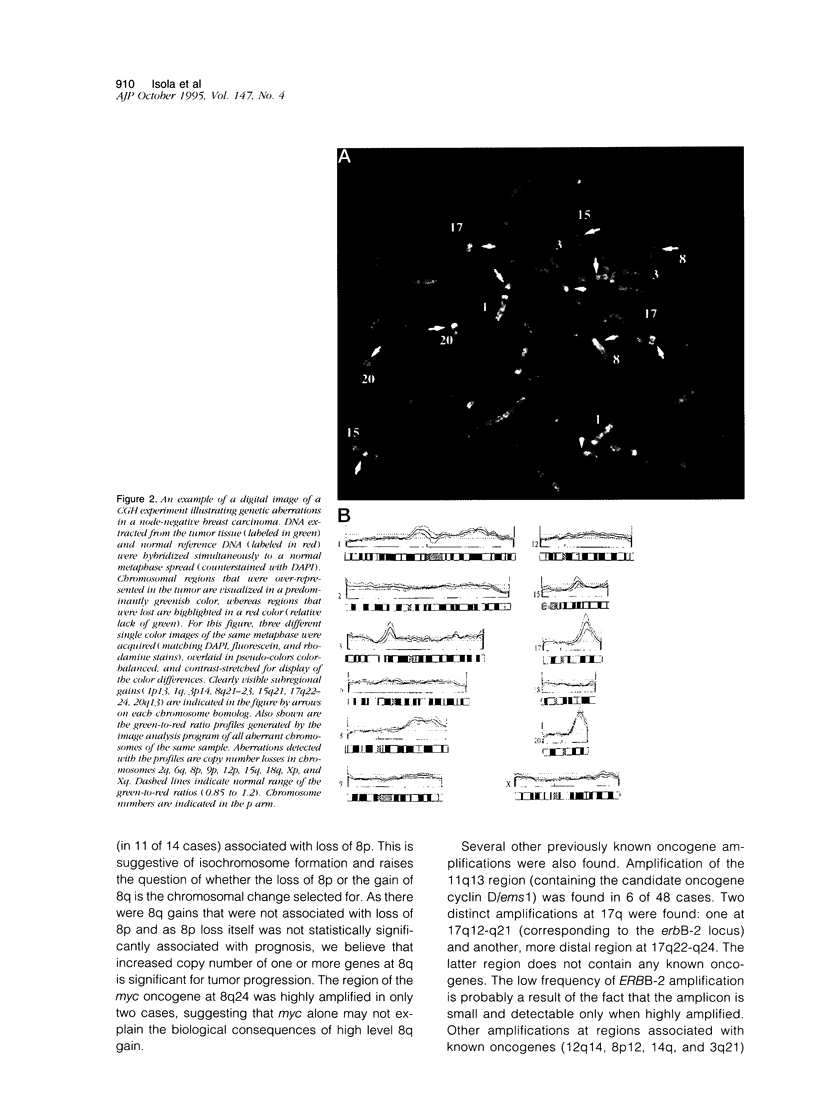
Abstract
Breast cancer progression is determined by a complex pattern of multiple genetic aberrations the association of which with patient prognosis is unknown. In this study, we have undertaken a genome-wide screening to detect genetic changes associated with clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. Comparative genomic hybridization was used to screen for DNA sequence gains and losses across all human chromosomes in 23 tumors from node-negative breast cancer patients with no disease recurrence after at least 5 years of follow-up and in 25 node-negative patients with recurrence during the first 5 years of follow-up. The total number of genetic aberrations (copy number gains and losses) per tumor was significantly greater in the recurrence group (P = 0.019) and in the subgroup of these patients who died as a result of breast cancer (P = 0.0022). When copy number losses and gains were analyzed separately, only losses were significant (P = 0.013 for recurrence and P = 0.002 for overall survival). Of the individual loci involved, a high level gain of the long arm of chromosome 8 was significantly associated with recurrence (P = 0.01, Fisher's exact test). Furthermore, amplification of DNA sequences at chromosome 20q12-13 was found in 7 cases (15%), 6 of which had early recurrence within 32 months of diagnosis. This genome-wide overview by comparative genomic hybridization suggests that genetically advanced node-negative breast cancers having a high overall number of genetic aberrations may have a poor prognosis and that increased copy number of two specific regions, 8q and 20q13, may confer a more aggressive phenotype. Results of this pilot study suggest that determination of the total number of DNA sequence copy number aberrations may help therapeutic decision making. Specific probes should be developed to test the prognostic value of 8q and 20q12-13 amplifications in large numbers of patients.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bièche I., Champème M. H., Matifas F., Hacène K., Callahan R., Lidereau R. Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 7q and aggressive primary breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Jan 18;339(8786):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)90208-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg A., Baldetorp B., Fernö M., Olsson H., Sigurdsson H. c-myc amplification is an independent prognostic factor in postmenopausal breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jul 9;51(5):687–691. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg A., Zhang Q. X., Olsson H., Wenngren E. Chromosome 1 alterations in breast cancer: allelic loss on 1p and 1q is related to lymphogenic metastases and poor prognosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Nov;5(4):311–320. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Cropp C. S., Merlo G. R., Liscia D. S., Cappa A. P., Lidereau R. Somatic mutations and human breast cancer. A status report. Cancer. 1992 Mar 15;69(6 Suppl):1582–1588. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920315)69:6+<1582::aid-cncr2820691313>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelisse C. J., Kuipers-Dijkshoorn N., van Vliet M., Hermans J., Devilee P. Fractional allelic imbalance in human breast cancer increases with tetraploidization and chromosome loss. Int J Cancer. 