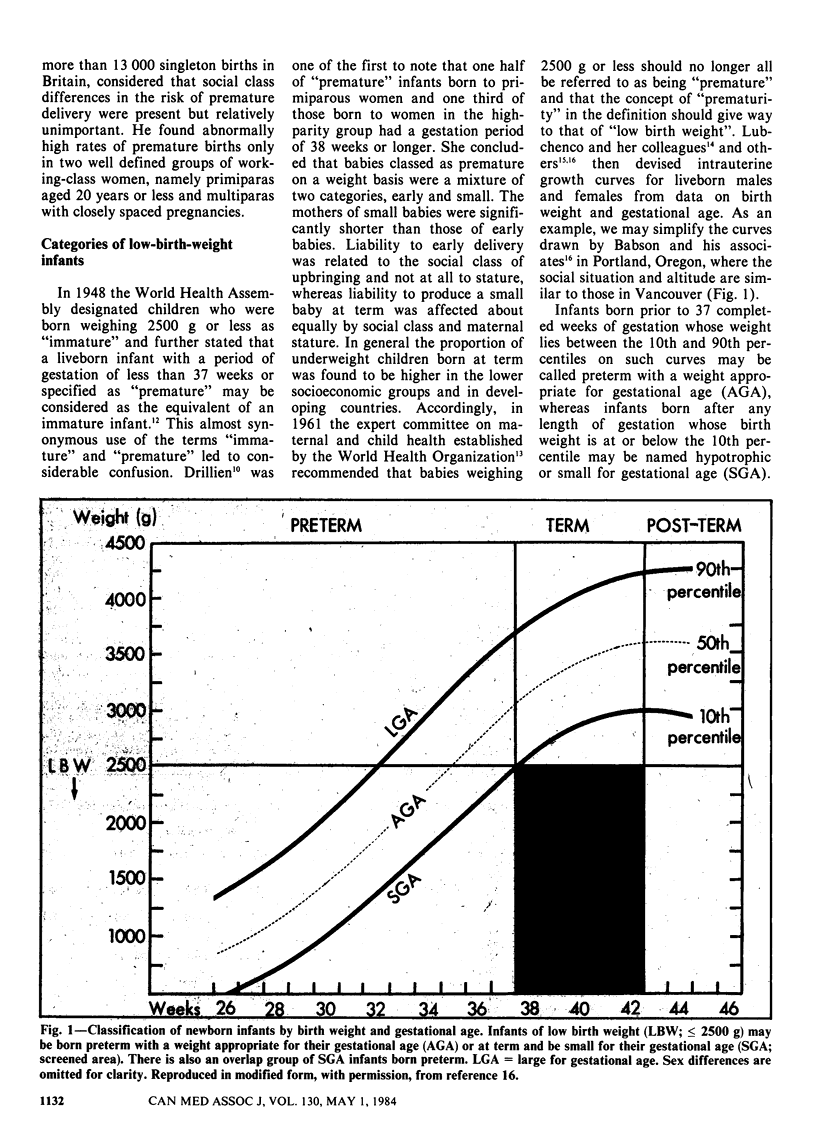
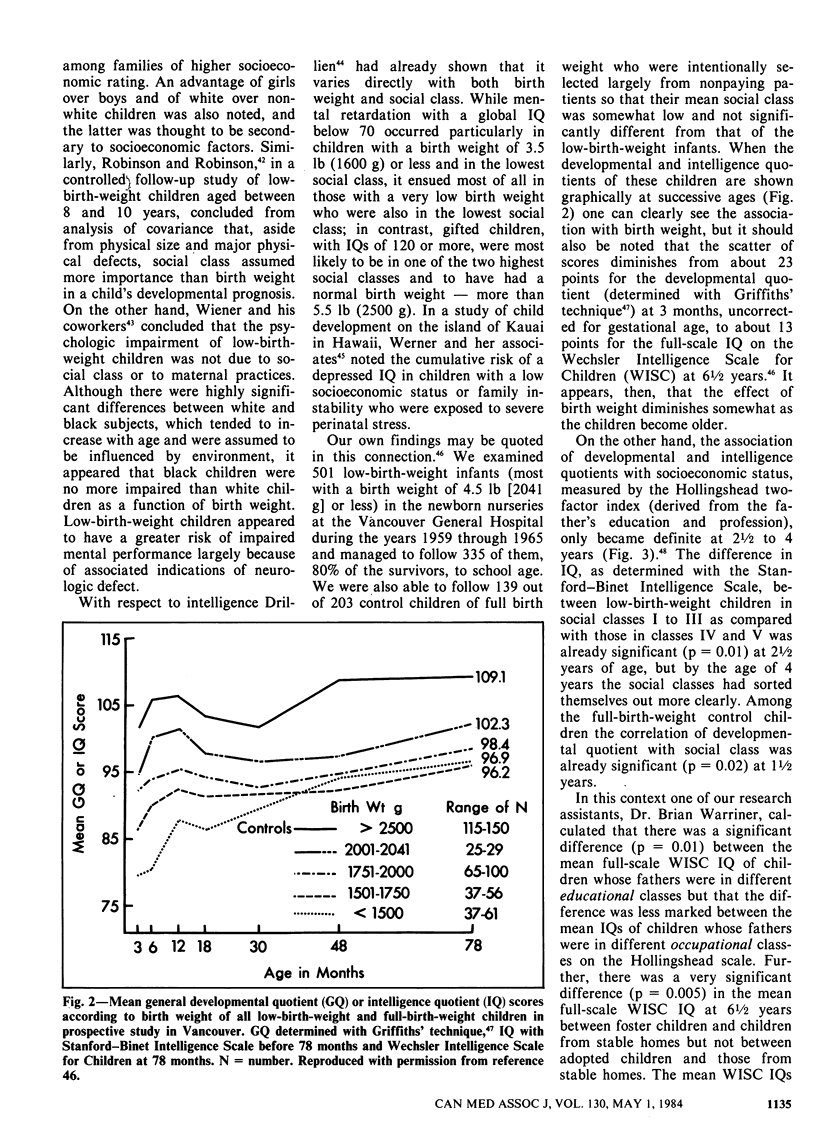
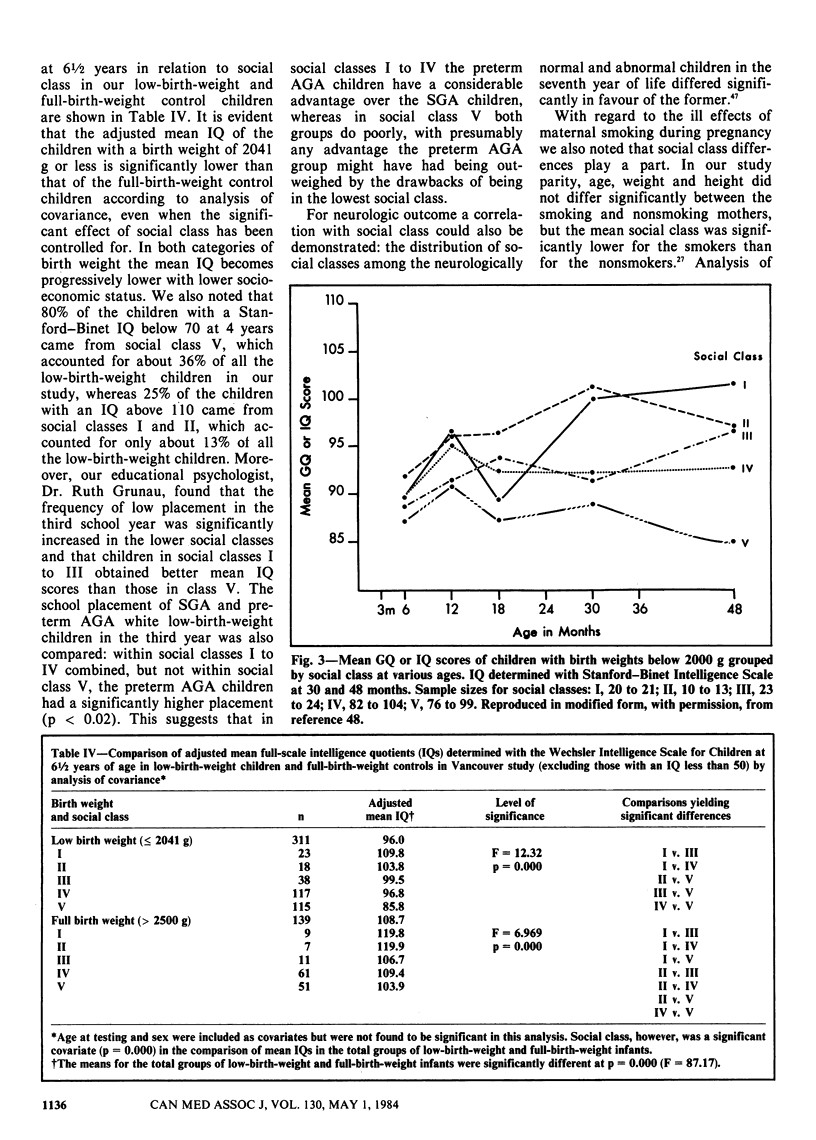
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babson S. G., Behrman R. E., Lessel R. Fetal growth. Liveborn birth weights for gestational age of white middle class infants. Pediatrics. 1970 Jun;45(6):937–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerre I., Värendh G. A study of some biological and socio-economic factors in low birth weight. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1975 Jul;64(4):605–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1975.tb03890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler N. R., Goldstein H. Smoking in pregnancy and subsequent child development. Br Med J. 1973 Dec 8;4(5892):573–575. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5892.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAMAN A. D., BELL H. M. PREGNANCY IN THE VERY YOUNG TEEN-AGER. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1964 Oct 1;90:350–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANN M., LEVINE S. Z., NEW E. V. The development of prematurely born children with birth weights or minimal postnatal weights of 1,000 grams or less. Pediatrics. 1958 Dec;22(6):1037–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS J. W. B. Some factors associated with prematurity; the results of a National Survey. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1950 Apr;57(2):143–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1950.tb05225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRILLIEN C. M. The social and economic factors affecting the incidence of premature birth. I. Premature births without complications of pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1957 Apr;64(2):161–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1957.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowding V. M. New assessment of the effects of birth order and socioeconomic status on birth weight. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 28;282(6265):683–686. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6265.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duenhoelter J. H., Jimenez J. M., Baumann G. Pregnancy performance of patients under fifteen years of age. Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Jul;46(1):49–52. doi: 10.1097/00006250-197507000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn H. G., Crichton J. U., Grunau R. V., McBurney A. K., McCormick A. Q., Robertson A. M., Schulzer M. Neurological, psychological and educational sequelae of low birth weight. Brain Dev. 1980;2(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(80)80008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn H. G., McBurney A. K., Ingram S., Hunter C. M. Maternal cigarette smoking during pregnancy and the child's subsequent development: I. Physical growth to the age of 6 1/2 years. Can J Public Health. 1976 Nov-Dec;67(6):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn H. G., McBurney A. K., Sandraingram, Hunter C. M. Maternal cigarette smoking during pregnancy and the child's subsequent development: II. Neurological and intellectual maturation to the age of 6 1/2 years. Can J Public Health. 1977 Jan-Feb;68(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaves L. C., Nuttall J. C., Klonoff H., Dunn H. G. Developmental and psychological test scores in children of low birth weight. Pediatrics. 1970 Jan;45(1):9–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedrick J., Adelstein P. Factors associated with low birth weight of infants delivered at term. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1978 Jan;85(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1978.tb15816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedrick J., Anderson A. B. Factors associated with spontaneous pre-term birth. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1976 May;83(5):342–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1976.tb00840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry P. C. On growing new neurons: are early intervention programs effective. Pediatrics. 1981 Jan;67(1):38–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREWAR D. A., MEDOVY H., WYLIE K. O. The fate of the expremature--prognosis of prematurity. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Jun 2;86:1008–1013. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenwald P., Funakawa H., Mitani S., Nishimura T., Takeuchi S. Influence of environmental factors on foetal growth in man. Lancet. 1967 May 13;1(7498):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer B., Wallach L. A., Rosen S. L. Birth-weight-standardized neonatal mortality rates and the prevention of low birth weight: how does Massachusetts compare with Sweden? N Engl J Med. 1982 May 20;306(20):1230–1233. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205203062011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins R., Finkelstein N. W., Stedman D. J. Infant-stimulation programs and their effects. Pediatr Ann. 1978 Feb;7(2):123–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks C. H. Delivery patterns and reproductive efficiency among groups of differing socioeconomic status and ethnic origins. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1967 Mar 1;97(5):608–624. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(67)90449-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth D. R., Kreutner A. K. Sounding board. Teenage pregnancy: solutions are evolving. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 28;303(9):516–518. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008283030910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illsley R. Preventive medicine in the perinatal period. Early prediction of perinatal risk. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Mar;59(3):181–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOBLOCH H., PASAMANICK B. Environmental factors affecting human development, before and after birth. Pediatrics. 1960 Aug;26:210–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBCHENCO L. O., HANSMAN C., DRESSLER M., BOYD E. INTRAUTERINE GROWTH AS ESTIMATED FROM LIVEBORN BIRTH-WEIGHT DATA AT 24 TO 42 WEEKS OF GESTATION. Pediatrics. 1963 Nov;32:793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Gartner L. M., Paneth N., Tyler L. Recent trends in neonatal mortality: the Canadian experience. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Feb 15;126(4):373–376. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEDOVY H., BRIGGS J. N. Reduction in neonatal mortality; the present and the future. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1958 May;:259–277. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)30648-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkatz I. R., Johnson K. G. Regionalization of perinatal care for the United States. Clin Perinatol. 1976 Sep;3(2):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. C., Hassanein K., Chin T. D., Hensleigh P. Socioeconomic factors in relation to fetal growth in white infants. J Pediatr. 1976 Oct;89(4):638–643. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor A. F., Myrianthopoulos N. C. The relation of ethnic and selected socio-economic factors to human birth-weight. Ann Hum Genet. 1967 Aug;31(1):71–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ounsted M., Ounsted C. Rate of intra-uterine growth. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):599–600. doi: 10.1038/220599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ounsted M., Scott A. Social class and birthweight: a new look. Early Hum Dev. 1982 Jan;6(1):83–89. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(82)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petros-Barvazian A., Béhar M. Low birth weight--what should be done to deal with this global problem. WHO Chron. 1978 Jun;32(6):231–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON N. M., ROBINSON H. B. A FOLLOW-UP STUDY OF CHILDREN OF LOW BIRTH WEIGHT AND CONTROL CHILDREN AT SCHOOL AGE. Pediatrics. 1965 Mar;35:425–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. G. Risk registers and early detection of handicaps. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1968 Oct;10(5):651–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1968.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. W., Turshen M. Fetal nutrition. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(6):785–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarr-Salapatek S., Williams M. L. The effects of early stimulation on low-birth-weight infants. Child Dev. 1973 Mar;44(1):94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher R., McLean F. Intrauterine growth of live-born Caucasian infants at sea level: standards obtained from measurements in 7 dimensions of infants born between 25 and 44 weeks of gestation. J Pediatr. 1969 Jun;74(6):901–910. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON DER AHE C. V., BACH J. L. Pregnancy in young girls. West J Surg Obstet Gynecol. 1951 May;59(5):235–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace H. M. Selected aspects of perinatal casualties. Looking ahead nationally. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1979 Apr;18(4):213–223. doi: 10.1177/000992287901800404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner E., Simonian K., Bierman J. M., French F. E. Cumulative effect of perinatal complications and deprived environment on physical, intellectual, and social development of preschool children. Pediatrics. 1967 Apr;39(4):490–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werry J. S. Studies on the hyperactive child. IV. An empirical analysis of the minimal brain dysfunction syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1968 Jul;19(1):9–16. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1968.01740070011002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener G., Rider R. V., Oppel W. C., Harper P. A. Correlates of low birth weight. Psychological status at eight to ten years of age. Pediatr Res. 1968 Mar;2(2):110–118. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196803000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


