Abstract
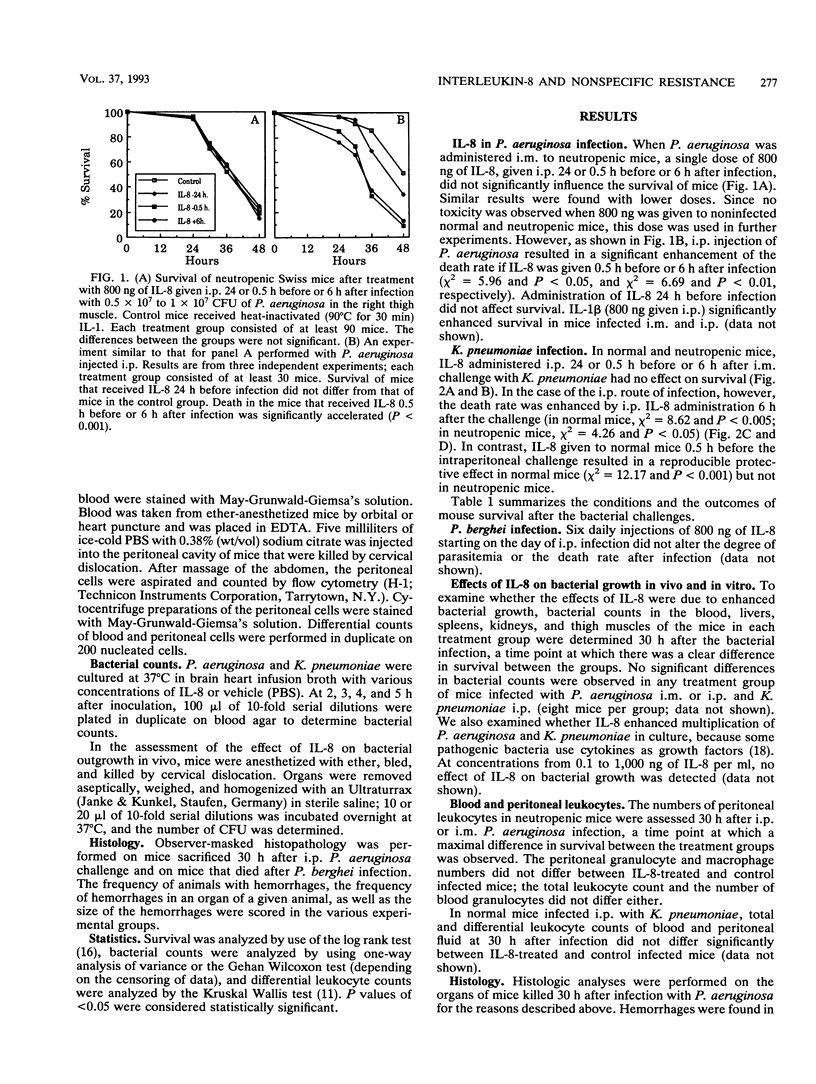
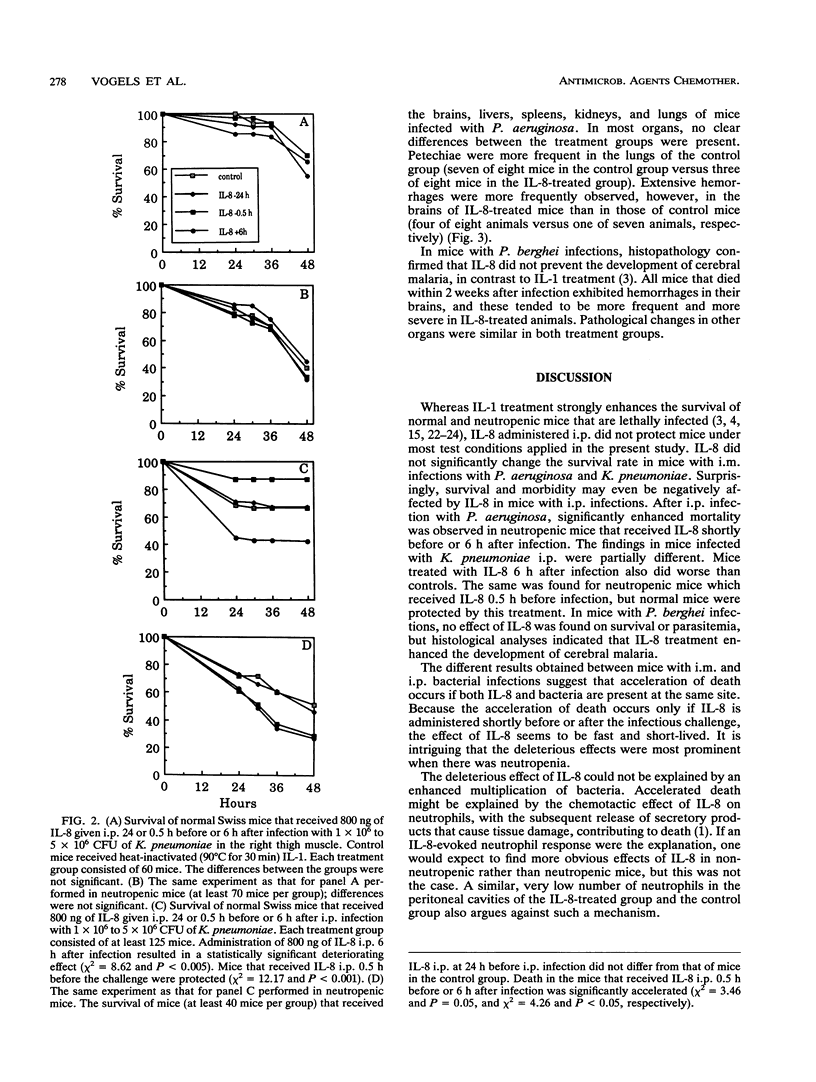
The effect of treatment with interleukin-8 (IL-8), a neutrophil-activating cytokine, was investigated in normal and neutropenic mice infected with a lethal dose of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Plasmodium berghei. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) IL-8 treatment was associated with accelerated death when IL-8 was administered shortly before i.p. infection with P. aeruginosa or shortly after i.p. infection with P. aeruginosa and K. pneumoniae. Histopathological analyses demonstrated a tendency to more severe organ lesions in IL-8-treated mice. Only nonneutropenic mice that received IL-8 shortly before the infectious challenge and at the site of infection were protected by IL-8. Whether IL-8 is protective of or detrimental to the survival of infection appeared to depend on the presence of bacteria at the injection site and on the presence of neutropenia. IL-8 may be an important participant in the cascade of interacting cytokines that is induced by the lethal infectious challenge.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Walz A., Kunkel S. L. Neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin 8, a novel cytokine that activates neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI114265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz I., Zwahlen R., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. In vivo inflammatory activity of neutrophil-activating factor, a novel chemotactic peptide derived from human monocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curfs J. H., van der Meer J. W., Sauerwein R. W., Eling W. M. Low dosages of interleukin 1 protect mice against lethal cerebral malaria. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1287–1291. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Brown J. F. Recombinant murine interleukin-1 alpha enhancement of nonspecific antibacterial resistance. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2061–2065. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2061-2065.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland J. S., Suputtamongkol Y., Remick D. G., Chaowagul W., Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., White N. J., Griffin G. E. Prolonged elevation of interleukin-8 and interleukin-6 concentrations in plasma and of leukocyte interleukin-8 mRNA levels during septicemic and localized Pseudomonas pseudomallei infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2402–2408. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2402-2408.