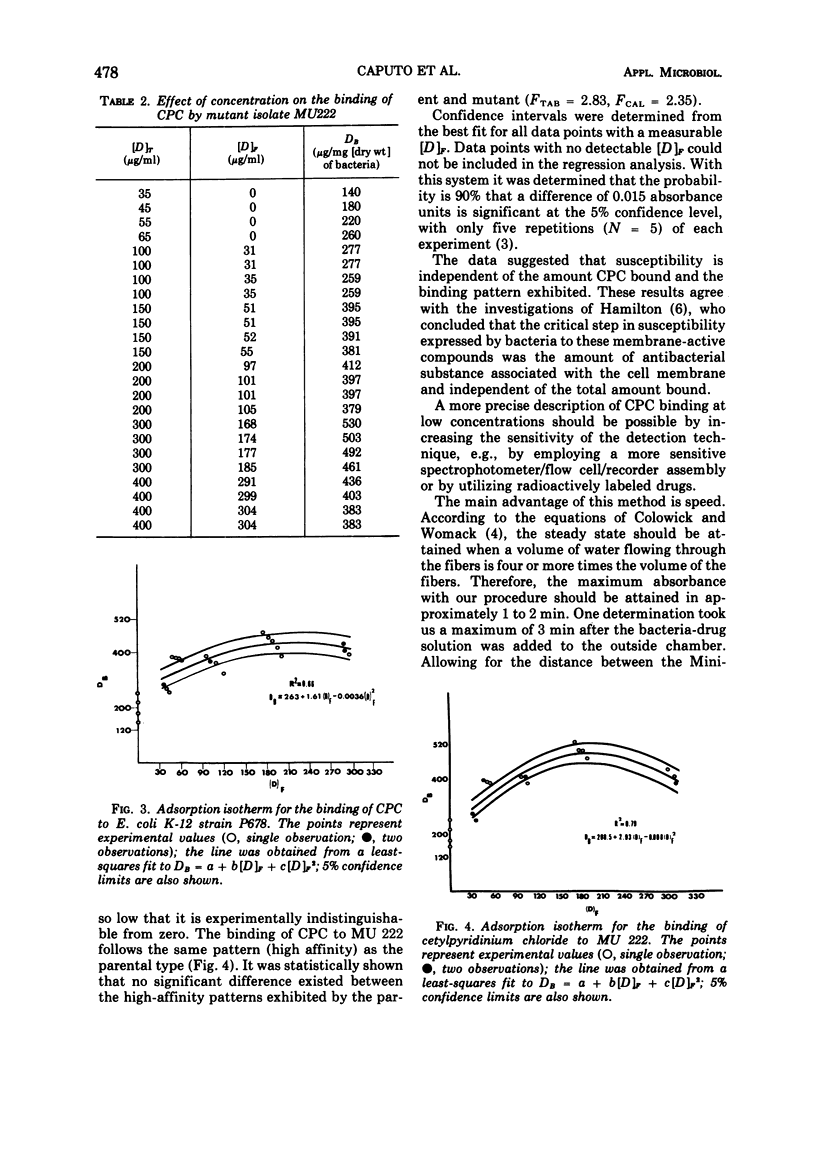
A modification of the Colowick and Womack procedure for measuring ligand binding by macromolecules is described for drug binding by bacteria. This technique is based on the determination of drug concentration in the dialysate from a bacteria-drug mixture at equilibrium. The dialysis cell of the original procedure was replaced by a Minibeaker (Bio-Rad), which has a larger membrane surface area, and the dialysate was continuously monitored with a spectrophotometer equipped with a flow cell. With this system, only 3 min was required to determine the amount of cetylpyridinium chloride bound by Escherichia coli K-12 strain P678. Possible applications of the technique are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKETT A. H., PATKI S. J., ROBINSON A. E. The interaction of phenolic compounds with bacteria. I. Hexylresorcinol and Escherichia coli. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1959 Jun;11(6):360–366. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1959.tb12564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGO W. B., NEWTON J. M. THE ADSORPTION OF IODINE FROM SOLUTION BY MICRO-ORGANISMS AND BY SERUM. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1964 Jan;16:49–55. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. A. The mechanism of the bacteriostatic action of tetrachlorosalicylanilide: a Membrane-active antibacterial compound. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Mar;50(3):441–458. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. J. The adsorption of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide by bacteria, its action in releasing cellular constituents and its bactericidal effects. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):391–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


