Abstract
Inositol phosphates and the enzymes that interconvert them are key regulators of diverse cellular processes including the transcriptional machinery of arginine synthesis [York (2006) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1761, 552–559]. Despite considerable interest and debate surrounding the role of Saccharomyces cerevisiae inositol polyphosphate kinase (ScIPK2, ARG82, ARGRIII) and its inositol polyphosphate products in these processes, there is an absence of data describing how the transcripts of the arginine synthetic pathway, and the amino acid content of ScIpk2Δ, are altered under different nutrient regimes. We have cloned an IPMK (inositol phosphate multikinase) from Solanum tuberosum, StIPMK (GenBank® accession number EF362785), that despite considerable sequence divergence from ScIPK2, restores the arginine biosynthesis pathway transcripts ARG8, acetylornithine aminotransferase, and ARG3, ornithine carbamoyltransferase of ScIpk2Δ yeast to wild-type profiles. StIPMK also restores the amino acid profiles of mutant yeast to wild-type, and does so with ornithine or arginine as the sole nitrogen sources. Our data reveal a lysine accumulation phenotype in ScIpk2Δ yeast that is restored to a wild-type profile by expression of StIPMK, including restoration of the transcript profiles of lysine biosynthetic genes. The StIPMK protein shows only 18.6% identity with ScIPK2p which probably indicates that the rescue of transcript and diverse amino acid phenotypes is not mediated through a direct interaction of StIPMK with the ArgR–Mcm1 transcription factor complex that is a molecular partner of ScIPK2p.
Keywords: arginine, inositol phosphate multikinase (IPMK), lysine, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Solanum tuberosum
Abbreviations: ARG3, ornithine carbamoyltransferase; ARG8, acetylornithine aminotransferase; GLD3, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IPMK, inositol phosphate multikinase; LYS1, saccharopine dehydrogenase; LYS2, α-aminoadipate reductase; LYS5, phosphopantetheinyl transferase; LYS9, saccharopine dehydrogenase; LYS20, homocitrate synthase isozyme; OPA, ortho-phthaldialdehyde; RT, reverse transcriptase; SD-U, synthetic defined medium lacking uracil; YPD medium, 1% yeast extract, 2% Bacto™ peptone and 2% dextrose;
INTRODUCTION
Much has been reported about members of the IPMK (inositol phosphate multikinase) family from mammals, yeast and plants (for a review see [1]). The catalytic flexibility of these enzymes makes them ideal candidates for regulating the levels of inositol phosphates involved in various signalling events, metabolic pathways and cellular processes. Indeed the role of multikinases in inositol hexakisphosphate biosynthesis in plants [2], the regulation of mRNA export from the nucleus in yeast [3,4], and their contribution to arginine biosynthesis in yeast [5–11], are a few examples of their biological importance.
The yeast inositol phosphate multikinase, ScIPK2 (also known as ARG82, ARGRIII), acts in association with the ArgR–Mcm1 transcription factor complex to regulate arginine biosynthesis. The ARG80p and ARG81p components of the complex bind to arginine boxes in the promoters of arginine biosynthetic and catabolic genes, and ScIPK2p stabilizes this complex [5]. Other studies indicate that the kinase activity of ScIPK2p is necessary [12], while more recent work [13] indicates that Ins(1,4,5)P3 6-kinase activity is sufficient to rescue a growth phenotype of ScIpk2Δ yeast. Remarkably, and not withstanding that the different groups have established loss or gain of arginine biosynthetic competence using a range of different growth and phenotypic assays, only the study of Dubois and Messenguy [8] has directly addressed the arginine content of yeast cells, and among recent studies of IPMKs only that of Resnick et al. [14] has examined the levels of transcripts, and only then of ARG8 (acetylornithine aminotransferase).
We have taken the approach of looking directly at the amino acids present in wild-type and ScIpk2Δ mutant strains, and have attempted to complement the ScIpk2Δ mutant strain phenotype by introducing an IPMK, StIPMK, cloned by ourselves from Solanum tuberosum (StIPMK GenBank® accession number EF362785). Moreover, by parallel analysis of transcripts in the yeast samples from which we have analysed amino acids, we have demonstrated that transformation with StIPMK restores arginine metabolic gene transcript levels of the ScIpk2Δ mutant to wild-type profiles.
In the present study, we report the cloning of StIPMK; an inositol polyphosphate kinase from potato (Desirée cv.). StIPMK recombinant protein exhibits a range of catalytic abilities. By way of sequence comparison at the amino acid level with other multikinases and by rescue of inositol phosphate synthesis in the ScIpk2Δ mutant strain, we demonstrate that StIPMK is a canonical member of the multikinase family, and that, despite its considerable dissimilarity to ScIPK2, it also alleviates a lysine overproduction phenotype of ScIpk2Δ.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Oligonucleotide primers were obtained from Sigma–Genosys. Chemicals were obtained from Sigma or Fisher Scientific. Restriction enzymes were obtained from Invitrogen, Roche, New England Biolabs or Promega, whereas bacterial and yeast strains were obtained from Novagen and EUROSCARF (EUROpean Saccharomyces Cerevisiae ARchive for Functional analysis) respectively.
Cloning StIPMK
The StIPMK cDNA sequence was identified by BLAST-searching the Solanum Genomic Network EST database (http://www.sgn.cornell.edu) with the sequence of Arabidopsis multikinase AtIPK2β [15]. StIPMK cDNA was isolated from whole potato cDNA using the following primers: forward, 5′-CTTTGTGTGTCGGGGACTTT-3′; reverse, 5′-TATCAGAGGCGGTATGGCTC-3′. The cDNA was cloned into the vector pGEX-4T-2 (Pfizer) which encodes an N-terminal glutathione S-transferase tag. This was achieved using mutagenic primers to replace the ATG start codon of StIPMK with an EcoR1 restriction site and the TAA stop codon with a Xho1 restriction site; inserting the StIPMK cDNA in-frame into the multiple cloning site of the vector. The primers used to achieve the mutagenesis were as follows: forward, 5′-TCACTTTCTGTGAGAATTCTTAAGGTTCCTC-3′; reverse, 5′-ACGTCTCGAGTTATTCAGAGGCGGTATGGCTC-3′.