1992 Feb 20;50(4):544–548. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910500408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isola J., DeVries S., Chu L., Ghazvini S., Waldman F. Analysis of changes in DNA sequence copy number by comparative genomic hybridization in archival paraffin-embedded tumor samples. Am J Pathol. 1994 Dec;145(6):1301–1308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Piper J., Tanner M., Stokke T., Chen L., Smith H. S., Pinkel D., Gray J. W., Waldman F. M. Detection and mapping of amplified DNA sequences in breast cancer by comparative genomic hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2156–2160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Sudar D., Rutovitz D., Gray J. W., Waldman F., Pinkel D. Comparative genomic hybridization for molecular cytogenetic analysis of solid tumors. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):818–821. doi: 10.1126/science.1359641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Kallioniemi A., Piper J., Isola J., Waldman F. M., Gray J. W., Pinkel D. Optimizing comparative genomic hybridization for analysis of DNA sequence copy number changes in solid tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1994 Aug;10(4):231–243. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870100403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., Clark G. M. Prognostic factors and treatment decisions in axillary-node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 25;326(26):1756–1761. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199206253262607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper J., Rutovitz D., Sudar D., Kallioniemi A., Kallioniemi O. P., Waldman F. M., Gray J. W., Pinkel D. Computer image analysis of comparative genomic hybridization. Cytometry. 1995 Jan 1;19(1):10–26. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ried T., Petersen I., Holtgreve-Grez H., Speicher M. R., Schröck E., du Manoir S., Cremer T. Mapping of multiple DNA gains and losses in primary small cell lung carcinomas by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer Res. 1994 Apr 1;54(7):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuuring E., Verhoeven E., van Tinteren H., Peterse J. L., Nunnink B., Thunnissen F. B., Devilee P., Cornelisse C. J., van de Vijver M. J., Mooi W. J. Amplification of genes within the chromosome 11q13 region is indicative of poor prognosis in patients with operable breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992 Oct 1;52(19):5229–5234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Godolphin W., Jones L. A., Holt J. A., Wong S. G., Keith D. E., Levin W. J., Stuart S. G., Udove J., Ullrich A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):707–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2470152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafrani B., Gerbault-Seureau M., Mosseri V., Dutrillaux B. Cytogenetic study of breast cancer: clinicopathologic significance of homogeneously staining regions in 84 patients. Hum Pathol. 1992 May;23(5):542–547. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90131-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]