Abstract
Spores of Bacillus sp. ATCC 27380 were exposed at intervals to dry-heat temperatures ranging from 125 to 150 C. D-values from 139 to 2.5 h were obtained.
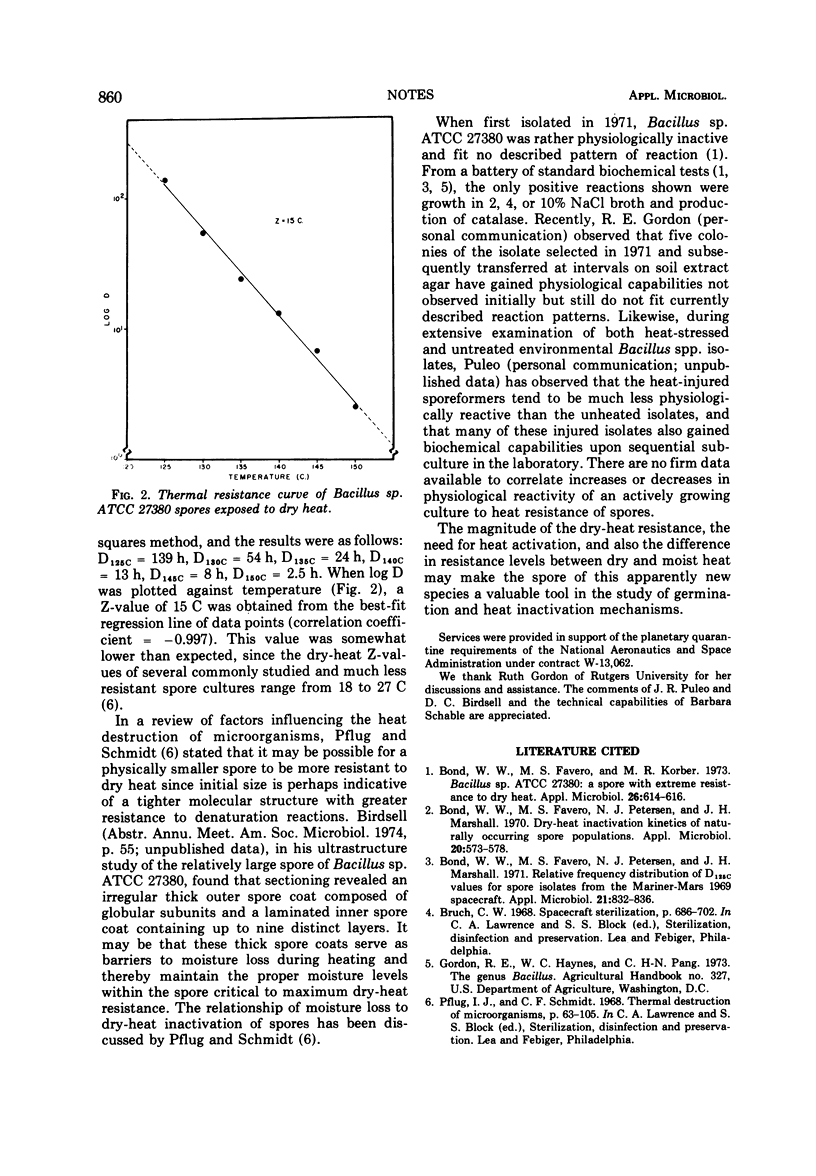
Full text
PDF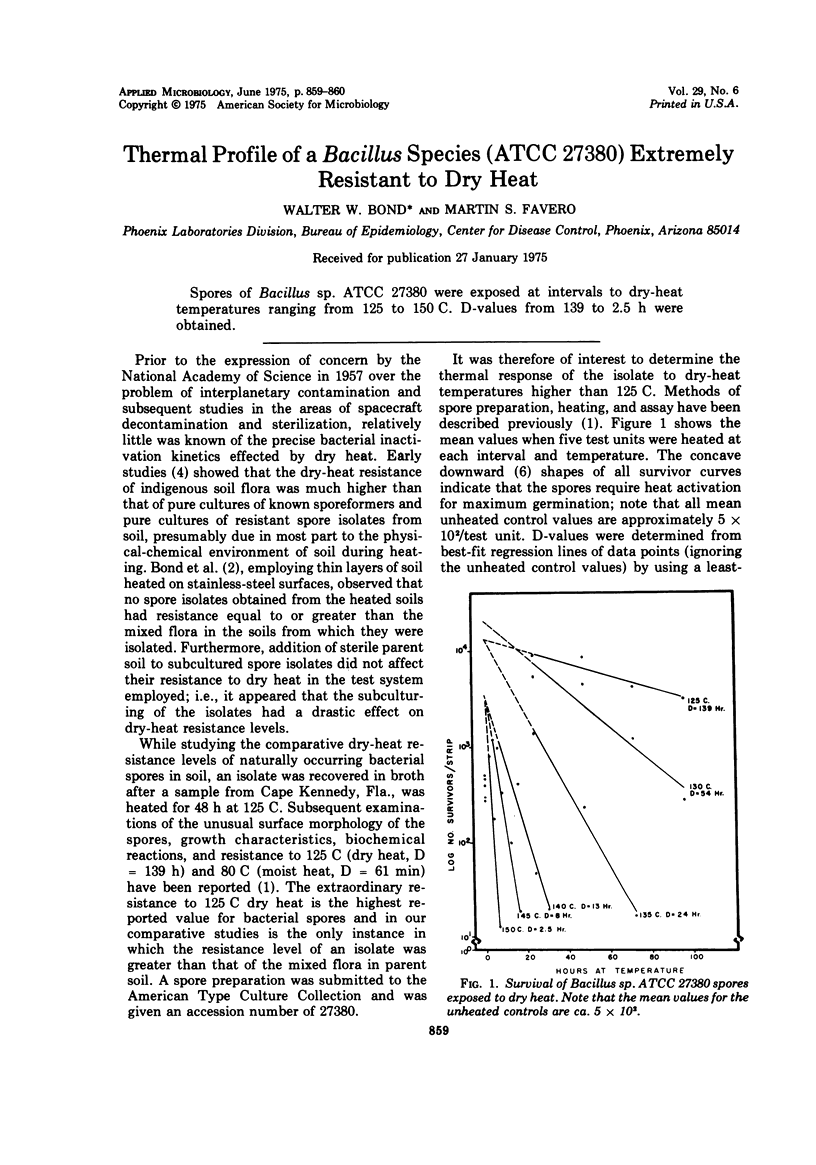
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond W. W., Favero M. S., Korber M. R. Bacillus sp. ATCC 27380: a spore with extreme resistance to dry heat. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):614–616. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.614-616.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond W. W., Favero M. S., Petersen N. J., Marshall J. H. Dry-heat inactivation kinetics of naturally occurring spore populations. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Oct;20(4):573–578. doi: 10.1128/am.20.4.573-578.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond W. W., Favero M. S., Petersen N. J., Marshall J. H. Relative frequency distribution of d(125 C) values for spore isolates from the mariner-Mars 1969 spacecraft. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):832–836. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.832-836.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