HPLC separation of inositol phosphates
Inositol polyphosphates were resolved by HPLC on a 25 cm Partisphere SAX (Strong Anion Exchange) column (Whatman) eluted at a flow rate of 1 ml/min with a gradient derived from buffer reservoirs containing A (water) and B [1.25 M (NH4)2HPO4 (pH 3.8), H3PO4] mixed as follows: 0 min, 0% B; 5 min, 0% B; 65 min, 100% B; 75 min, 100% B. A [3H]InsP6 standard (740 MBq/mmol) obtained from DuPont/NEN was included during analysis of yeast inositol phosphates. Radioactivity was determined on-line with a Canberra Packard A510 Radiochemical Flo-Detector fitted with a 0.5 ml flow-cell, either by Cerenkov counting or for 3H analysis by admixture of Flo-Scint AP (Canberra Packard) scintillation cocktail. Radioactivity was estimated with an integration interval of 12 s.
Yeast growth media
Rich medium (YPD) contained: 1% yeast extract (Duchefa Biochemie), 2% Bacto™ peptone (BD Biosciences Clontech) and 2% dextrose prepared at pH 6.5. For solid medium, micro agar (Duchefa Biochemie) was added at 20 g per litre of liquid medium. Synthetic defined medium lacking uracil (SD-U) contained: 37 g of minimal SD Base with dextrose and 0.77 g of uracil drop out supplement (Clontech) adjusted to pH 5.8 in a 1 litre volume. For solid medium, 46.7 g of Minimal SD Agar Base was used with 0.77 g of uracil drop out supplement. Minimal medium lacking inositol for labelling experiments was prepared from stock solutions of macronutrients, trace elements and vitamins. A 5× stock of macronutrients (1 litre) was prepared with 5 g of KH2PO4, 2.5 g of MgSO4·7H2O, 2.5 g of NaCl and 1.67 g of CaCl2·6H2O. A 100× stock (1 litre) of trace elements was prepared with 50 mg of H3BO3, 40 mg of ZnSO4·7H2O, 20 mg of FeCl3·6H2O, 20 mg of NaMnO4·2H2O, 10 mg of KI and 4 mg of CuSO4·5H2O. A 500× stock (1 litre) of vitamins was prepared with 1 g of calcium pantothenate, 200 mg of niacin, 200 mg of pyridoxine/HCl, 200 mg of thiamine/HCl, 200 mg of p-aminobenzoic acid, 100 mg of riboflavin, 10 mg of biotin and 1 mg of folic acid. The pH was adjusted to 7.0. Minimal medium (1 litre) was made combining the following: 4 g of galactose, 3.5 g of ammonium sulfate, 1.5 g of asparagine, 200 ml of macronutrient stock, 10 ml of trace element stock and 2 ml of the 500× vitamin stock, at a final pH of 5.7. Minimal medium containing ornithine/arginine was made as above, but ammonium sulfate and asparagine were omitted. Ornithine or arginine was added to a final concentration of 3 mg/ml, and inositol was added at 1 mg/ml.
S. cerevisiae strains and transformation
The yeast strains YDR173c (accession number: Y03531, genotype: BY4741; Mat a; his3Δ1; leu2Δ0; met15Δ0; ura3Δ0; YDR173c::kanMX4) and Y0000 (wild-type) were obtained from EUROSCARF. A 10 ml YPD overnight culture of YDR173c was grown from a single plated (YPD) colony at 30 °C with shaking at 3.8 Hz. A 3 ml aliquot was sub-cultured into 30 ml of YPD and grown to a cell density of approx. 0.5–1×107 cells/ml. Yeast were transformed according to [16], and 100 μl aliquots of transformed cells were plated on solid SD-U medium with 50 μg/ml G418 antibiotic selection.
RNA isolation from S. cerevisiae and cDNA synthesis
RNA was extracted using Trizol (Sigma–Aldrich) and acid-washed glass beads (150–212 micron) following the manufacturer's protocol. RNA was precipitated with propan-1-ol, washed with 70% ethanol and pellets were resuspended in 30 μl of RNAse-free water. RNAsin Plus (Promega) was used to inhibit RNAse. Contaminating DNA was removed using the TURBO DNA-free system (Ambion).
First strand cDNA synthesis from RNA was performed with M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase RNase H Minus, Point Mutant (Promega) using a poly dT (20-mer) oligonucleotide primer (Sigma–Genosys).
Primers were designed to anneal to the following genes from S. cerevisiae: ARG8: forward, 5′-ATTGTCGAGCCCATACAAGG-3′, reverse, 5′-GAACTCAGCACCAAGCATCA-3′; ARG3, ornithine carbamoyltransferase: forward, 5′-TGTATTTTTGCCCGTGTGAA-3′, reverse, 5′-GTTTCAGCTTGGCCTGTTTC-3′; GLD3, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: forward, 5′-CTCTACCGGTGCTGCTAAGG-3′, reverse, 5′-TCAAGTCAACAACTCTGGCG-3′; LYS1, saccharopine dehydrogenase: forward, 5′-CCACGAACACATCCAGTTTG-3′, reverse, 5′-GAATTTCGTCAAAGGGACCA-3′; LYS2, α-aminoadipate reductase: forward, 5′-CCAAACGGTGACTGTGAATG-3′, reverse, 5′-TTGGGAGTTGGGAATTGAAG-3′; LYS5, phosphopantetheinyl transferase: forward, 5′-CGTCTCAAGCCAGAATCCTC-3′, reverse, 5′-AAAAAGCTGATAGCGCCAAA-3′; LYS9, saccharopine dehydrogenase: forward, 5′-GAAGCCGAAACGGTCATTAG-3′, reverse, 5′-TGGCAACTGGATAACCAACA-3′; LYS20, homocitrate synthase isozyme: forward, 5′-CGATACTGGTTGTGCCATTG-3′, reverse, 5′-TTGGTCATCCGTCAAGTTCA-3′.
End point RT (reverse transcriptase)-PCR analysis
Yeast were grown in liquid SD-U with 50 μg/ml G418 antibiotic (ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK) or liquid YPD (wild-type) with 50 μg/ml G418 antibiotic (ScIpk2Δ) to mid-log phase approx. 0.5–1×107 cells/ml and then transferred to minimal medium containing 2% galactose and either ornithine or arginine as the sole nitrogen source. Cultures were grown at 30 °C with shaking at 3.8 Hz for either 5 or 16 h.
