Abstract
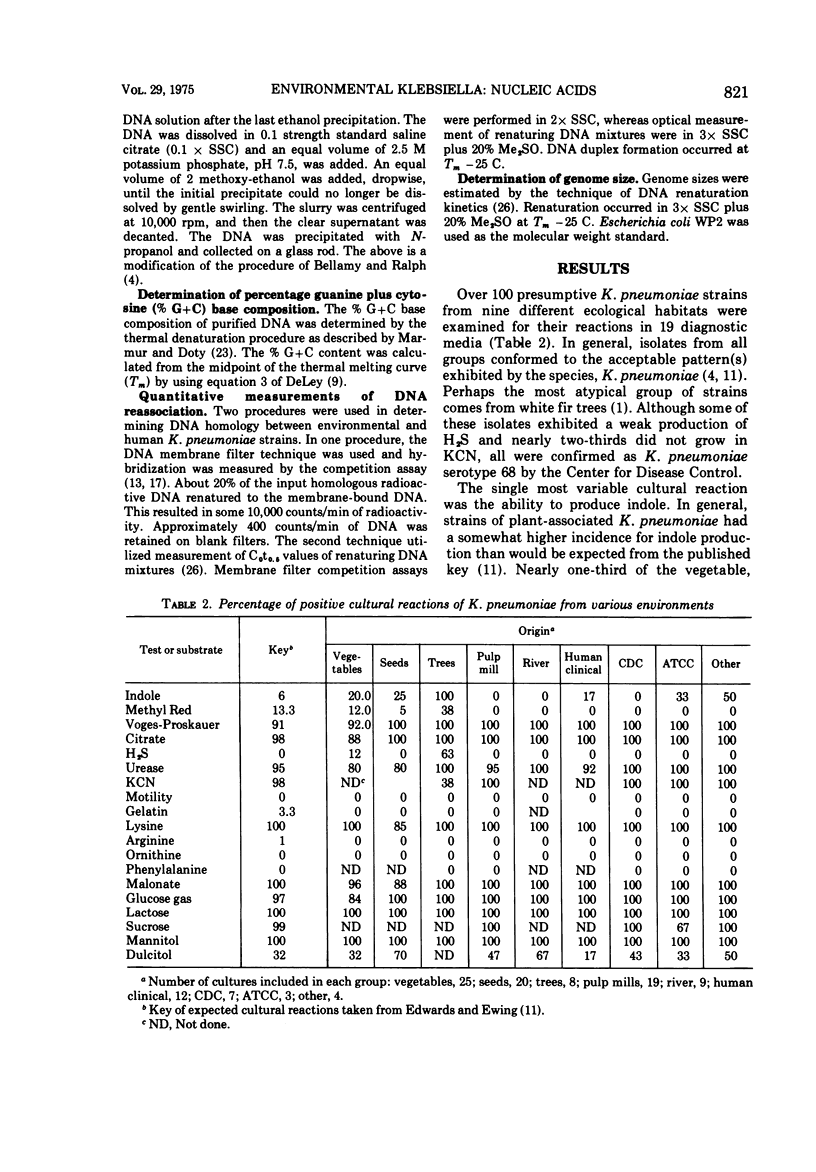
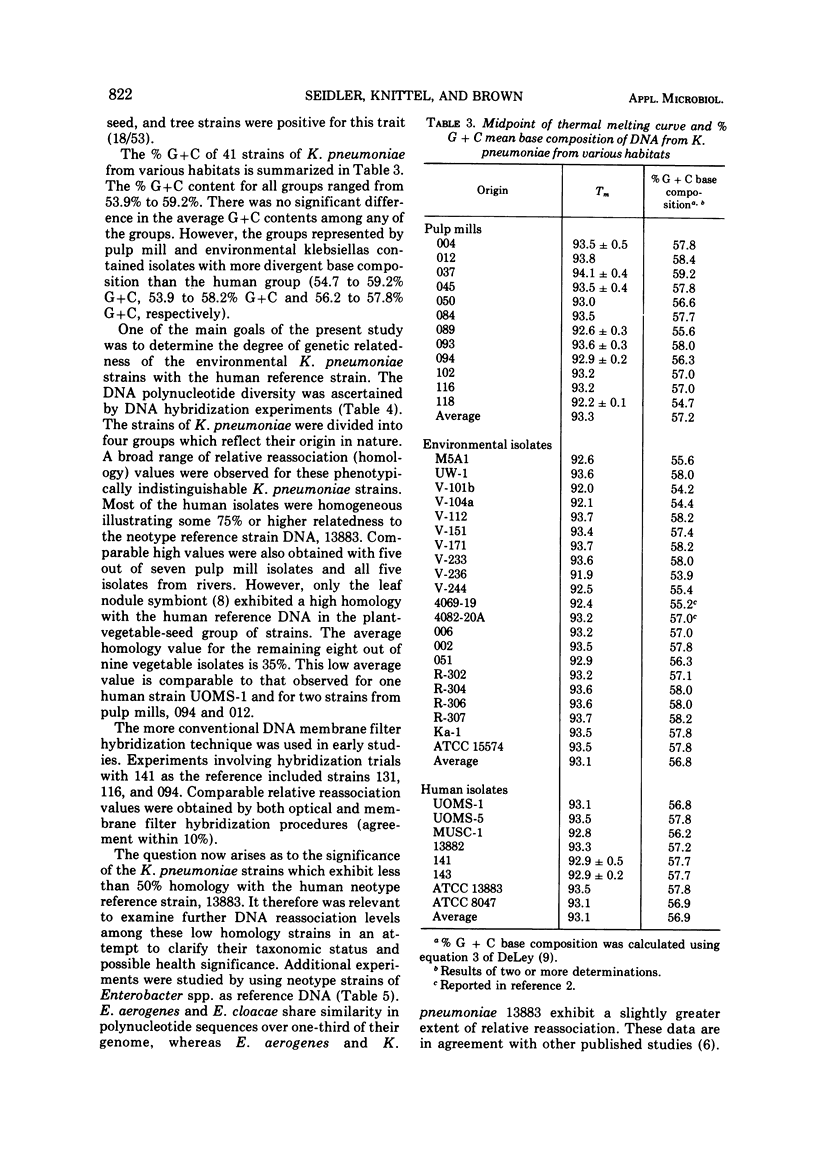
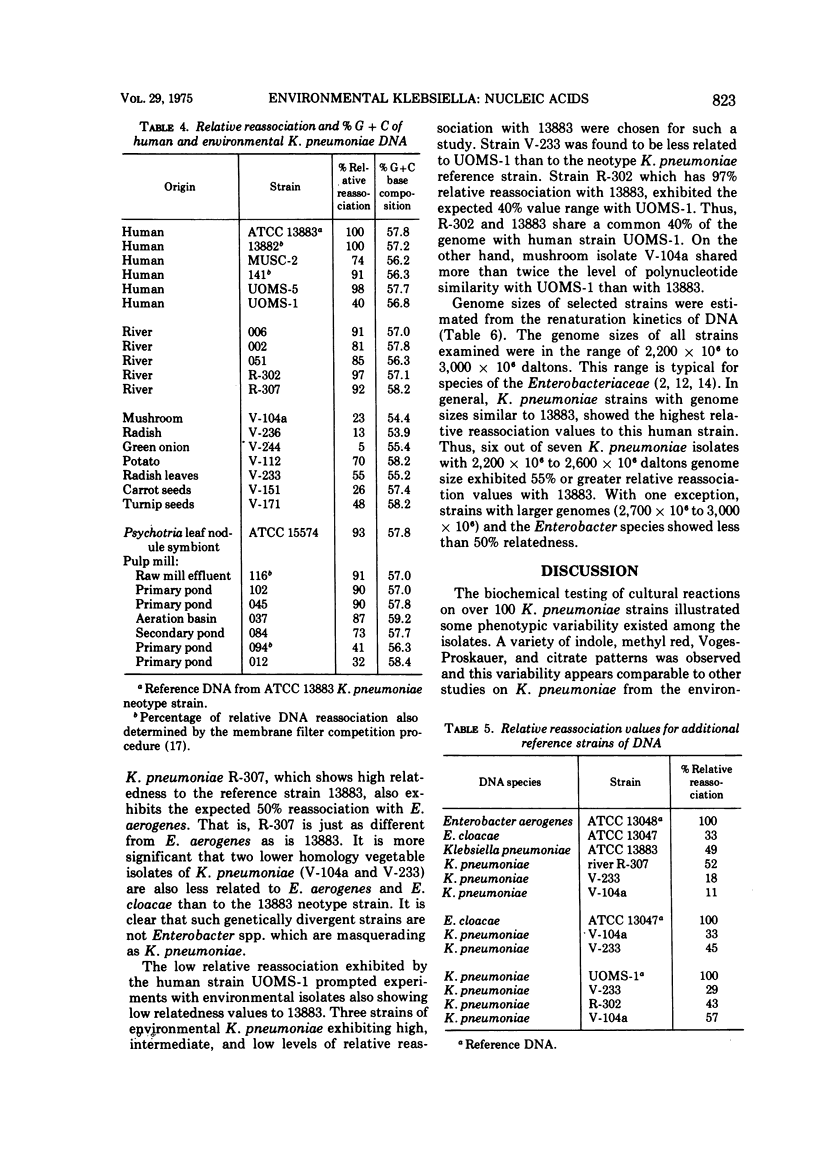
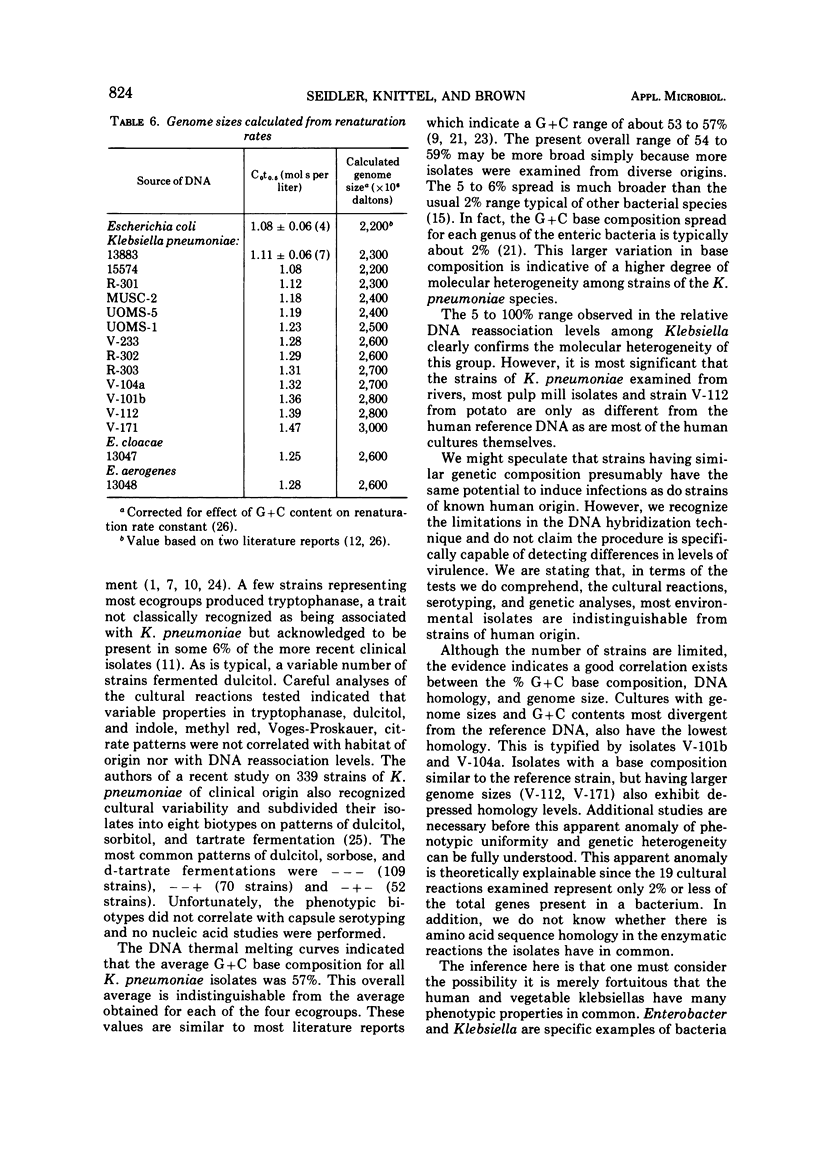
The phenotypic and nucleic acid properties of Klebsiella pneumoniae have been studied on cultures obtained from six different habitats (humans, vegetables, seeds, trees, rivers, and pulp mills). The 19 cultural reactions of 107 isolates varied significantly only in tryptophanase activity and dulcitol fermentation. The percentage of guanine plus cytosine base composition of 41 isolates varied from 53.9 to 59.2%. The range of percentage of guanine plus cytosine base composition for environmental klebsiellas was broader than that for the cultures of human origin. The range of deoxyribonucleic acid relative reassociation (homology) to the human K. pneumoniae reference strain extended from 5% to 100% and the chromosome molecular weights ranged from 2,200 × 106 to 3,000 × 106. The species of K. pneumoniae is thus molecularly more heterogeneous than previously thought and most isolates of human, pulp mill, and river origin are genetically indistinguishable. The presence of K. pneumoniae therefore represents a deterioration of the microbiological quality of the environment and should be considered of public health significance. At the present time the health significance of the molecularly more divergent strains, primarily of vegetable and seed origin, their relationship to klebsiellas of human origin, or to other genera of the Enterobacteriaceae is unclear.