Abstract
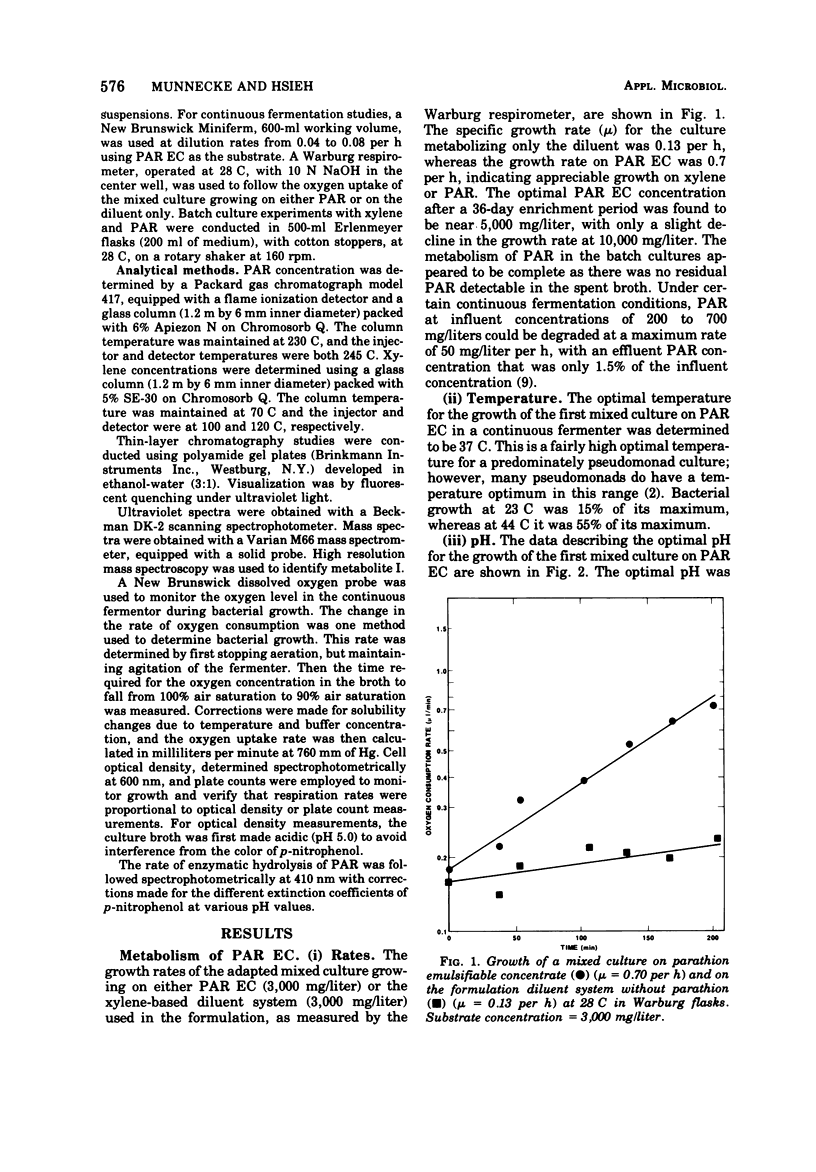
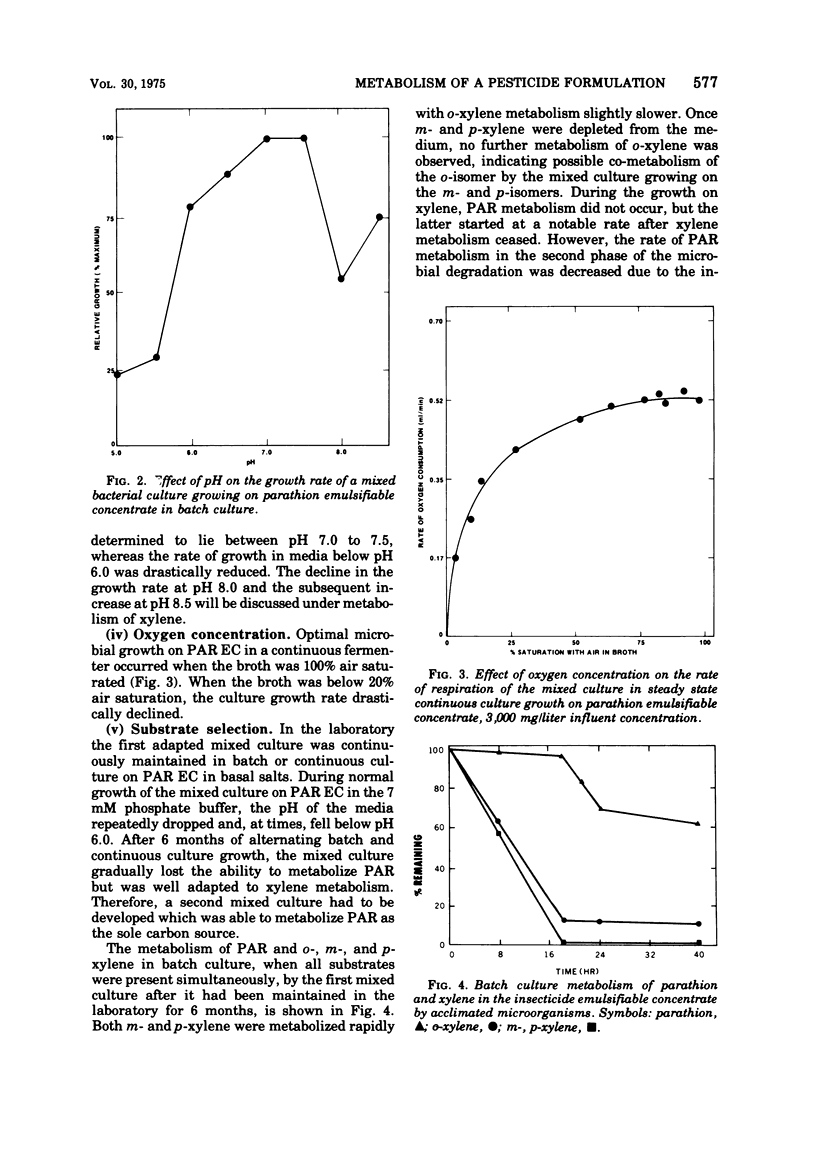
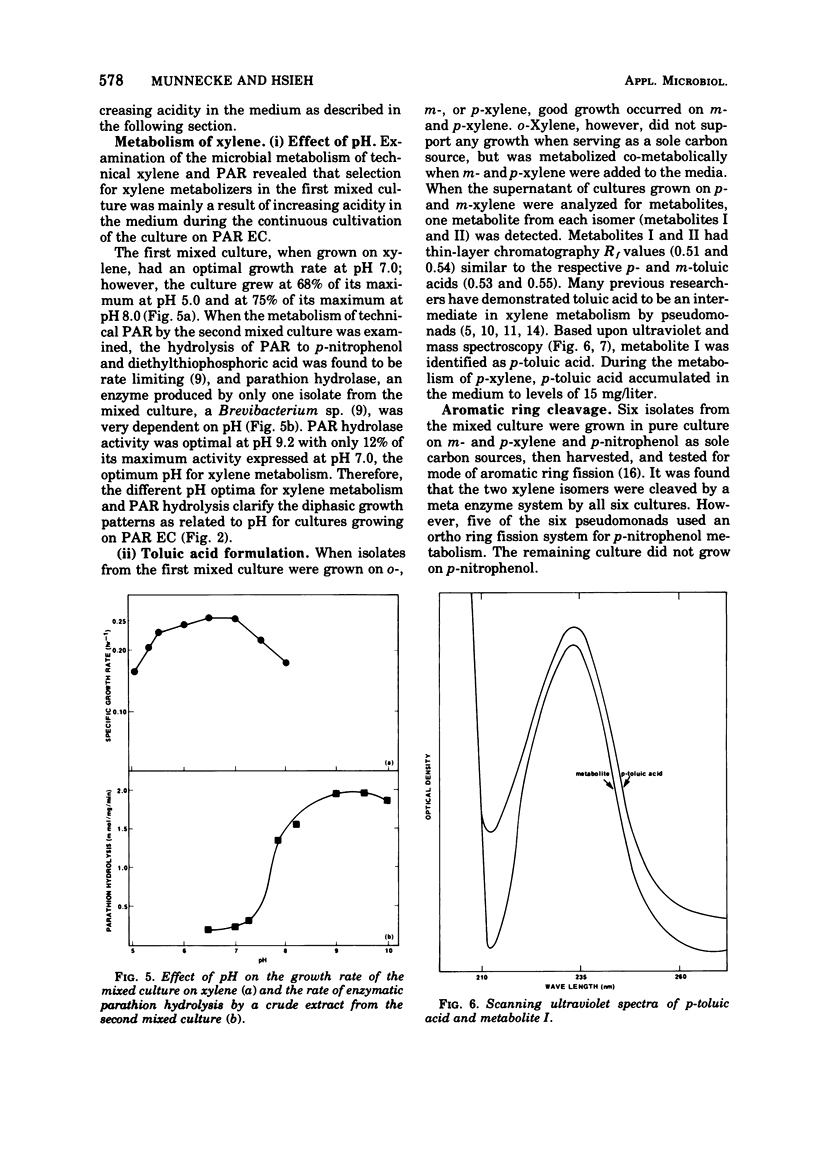
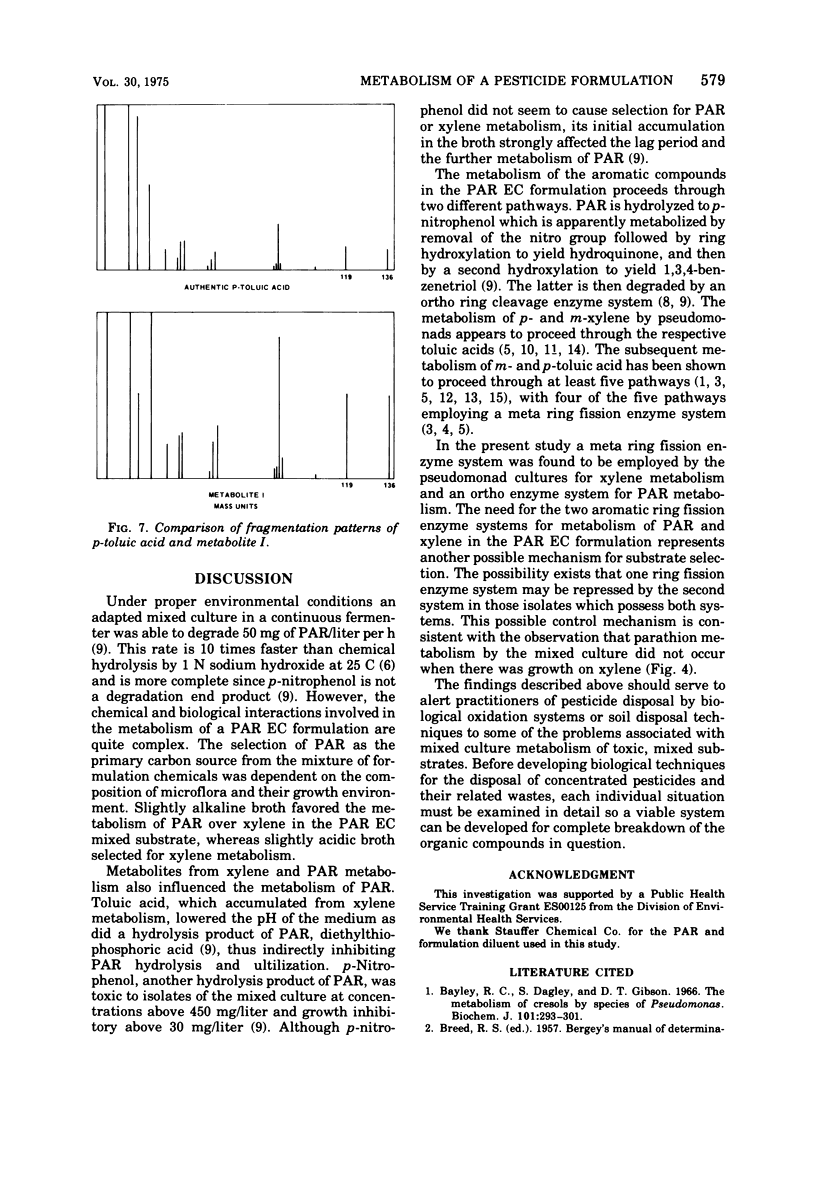
A mixed bacterial culture was adapted to growth on a mixed carbon substrate consisting of the pesticide parathion and its xylene-based formulation. The environmental growth parameters of temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen concentration were optimized to obtain complete metabolism of parathion from this mixed carbon substrate. This adapted culture grew rapidly (μ = 0.7 per h) on the pesticide formulation at high parathion suspensions (3,000 mg/liter). Carbon utilization from this mixed substrate was strongly dependent on pH. At slightly acidic pH, xylene was preferentially metabolized, whereas at slightly alkaline pH, parathion was preferentially metabolized. Diethylthiophosphoric acid, a metabolite from parathion, and toluic acid, a metabolite from xylene, also influenced the selection of the primary carbon source.