PCR reactions were performed using cDNA from each yeast strain for all growth conditions and for all three genes of interest normalized with respect to GLD3 product formation by adjusting template concentration, number of cycles and annealing temperature. Final reaction conditions were: annealing temperature: 45 °C, extension time: 40 s; repeated for 20 cycles at 2.5 mM MgCl2 using Taq DNA Polymerase. Control reactions using RNA confirmed the absence of contaminating DNA. The products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized using ethidium bromide and ultraviolet light.
myo-[2–3H]Inositol labelling of yeast
For inositol polyphosphate analysis, 1 ml of cells from a 10 ml overnight culture were sub-cultured into 10 ml of YPD of medium (wild-type and ScIpk2Δ) with G418 antibiotic selection for the mutant, or SD-U with G418 antibiotic selection (for ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK). Yeast were grown to a D600 of 0.6, and then pelleted at 2000 g. Pellets were washed three times with minimal medium without galactose or inositol and then resuspended in 10 ml of minimal medium containing 2% galactose and 1.85 MBq myo-[2–3H]inositol. Cells were grown overnight at 30 °C with shaking at 3.8 Hz. Inositol phosphates were extracted as described in [16]. The extracts were analysed by HPLC.
Extraction of amino acids from yeast and HPLC analysis
Overnight cultures were pelleted at 5000 g and resuspended in 0.5 ml of distilled water. Then, 0.8 g of acid-washed glass beads (150–212 μm) were added and the mixture, vortexed for 1 min, frozen in liquid nitrogen and thawed. This was repeated 5 times followed by centrifugation at 13000 g for 5 min at 4 °C. Samples were diluted 14× in 1 M potassium borate (pH 10.4) with KOH, and 50 μl aliquots were reacted for 5 min with an equal volume of OPA (ortho-phthaldialdehyde) prepared as described in [17]. The fluorescent adducts were resolved by reverse-phase chromatography; 50 μl samples were injected, on to a 250×4.6 mm Phenomenex Synergi 4μ Hydro-RP column and eluted at 1 ml/min. A gradient was delivered from buffer reservoirs: A [25 mM NaH2PO4 (pH 2.5) with H3PO4] and B [acetonitrile/methanol/water at a ratio of 4:5:1, (v/v/v)] using the following gradient: time (min), % of B; 0,5; 20,80; 30,95. A Jasco FP-920 fluorescence detector was used to detect the products with excitation at 332 nm and emission at 445 nm.
RESULTS
To confirm the homology of StIPMK to other multikinases, the predicted amino acid sequence was submitted, with others, to the CLUSTAL W program available from http://www.ebi.ac.uk (Figure 1). The alignment revealed that StIPMK is most similar to AtIPK2β from Arabidopsis, with which it shares 54.9% identity. There is a high degree of similarity across kingdoms among the multikinases, and certain domains are conserved in all members of the family [1]. Most importantly, the StIPMK amino acid sequence contains the conserved motif, PxxxDxKxG (amino acids 96–104; single letter amino acid codes are used and x is any amino acid), identified by others as a putative inositol phosphate binding site [15]. Like the other plant kinases cloned thus far [7,15], StIPMK lacks an obvious calmodulin-binding site. In contrast, mammalian kinases have an extended and regulatory C-terminal region, a nuclear localization signal [18] and a calmodulin-binding site. Although we did not test the ability of recombinant StIPMK protein to bind calmodulin, we have shown that AtIPK2β protein, which also lacks an obvious calmodulin-binding site, exhibits no ability to bind the molecule, and is localized to the nucleus [7].
Figure 1. Alignment of predicted amino acid sequences of members of the inositol phosphate multikinase family.
Potato: Solanum tuberosum (StIPMK); Yeast: S. cerevisiae (ScIPK2, protein accession: NP_010458); Arabidopsis a: Arabidopsis thaliana (AtIPK2α, protein accession: CAB96043); Arabidopsis b: Arabidopsis thaliana (AtIPK2β, protein accession: CAC43071); Rat: Rattus norvegicus (mIPMK, protein accession: NP_599244); and Human: Homo sapiens (HsITPKa, protein accession: NP_002211). The alignment was performed using CLUSTAL W available from http://www.ebi.ac.uk and shaded with BOXSHADE available from http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html. Amino acid residues shared by at least half of the sequences are shaded black, and those that are similar are shaded grey.
StIPMK possesses the putative ATP-binding site (amino acids 245–250) identified by Saiardi et al. [19] and the SSLL-like motif required for the enzymatic activity of Ins(1,2,3,4,5,6)P6 kinases [20]. Indeed, one proposal [21] is that the more specific Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinases present in mammals (thought not yeast or plants) may have evolved from multikinases. Given that Ins(1,2,3,4,5,6)P6 kinases possess PxxxDxKxG and SSLL-like motifs, it is possible that they too evolved from multikinases, though it should be noted that no multikinase, thus far, has shown the ability to phosphorylate InsP6 to PP-InsP7.
In vitro catalytic assay of recombinant StIPMK protein
Recombinant StIPMK protein, purified by batch elution from a Ni-NTA (Ni2+-nitrilotriacetate) agarose resin (Qiagen), was catalytically active against a wide range of inositol phosphate substrates (results not shown). Its behaviour is typical of inositol polyphosphate multikinases [1,5–7,11,15,18,19,22], and product formation was witnessed with the following inositol phosphates as substrates: Ins(1,4)P2, Ins(1,4,5)P3, a racemic mixture of Ins([1/3],4,6)P3, Ins(1,3,4,6)P4, Ins(1,3,4,5)P4, Ins(3,4,5,6)P4, Ins(1,3,4,5,6)P5, Ins(,1,2,3,4,5,6)P6. We find it likely that activity against InsP5 and InsP6 generates diphosphoinositol phosphates. StIPMK was inactive against Ins(4,5)P2, but generated unidentified InsP3, InsP4 and InsP5 products from Ins(1,4)P2.
