Abstract
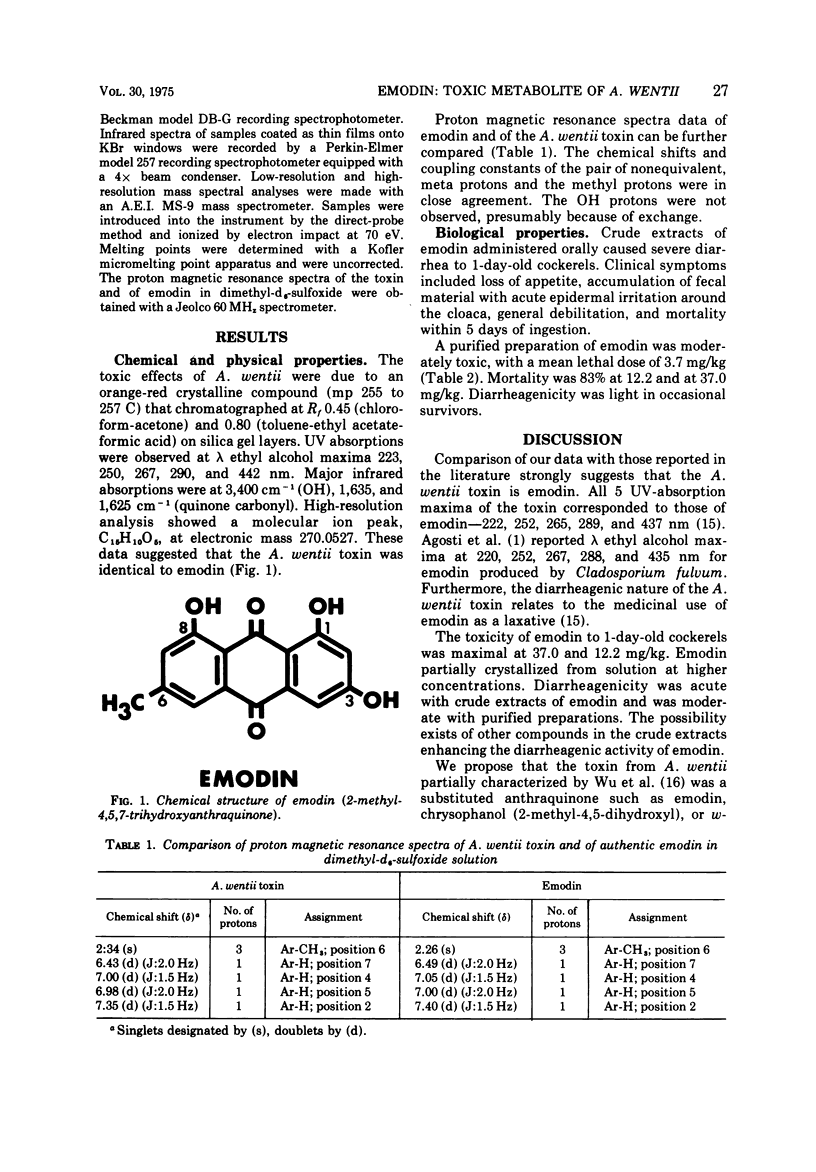
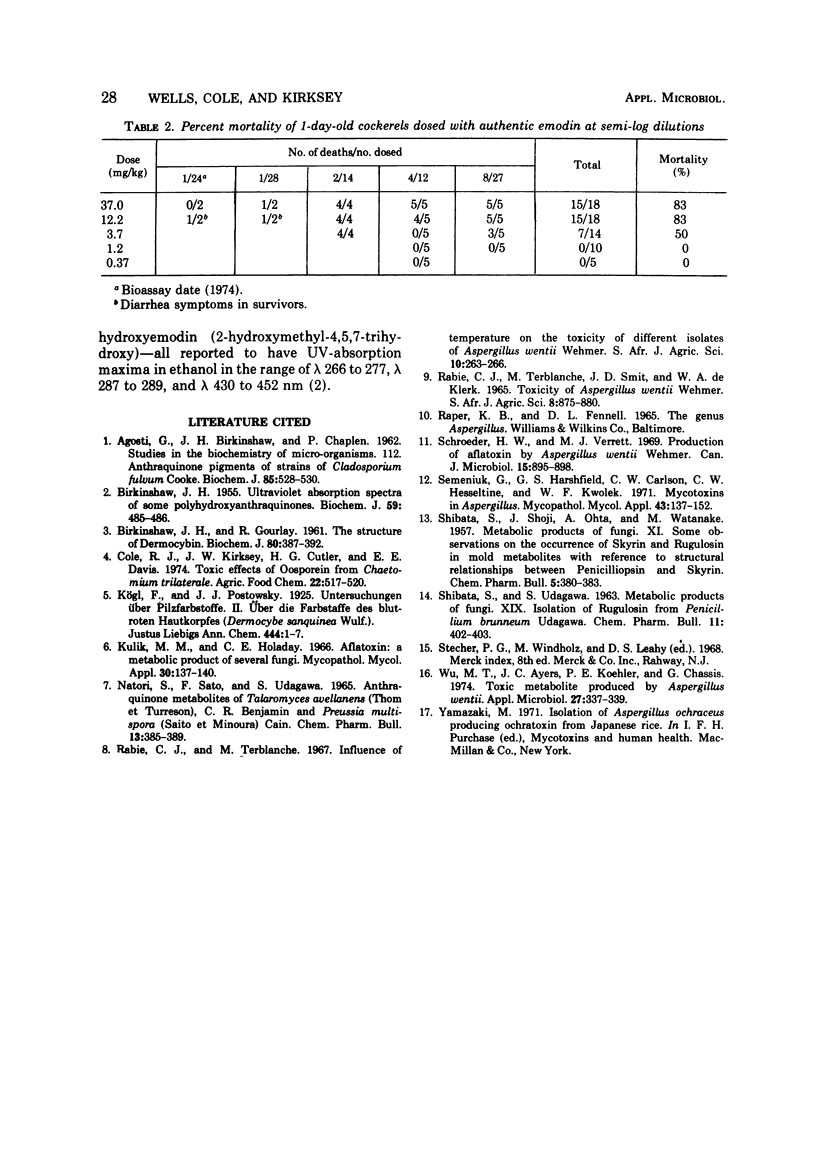
A diarrheagenic toxin from culture extracts of Aspergillus wentii Wehmer isolated from weevil-damaged Chinese chestnuts was identified as emodin (2-methyl-4,5,7-trihydroxyanthraquinone). The orange-red, crystalline toxin (mp 255 to 257 C) showed ultraviolet absorption maxima in ethyl alcohol at 223, 250, 267, 290, and 442 nm, and infrared absorption maxima at 3,400 cm-1 (OH), 1,635, and 1,625 cm-1. Chemical shifts and coupling constants of the proton magnetic resonance spectra of the A. wentii toxin and of authentic emodin agreed. Mean lethal dose of emodin orally administered to 1 day old DeKalb cockerels was 3.7 mg/kg.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOSTI G., BIRKINSHAW J. H., CHAPLEN P. Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms. 112. Anthraquinone pigments of strains of Cladosporium fulvum Cooke. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:528–530. doi: 10.1042/bj0850528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKINSHAW J. H. Ultraviolet absorption spectra of some polyhydroxyanthraquinones. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):485–486. doi: 10.1042/bj0590485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkinshaw J. H., Gourlay R. The structure of dermocybin. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80(2):387–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0800387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. J., Kirksey J. W., Cutler H. G., Davis E. E. Toxic effects of oosporein from Chaetomium trilaterale. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 May-Jun;22(3):517–520. doi: 10.1021/jf60193a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulik M. M., Holaday C. E. Aflatoxin: a metabolic product of several fungi. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1966 Nov 10;30(2):137–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02130360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATORI S., SATO F., UDAGAWA S. ANTHRAQUINONE METABOLITES OF TALAROMYCES AVELLANEUS (THOM ET TURRESON) C. R. BENJAMIN AND PREUSSIA MULTISPORA (SAITO ET MINOURA) CAIN. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1965 Mar;13:385–386. doi: 10.1248/cpb.13.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIBATA S., SHOJI J., OHTA A., WATANABE M. Metabolic products of fungi. XI. Some observation on the occurrence of skyrin and rugulosin in mold metabolites, with a reference to structural relationship between penicilliopsin and skyrin. Pharm Bull. 1957 Aug;5(4):380–382. doi: 10.1248/cpb1953.5.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Verrett M. J. Production of aflatoxin by Aspergillus wentii Wehmer. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Aug;15(8):895–898. doi: 10.1139/m69-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semeniuk G., Harshfield G. S., Carlson C. W., Hesseltine C. W., Kwolek W. F. Mycotoxins in Aspergillus. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1971 Feb 19;43(2):137–152. doi: 10.1007/BF02051714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M. T., Ayres J. C., Koehler P. E., Chassis G. Toxic metabolite produced by Aspergillus wentii. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):337–339. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.337-339.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


