Abstract
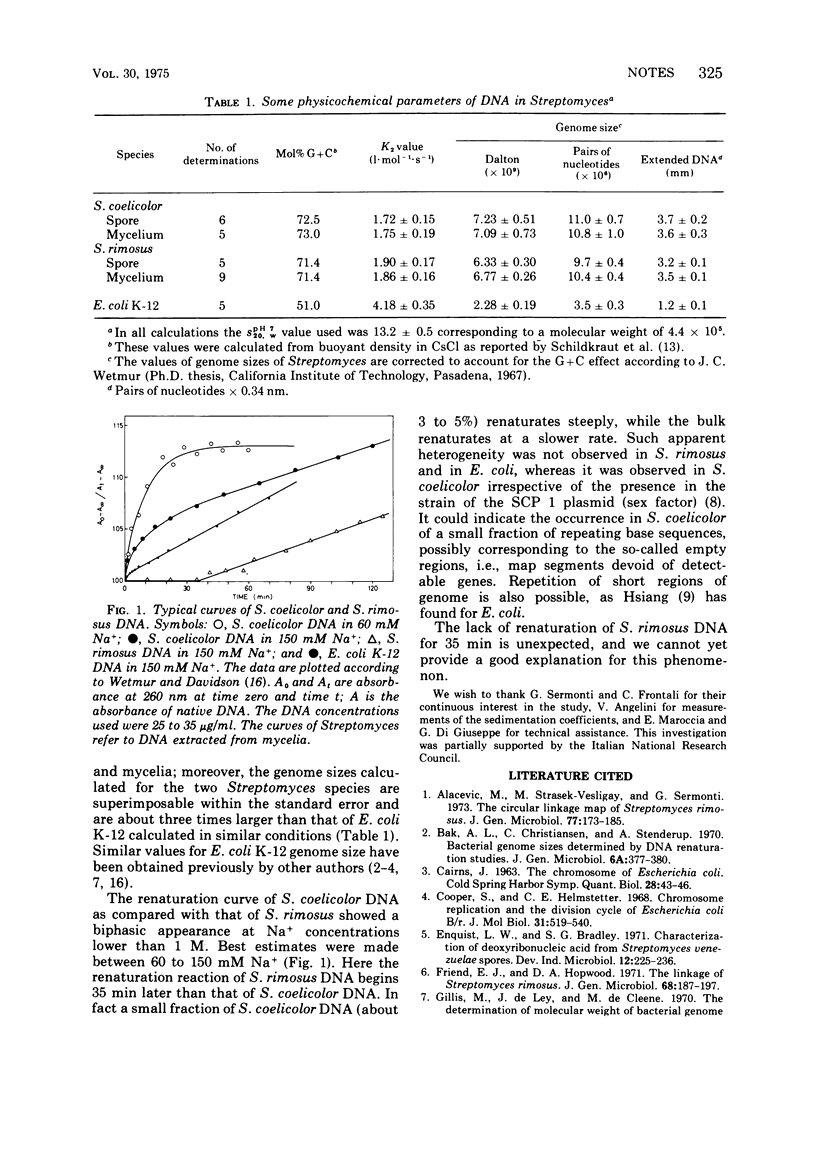
The genome sizes of Streptomyces coelicolor and Streptomyces rimosus as calculated by deoxyribonucleic acid reassociation kinetics are approximately 10.5 × 106 nucleotide pairs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bak A. L., Christiansen C., Stenderup A. Bacterial genome sizes determined by DNA renaturation studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):377–380. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Helmstetter C. E. Chromosome replication and the division cycle of Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend E. J., Hopwood D. A. The linkage map of Streptomyces rimosus. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Oct;68(2):187–197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-68-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis M., De Ley J., De Cleene M. The determination of molecular weight of bacterial genome DNA from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):143–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Chater K. F., Dowding J. E., Vivian A. Advances in Streptomyces coelicolor genetics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):371–405. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.371-405.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J. Isolation of a short, cytosine-rich repeating unit from the DNA of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 27;349(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson A. M., Bradley S. G., Enquist L. W., Cruces G. Genetic homologies among Streptomyces violaceoruber strains. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):702–706. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.702-706.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewfik E. M., Bradley S. G. Characterization of deoxyribonucleic acids from streptomycetes and nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1994–2000. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1994-2000.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Davidson N. Kinetics of renaturation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):349–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