Complementation of the inositol phosphate profile of an ScIpk2Δ yeast mutant
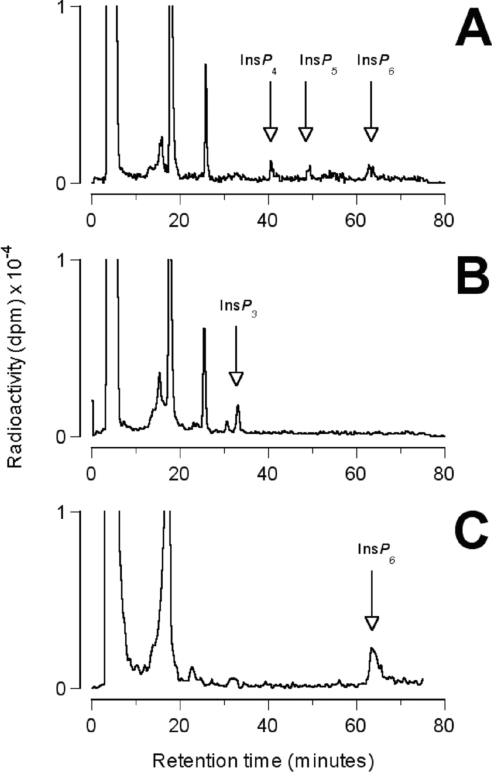
Deletion of ScIPK2, the yeast multikinase, causes pleiotropic effects including altered transcriptional control of arginine metabolism [5,8,23,24], altered vacuolar morphology [25], and defects in mRNA export [26] and chromatin remodelling [27]. These phenotypes have variously been attributed to the absence either of the ScIPK2p protein [5] or the inositol phosphate, diphosphoinositol phosphate, and phosphoinositide products of the enzyme [14]. The S. cerevisiae yeast strain YDR173c, obtained from EUROSCARF, lacks the ScIPK2 open reading frame which is replaced by a KANMX4 marker cassette conferring resistance to the antibiotic G418. To investigate the competence of StIPMK to restore the inositol polyphosphate profile of the ScIpk2Δ strain, we transformed ScIpk2Δ mutant yeast with the vector pYES2.1 harbouring the StIPMK cDNA. Protein expression was induced with galactose. The ScIpk2Δ strain, lacking multikinase activity, is unable to synthesize InsP6 and accumulates Ins(1,4,5)P3 [7,13]. Yeast were labelled overnight in minimal medium containing myo-[2–3H]inositol. Inositol phosphates were extracted from all three strains and applied to a Partisphere SAX HPLC column (Figure 2).
Figure 2. HPLC profiles of inositol phosphates present in S. cerevisiae strains grown in the presence of myo-[2–3H]inositol.
(A) ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK possesses a complement of higher inositol polyphosphates with retention times characteristic of InsP4, InsP5 and InsP6. (B) The ScIpk2Δ strain accumulates InsP3 and has no obvious higher inositol polyphosphates. (C) Wild-type accumulates InsP6. The data were 3-point smoothed with the flow-detector software.
It is apparent from Figure 2 that, while the ScIpk2Δ mutant is unable to synthesis InsP6 and accumulates InsP3, the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains are able to synthesize peaks with the chromatographic properties of InsP4, InsP5 (ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK only) and InsP6. StIPMK is therefore able to substitute for the catalytic activities of ScIPK2p in vivo in yeast, generating InsP6, much as AtIPK2β does [15].
Though there is low overall homology between StIPMK and ScIPK2p, the domain organization within multikinase proteins and a number of regions of high homology are highly conserved, as highlighted by Shears [10] and confirmed by our own bioinformatic analysis (results not shown). The conservation of these domains appears to be sufficient to permit members of the family to participate in pathways of InsP6 synthesis in heterologous systems. The crystal structure of ScIPK2p has recently been solved [28], and is clearly related to that of the human Ins(1,4,5)P3 3-kinase [29]. Although considerable information regarding the substrate specificity of the ScIPK2p is revealed, the report does not afford equal assistance in consideration of the interaction of ScIPK2p with the arginine biosynthetic machinery of yeast.
Complementation of the amino acid profile of an ScIpk2Δ yeast mutant
Despite the considerable interest in the role of ScIPK2p and the mechanism by which it contributes to arginine metabolism in yeast, only one of the host of recent studies [14] has addressed the transcript levels of metabolic genes involved in the arginine synthetic pathway in S. cerevisiae, and only that of Dubois and Messenguy [8] has analysed amino acid content in ScIpk2Δ mutant and ScIPK2-transformed yeast, though data for the wild-type was not provided. Thus the current debate [13,14,30] that addresses ArgR–Mcm1-independent control of arginine biosynthesis assumes that the complicated growth phenotypes of ScIpk2Δ, and the various complementations, have explanation in the regulation of arginine biosynthesis, notwithstanding considerable variation in the composition of the media on which these phenotyping studies have been undertaken.
Because the ScIpk2Δ mutant is limited in its ability to convert ornithine into arginine, most commonly observed as weak growth on poor nitrogen sources [5], we decided to assess the effect of the loss of the ScIPK2 open reading frame in the ScIpk2Δ mutant on: (i) the ability of the mutant to regulate arginine biosynthetic gene transcripts, and (ii) the relative levels of arginine and ornithine in yeast grown on ornithine or arginine. Thus we grew yeast in minimal medium containing either ornithine or arginine as the sole nitrogen source for either 5 h or 16 h. Transcript levels were assessed by end-point RT-PCR, and yeast amino acid profiles were determined after derivatization with OPA.
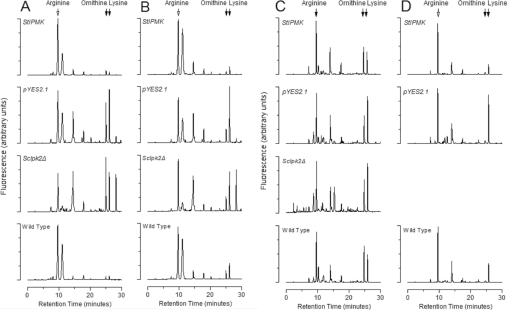
Figure 3 shows the chromatograms for all four strains grown for 5 h and 16 h in medium containing either ornithine or arginine. We chose two time points to accommodate variations in amino acid profiles that may accompany transfer of yeast to fresh or new medium.
Figure 3. Amino acid profiles of yeast grown for 5 h or 16 h in ornithine or arginine medium.