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak A. L., Christiansen C., Stenderup A. Bacterial genome sizes determined by DNA renaturation studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):377–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braman S. K., Eberhart R. J., Asbury M. A., Hermann G. J. Capsular types of Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with bovine mastitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1973 Jan 15;162(2):109–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C., Seidler R. J. Potential pathogens in the environment: Klebsiella pneumoniae, a taxonomic and ecological enigma. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):900–904. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.900-904.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CENTIFANTO Y. M., SILVER W. S. LEAF-NODULE SYMBIOSIS. I. ENDOPHYTE OF PSYCHOTRIA BACTERIOPHILA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:776–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.776-781.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Ley J. Reexamination of the association between melting point, buoyant density, and chemical base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):738–754. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.738-754.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan D. W., Razzell W. E. Klebsiella biotypes among coliforms isolated from forest environments and farm produce. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):933–938. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.933-938.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis M., De Ley J., De Cleene M. The determination of molecular weight of bacterial genome DNA from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):143–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill L. R. An index to deoxyribonucleic acid base compositions of bacterial species. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Sep;44(3):419–437. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Ordal E. J. Deoxyribonucleic acid homology in bacterial taxonomy: effect of incubation temperature on reaction specificity. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):893–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.893-900.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R., Neufeld R., Simpson S. Acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) by pulp and paper mill effluents and by Klebsiella isolated from effluents and environmental situations. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):608–613. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.608-613.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHL M. C., WILSON P. W., FIFE M. A., EWING W. H. NITROGEN FIXATION BY MEMBERS OF THE TRIBE KLEBSIELLEAE. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1482–1487. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1482-1487.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez W. J., Colmer A. R. Differentiation of Aerobacter-Klebsiella isolated from sugarcane. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Dec;16(12):1875–1878. doi: 10.1128/am.16.12.1875-1878.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard C. Etude antigénique et biochimique de 500 souches de Klebsiella. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1973;31(4):295–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Mandel M. Quantitative aspects of deoxyribonucleic acid renaturation: base composition, state of chromosome replication, and polynucleotide homologies. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):608–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.608-614.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R., Lee S., Wang W. L., Bennett J. V., Eickhoff T. C. Nosocomial klebsiella infections: intestinal colonization as a reservoir. Ann Intern Med. 1971 May;74(5):657–664. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer B. W., Eickhoff T. C., Kislak J. W., Finland M. The Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia division. Clinical and epidemiologic characteristics. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Dec;65(6):1180–1194. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-6-1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyand D. S., Hayden D. W. Klebsiella infection in muskrats. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1973 Sep 15;163(6):589–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