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S., Gibson D. T. The metabolism of cresols by species of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):293–301. doi: 10.1042/bj1010293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAGLEY S., GIBSON D. T. THE BACTERIAL DEGRADATION OF CATECHOL. Biochem J. 1965 May;95:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0950466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagley S., Geary P. J., Wood J. M. The metabolism of protocatechuate by Pseudomonas testosteroni. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):559–568. doi: 10.1042/bj1090559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. S., Hossler F. E., Stone R. W. Metabolism of p- and m-xylene by species of Pseudomonas. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Sep;14(9):1005–1009. doi: 10.1139/m68-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M., Hsieh D. P. Microbial decontamination of parathion and p-nitrophenol in aqueous media. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.212-217.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N. The conversion of catechol and protocatechuate to beta-ketoadipate by Pseudomonas putida. IV. Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 25;241(16):3800–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond R. L., Jamison V. W., Hudson J. O. Microbial hydrocarbon co-oxidation. I. Oxidation of mono- and dicyclic hydrocarbons by soil isolates of the genus Nocardia. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):857–865. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.857-865.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Murray K. The physiologic significance of the two divergent metabolic steps in the meta cleavage of catechols by Pseudomonas putida N.C.I.B. 10105. Biochem J. 1971 Sep;124(2):20P–21P. doi: 10.1042/bj1240020p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