Yeast strains were grown to mid-log phase in selective medium and then transferred to grow for 5 h in minimal medium containing either (A) ornithine or (B) arginine, or for 16 h in either (C) ornithine or (D) arginine. Amino acids were extracted, derivatized with OPA, and the fluorescent adducts resolved on a Phenomenex Synergi 4μ Hydro-RP column. Samples are: wild-type, ScIpk2Δ, ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 (pYES2.1), and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK (StIPMK). The results shown are representative of four experiments (5 h) and eight experiments (16 h).
All strains, including the mutant and empty vector strains, were able to generate arginine when grown for 5 h on ornithine (Figures 3A and 3C), but the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains displayed higher arginine/ornithine ratios than the ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains. These results suggest that the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains are able to synthesize arginine from ornithine more effectively than the mutant. This result is, despite the differences in yeast strains and growth conditions used, in agreement with the study of Dubois and Messenguy [8] (Table 1B of [8]), which reported a 3-fold increase in arginine on transformation of the ScIpk2Δ mutant [strain 02466c (argRIII::URA3)] with ScIPK2. Our analysis of ARG8 and ARG3 transcripts (see Figure 4 later), which revealed enhanced transcript levels in wild-type compared with the ScIpk2Δ mutant, is consistent with our measurements of amino acids.
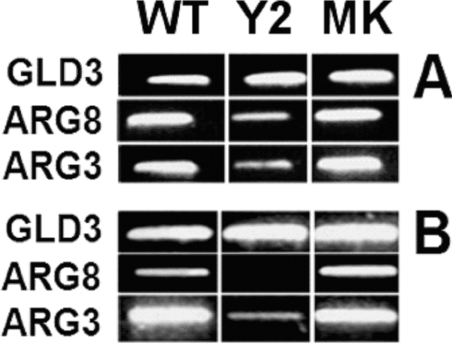
Figure 4. End-point RT-PCR of arginine metabolic gene transcripts in S. cerevisiae in response to ornithine or arginine nitrogen sources.
Yeasts were grown as in Figures 3(C) and 3(D) and RNA was prepared from them. (A) Transcript expression levels after growth in ornithine for 16 h, whereas (B) shows expression after growth in arginine for 16 h. Samples are: wild-type (WT), ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 (Y2), and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK (MK). These data are representative of more than eight experiments.
The former study [8] noted poor correlation between ARG3 activity of yeast extracts and arginine content: repression by arginine in the wild-type, subsequent de-repression in the 02466c mutant strain, and, further to this, repression in the ARGRIII-transformed 02466c strain. In searching for an explanation of the poor correlation between enzyme activity and arginine levels, the authors of the former study [8] assayed the activity of argininosuccinase encoded by ARG4, expression of which is not regulated in an arginine-specific manner. The levels of argininosuccinase activity were similar in mutant, wild-type and ScIPK2-transformed strains, implying that the control of arginine accumulation was not manifest most strongly at this step.
In retrospect, the poor correlation between enzyme activities and amino acid levels may have an explanation in inositol phosphate- or phosphoinositide-dependent control of arginine-related phenotypes, independent of the interaction of ScIPK2p protein with the ArgR–Mcm1 complex [13,14,30]. Returning to the present study, the most significant phenotype was the overproduction of lysine in the ScIpk2Δ mutant (Figures 3A and 3C). Although all four strains showed this peak, the peak in the mutant strains was almost as large as the arginine peak and also often larger than the ornithine peak. In the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains, this lysine peak is smaller than both the arginine and ornithine peaks when grown in ornithine (Figures 3A and 3C). Again, the study of Dubois and Messenguy [8] is relevant. The authors reported variations in lysine levels between the 02466c mutant and ScIPK2-transformed 02466c strains, but did not measure this in the wild-type; lysine was elevated 4-fold in the transformed strain, but again without change in the activities of the lysine pathway, namely of NADP-glutamate forming saccharopine dehydrogenase (product of LYS9) and NAD-lysine forming saccharopine dehydrogenase (product of LYS4). While the present study seems at variance with respect to lysine, we are reassured that StIPMK reduced lysine levels of the ScIpk2Δ mutant to wild-type levels. Again, it is likely that growth conditions are critical determinants in experiments of this sort.
It is noticeable from a comparison of Figure 3(A) (5 h growth) and Figure 3(C) (16 h growth) that, on the ornithine nitrogen source (Figure 3A), the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains have higher arginine/ornithine ratios at 5 h growth. One explanation of this is that the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains show efficient response to accumulating arginine. Comparing strains grown for 5 h, the ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains have a reduced capacity to effect the conversion of ornithine into arginine, witnessed by a much lower arginine/ornithine ratio. Nevertheless, the conversion of ornithine into arginine is significant.
Regarding the levels of lysine, we notice that after 5 h growth on ornithine the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 control and ScIpk2Δ strain, especially, have a higher lysine/arginine ratio than the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains. Perhaps the simplest explanation is that excess ornithine is converted into lysine and that, after 5 h, more ornithine has been converted into lysine in the ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains because they have limited capacity to convert ornithine into arginine, seen as lower levels of ARG3 and ARG8 transcipts relative to wild-type (Figure 4A). It is also possible that ScIPK2p or its InsP products are involved in transcriptional regulation of lysine synthesis, in which case our present studies indicate that StIPMK can substitute for ScIPK2 in regulation of other pathways of amino acid metabolism (see Figure 5 later).
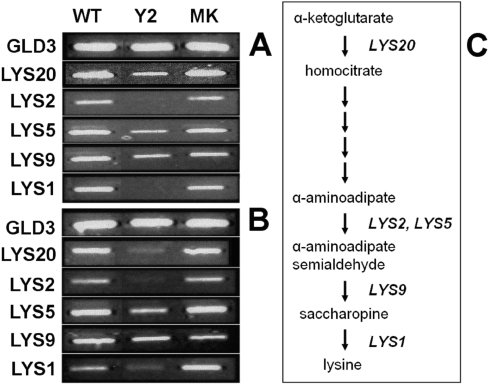
Figure 5. End-point RT-PCR of lysine metabolic gene transcripts in S. cerevisiae in response to ornithine or arginine nitrogen sources.
Yeasts were grown as in Figures 3(C) and (D) and RNA was prepared from them. (A) Transcript expression levels after growth in ornithine for 16 h, whereas (B) shows expression after growth in arginine for 16 h. Samples are: wild-type (WT), ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 (Y2) and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK(MK). For details of the gene products see the main text. These data are representative of three experiments. (C) The lysine biosynthetic pathway in yeast showing those steps catalysed by the products of the genes (A) and (B).
In arginine medium (Figure 3B), wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains have slightly lower arginine/ornithine ratios than the same yeast grown in ornithine (Figure 3A), and slightly higher lysine/arginine ratios. The ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains have a lower arginine/ornithine ratio than the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains. In the presence of arginine (Figure 3B), the mutant strains again have higher lysine/arginine ratios than wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains.
Arginine metabolic gene transcript levels
To analyse transcript levels of arginine metabolic genes, we split yeast samples between our amino acid analysis and an end-point RT-PCR analysis. The expression of two arginine metabolic genes was investigated. The first was ARG8 encoding acetylornithine aminotransferase which catalyses the conversion of N-acetyl-L-glutamyl-5-phosphate into N-acetyl-ornithine, this is the fourth step from glutamate in the biosynthesis of arginine; and the second was ARG3 encoding ornithine carbamoyltransferase which catalyses the formation of L-citrulline from L-ornithine, the sixth step in the biosynthesis of arginine. GLD3, encoding glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1, was chosen as a ubiquitously expressed control gene (Figure 4).
It is apparent that with both ornithine (Figure 4A) and arginine (Figure 4B) nitrogen sources the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains showed similar levels of expression of ARG3 and ARG8, whereas the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 control strain showed much lower levels of expression of these two genes in both media. Though the expression levels in Figure 4(A) and 4(B) are not directly comparable, it does appear, comparing growth on ornithine (Figure 4A) with growth on arginine (Figure 4B), that the wild-type and StIPMK strains showed reduced expression of ARG8, in comparison with ARG3 when grown on arginine. While reduced expression of ARG8 in ScIpk2Δ is at variance with the study of Resnick et al. [14] which addressed only ARG8 expression, we have repeated this experiment on eight occasions with similar results. Using Northern blotting techniques, the authors of the former study [14] showed that, when grown in complete medium, ScIpk2Δ yeast were unable to regulate ARG8 gene transcript levels, and showed elevated levels of expression compared with the wild-type. Expression of a functional multikinase in the ScIpk2Δ mutant yeast restored ARG8 transcript levels to wild-type, while a catalytically inactive version of IPMK did not rescue this phenotype. It is not clear to what the differences between our and the former study may be attributed, though it is likely that the differences in growth conditions are critical parameters, given the plasticity of amino acid metabolism revealed here (Figures 3 and 4).
Given our findings (Figure 3) that the ScIpk2Δ strain is unable to synthesize arginine to the levels of the wild-type strain when grown in ornithine, we do not find it surprising that transcript levels of ARG3 and ARG8 genes are lower in the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strain than in the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains. That is to say, we find a positive correlation between transcript levels and the capacity to synthesize arginine. It is likely, given the lower expression of ARG3 and ARG8 genes in the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strain, that the enhanced capacity of wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strains to effect ornithine into arginine conversion, compared with the mutant, is maintained even on arginine medium, though in this environmental condition the dominant metabolic fluxes must be away from arginine. This result again highlights the likelihood of inositol phosphate-dependent and ScIPK2p/Arg1–Mcm1-independent control of arginine-related phenotypes in transformed ScIpk2Δ strains.
Nevertheless, comparing ARG3 and ARG8, the ability of the yeast to repress arginine synthetic transcripts when grown on arginine (Figure 4B) is manifest most strongly at the level of ARG8. That is, ARG8 and ARG3 are expressed at similar levels on ornithine (Figure 4A), but expression of ARG8 is lower than that of ARG3 in wild-type, ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK yeast strains grown on arginine. In this context, we note that the ARG8 protein acts within the mitochondrion, whereas ARG3 and later enzymes of the pathway reside outside the mitochondrion. Feedback inhibition of N-acetylglutamate synthase (encoded by ARG2) and N-acetylglutamate kinase (encoded by ARG5,6) by arginine has also been demonstrated in S. cerevisiae and Neurospora crassa [31].
Lysine metabolic gene transcript levels
To establish whether the accumulation of lysine in the ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains is a metabolic consequence of compromised arginine biosynthesis, or a result of altered transcriptional regulation of lysine biosynthetic genes normally requiring the presence of ScIPK2p or its catalytic products, we looked at the levels of transcription of lysine biosynthetic genes in yeast grown in either ornithine or arginine (Figure 5).
The synthesis of lysine in S. cerevisiae proceeds via a pathway involving L-α-aminoadipic acid [32,33]. We have chosen five genes from this pathway as follows: LYS20, one of two nuclear homocitrate synthases [34] that catalyse the condensation of acetyl-CoA and α-ketoglutarate to form homocitrate; LYS2 that catalyses the reduction of α-aminoadipate to α-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde; LYS9 (NADP+, glutamate-forming) that catalyses the formation of saccharopine from α-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde; LYS1 (NAD+, lysine forming) that catalyses the conversion of saccharopine to L-lysine; and LYS5 that converts the inactive apo-form of LYS2 into the catalytically active holo-form. GLD3 was used as a control transcript and the expression of the LYS genes analysed with respect to levels of GLD3.
It is evident from growth in both ornithine (Figure 5A) and arginine (Figure 5B) nitrogen sources that the wild-type and ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK yeast have consistently higher expression of all transcripts than the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 yeast, with the possible exception of LYS9 in arginine medium (Figure 5B). We find the most likely explanation for this pattern is that the transcriptional regulation of lysine metabolic genes is not compromised in ScIpk2Δ mutant yeast and that repression of metabolic transcripts is occurring in response to accumulating lysine which is greatest in the ScIpk2Δ mutant (Figure 3).
In the presence of exogenous lysine, S. cerevisiae shows an apparent repression of anabolic transcripts. Lysine is a feedback inhibitor of LYS20, inhibition of which reduces metabolic flux, lowering the levels of α-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde. The latter pathway intermediate is a co-inducer of the LYS14 regulatory protein [35] that activates expression of pathway transcripts [34]. We did not measure the levels of α-aminoadipate 6-semialdehyde, nor transcripts of LYS14, but nevertheless our data (Figure 5) show ‘repression’ of pathway transcripts in ScIpk2Δ that is ‘rescued’ in the ScIpk2Δ/StIPMK strain. This ‘repression’ of pathway transcripts is manifest most strongly at LYS1 and LYS2, i.e. at the end of the pathway, and less strongly at the level of the LYS9 and LYS20, and LYS5, which is a transcriptional activator of LYS3. Strongest repression of LYS20 was evident in arginine medium (compare Figure 5B with Figure 5A) in which lysine/arginine and lysine/ornithine ratios were highest (compare Figure 3D with Figure 3C), suggesting the ‘repression’ is lysine-induced.
Our data, in support of Feller et al. [34], imply that transcriptional control of lysine anabolic transcripts is manifest markedly at the level of LYS20, and perhaps unexpectedly at LYS1 and LYS2. Considerations of flux control inform us that control of flux through metabolic pathways is manifest throughout a pathway. A corollary of this is that the step of predominant control (highest flux control co-efficient) will vary according to ambient cellular conditions, reflecting the network of interactions impinging on the pathway. That we observe control of the lysine pathway in ScIpk2Δ mutants is an unanticipated result, and is all the more remarkable for its ‘rescue’ by a plant IPMK. Perhaps the most parsimonious explanation is that the accumulation of lysine witnessed in ScIpk2Δ and ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 strains grown in ornithine or arginine is a direct result of altered metabolic flux towards lysine from ornithine/arginine due to an impaired ability to efficiently convert ornithine into arginine.
However, we cannot rule out the possibility that ScIPK2 and StIPMK are involved somehow in regulating the levels of transcription of LYS genes, resulting in reduced levels of transcript in the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 compared with wild-type. However, in this case, we would find it hard to rationalize how reduced transcript levels would lead to increased lysine production, particularly given that previously characterized lysine-overproducing mutants show loss of repression of homocitrate synthase, encoded by LYS20 [36].
DISCUSSION
We have shown that when grown on minimal medium with a single defined source of nitrogen, ornithine or arginine, not only does ScIpk2Δ mutant yeast have reduced levels of transcripts of ARG3 and ARG8, but it shows a concomitant reduction in arginine biosynthesis. Both these phenotypes, transcript and amino acid, are restored by expression of a potato multikinase gene, StIPMK. Our data strongly argue that StIPMK or its inositol phosphate products are involved, in this heterologous system, in the formation/stabilization of the ArgR–Mcm1 transcription complex, as indicated by reduced levels of ARG3 and ARG8 transcripts in the absence of multikinase protein and their restoration with StIPMK. However, these results are different to the work of Resnick et al. [14], who reported that in the absence of multikinase protein, ARG8 transcript levels were mis-regulated, i.e. specifically overexpressed. Our results demonstrate that, despite having reduced levels of ARG8 transcript relative to wild-type, the ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1 mutant still displays a further reduction in the level of this transcript, relative to the ARG3 transcript, when grown with arginine (Figure 4B) compared with the situation when grown on ornithine (Figure 4A). We find this scenario entirely plausible, given that it is the complex of Mcm1, ARG80 and ARG81 that binds to DNA, and it is the ARG81 protein that senses levels of arginine. Thus some transcriptional control is still evident in ScIpk2Δ/pYES2.1.
One unanticipated effect that we have observed is an accumulation of lysine in ScIpk2Δ mutant yeast, and an alteration of lysine/ornithine and lysine/arginine ratios that may reflect the diversion of amino acids towards lysine in mutant yeast. Once again, these processes are rescued by expression of a functional potato multikinase. Though lysine is metabolically somewhat distant from arginine, and also ornithine, both arginine and lysine ultimately share origins in the tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates; the two branches of amino acid metabolism are more closely linked however at the level of glutamate. Thus, in yeast, L-glutamate participates in the α-aminoadipate aminotransferase and saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, glutamate forming, LYS9) catalysed steps of lysine synthesis as a nitrogen donor. Moreover, glutamate entry into the mitochondrion is the ‘start’ of the arginine synthetic pathway [31].
The huge sequence dissimilarity between plant IPMKs and ScIPK2, the equivalent of more than 300 point mutations, highlights, in an analysis of temperature sensitive growth phenotype, a transcriptional role for inositol polyphosphates or other products independent of direct interaction of multikinase protein with the ArgR–Mcm1 transcription machinery [13]. Our results highlight the pleiotropic nature of the regulation of amino acid metabolism in yeast. By analysis of transcripts and amino acid profiles, our experiments extend analysis of ScIpk2Δ phenotypes, and highlight the ability of divergent IPMKs to restore control of lysine and arginine biosynthesis in ScIpk2Δ yeast.
Acknowledgments
S. E. K. C. was supported by a BBSRC Special Committee Studentship (Ref. 01/B1/P/07138). C. J. H. was supported by a BBSRC grant (Ref. D14483) awarded to C. A. B. I. S. and S. J. were supported by a BBSRC grant (Ref. D18101) awarded to C. A. B. Yeast Strains were provided by EUROSCARF, University of Frankfurt, Germany.
References
- 1.Shears S. B. How versatile are inositol phosphate kinases? Biochem. J. 2004;377:265–280. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stevenson-Paulik J., Bastidas R. J., Chiou S. T., Frye R. A., York J. D. Generation of phytate-free seeds in Arabidopsis through disruption of inositol polyphosphate kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:12612–12617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504172102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Saiardi A., Caffrey J. J., Snyder S. H., Shears S. B. Inositol polyphosphate multikinase (ArgRIII) determines nuclear mRNA export in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett. 2000;468:28–32. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01194-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Miller A. L., Suntharalingam M., Johnson S. L., Audhya A., Emr S. D., Wente S. R. Cytoplasmic inositol hexakisphosphate production is sufficient for mediating the Gle1-mRNA export pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:51022–51032. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409394200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dubois E., Dewaste V., Erneux C., Messenguy F. Inositol polyphosphate kinase activity of Arg82/ArgRIII is not required for the regulation of the arginine metabolism in yeast. FEBS Lett. 2000;486:300–304. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)02318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.el Alami M., Messenguy F., Scherens B., Dubois E. Arg82p is a bifunctional protein whose inositol polyphosphate kinase activity is essential for nitrogen and PHO gene expression but not for Mcm1p chaperoning in yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2003;49:457–468. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Xia H., Brearley C. A., Elge S., Kaplan B., Fromm H., Mueller-Roeber B. Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-kinase is a nuclear protein that complements a yeast mutant lacking a functional ArgR–Mcm1 transcription complex. Plant Cell. 2003;15:1–16. doi: 10.1105/tpc.006676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dubois E., Messenguy F. Pleiotropic function of ArgRIIIp (Arg82p), one of the regulators of arginine metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Role in expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994;243:315–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00301067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Qiu H. F., Dubois E., Broen P., Messenguy F. Functional analysis of ARGRI and ARGRIII regulatory proteins involved in the regulation of arginine metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1990;222:192–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00633817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shears S. B. Transcriptional regulation: a new dominion for inositol phosphate signaling? BioEssays. 2000;22:786–789. doi: 10.1002/1521-1878(200009)22:9<786::AID-BIES3>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhang T., Caffrey J. J., Shears S. B. The transcriptional regulator, Arg82, is a hybrid kinase with both monophosphoinositol and diphosphoinositol polyphosphate synthase activity. FEBS Lett. 2001;494:208–212. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02351-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Odom A. R., Stahlberg A., Wente S. R., York J. D. A role for nuclear inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate kinase in transcriptional control. Science. 2000;287:2026–2029. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5460.2026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Seeds A. M., Bastidas R. J., York J. D. Molecular definition of a novel inositol polyphosphate metabolic pathway initiated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:27654–27661. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505089200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Resnick A. C., Snowman A. M., Kang B. N., Hurt K. J., Snyder S. H., Saiardi A. Inositol polyphosphate multikinase is a nuclear PI3-kinase with transcriptional regulatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005;102:12783–12788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506184102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stevenson-Paulik J., Odom A. R., York J. D. Molecular and biochemical characterization of two plant inositol polyphosphate 6-/3-/5-kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:42711–42718. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209112200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sweetman D., Johnson S., Caddick S. E., Hanke D. E., Brearley C. A. Characterization of an Arabidopsis inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate 2-kinase (AtIPK1) Biochem. J. 2006;394:95–103. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.van Eijk H. M., Rooyakkers D. R., Soeters P. B., Deutz N. E. Determination of amino acid isotope enrichment using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1999;271:8–17. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nalaskowski M. M., Deschermeier C., Fanick W., Mayr G. W. The human homologue of yeast ArgRIII protein is an inositol phosphate multikinase with predominantly nuclear localization. Biochem. J. 2002;366:549–556. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Saiardi A., Nagata E., Luo H. R., Sawa A., Luo X., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Mammalian inositol polyphosphate multikinase synthesizes inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and an inositol pyrophosphate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2001;98:2306–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.041614598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Saiardi A., Nagata E., Luo H. R., Snowman A. M., Snyder S. H. Identification and characterization of a novel inositol hexakisphosphate kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:39179–39185. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106842200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Schell M. J., Letcher A. J., Brearley C. A., Biber J., Murer H., Irvine R. F. PiUS (Pi uptake stimulator) is an inositol hexakisphosphate kinase. FEBS Lett. 1999;461:169–172. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)01462-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.York J. D., Guo S., Odom A. R., Spiegelberg B. D., Stolz L. E. An expanded view Of inositol signalling. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 2001;41:57–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2571(00)00025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bechet J., Greenson M., Wiame J. M. Mutations affecting the repressibility of arginine biosynthetic enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur. J. Biochem. 1970;12:31–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Messenguy F., Dubois E. Genetic evidence for a role for MCM1 in the regulation of arginine metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993;13:2586–2592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dubois E., Scherens B., Vierendeels F., Ho M. M. W., Messenguy F., Shears S. B. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the inositol polyphosphate kinase activity of Kcs1p is required for resistance to salt stress, cell wall integrity, and vacuolar morphogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:23755–23763. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202206200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.York J. D., Odom A. R., Murphy R., Ives E. B., Wente S. R. A phospholipase C-dependent inositol polyphosphate kinase pathway required for efficient messenger RNA export. Science. 1999;285:96–100. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5424.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Steger D. J., Haswell E. S., Miller A. L., Wente S. R., O'Shea E. K. Regulation of chromatin remodeling by inositol polyphosphates. Science. 2003;299:114–116. doi: 10.1126/science.1078062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Holmes W., Jogl G. Crystal structure of inositol phosphate multikinase 2 and implications for substrate specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:38109–38116. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606883200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gonzalez B., Schell M. J., Letcher A. J., Veprintsev D. B., Irvine R. F., Williams R. L. Structure of a human inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase: substrate binding reveals why it is not a phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Mol. Cell. 2004;15:689–701. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.York J. D. Regulation of nuclear processes by inositol polyphosphates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1761:552–559. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pauwels K., Abadjieva A., Hilven P., Stankiewicz A., Crabeel M. The N-acetylglutamate synthase/N-acetylglutamate kinase metabolon of Saccharomyces cerevisiae allows co-ordinated feedback regulation of the first two steps in arginine biosynthesis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003;270:1014–1024. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zabriskie T. M., Jackson M. D. Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000;17:85–97. doi: 10.1039/a801345d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nishida H., Nishiyama M. What is characteristic of fungal lysine synthesis through the α-aminoadipate pathway? J. Mol. Evol. 2000;51:299–302. doi: 10.1007/s002390010091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Feller A., Ramos F., Pierard A., Dubois E. In Saccharomyces cerevisae, feedback inhibition of homocitrate synthase isoenzymes by lysine modulates the activation of LYS gene expression by Lys14p. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999;261:163–170. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ramos F., Dubois E., Pierard A. Control of enzyme synthesis in the lysine biosynthetic pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Evidence for a regulatory role of gene LYS14. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988;171:171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gasent-Ramirez J. M., Benitez T. Lysine-overproducing mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae baker's yeast isolated in continuous culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997;63:4800–4806. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.12.4800-4806.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]