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuta R., Yamagishi J., Kotani H., Sakamoto F., Fukui T., Matsui Y., Sohmura Y., Yamada M., Yoshimura T., Larsen C. G. Production and characterization of recombinant human neutrophil chemotactic factor. J Biochem. 1989 Sep;106(3):436–441. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Young J., Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Structure determination of a human lymphocyte derived neutrophil activating peptide (LYNAP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):883–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert C. A., Luscinskas F. W., Kiely J. M., Luis E. A., Darbonne W. C., Bennett G. L., Liu C. C., Obin M. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Baker J. B. Endothelial and leukocyte forms of IL-8. Conversion by thrombin and interactions with neutrophils. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):3033–3040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley I., Aschauer H., Seifert J. M., Lam C., Brunowsky W., Kownatzki E., Thelen M., Peveri P., Dewald B., von Tscharner V. Synthesis and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding monocyte-derived neutrophil-activating factor: biological equivalence between natural and recombinant neutrophil-activating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9199–9203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Morishita K., Yoshimura T., Lavu S., Kobayashi Y., Lew W., Appella E., Kung H. F., Leonard E. J., Oppenheim J. J. Molecular cloning of a human monocyte-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor (MDNCF) and the induction of MDNCF mRNA by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1883–1893. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Unowsky J., DeLorenzo W., Benjamin W. Enhancement of antibacterial resistance of neutropenic, bone marrow-suppressed mice by interleukin-1 alpha. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):48–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.48-54.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porat R., Clark B. D., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Enhancement of growth of virulent strains of Escherichia coli by interleukin-1. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):430–432. doi: 10.1126/science.1833820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A. Chemotactic potency of recombinant human neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1 (interleukin-8) for polymorphonuclear leukocytes of different species. Cytokine. 1991 Jan;3(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90006-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Secretion of novel and homologous neutrophil-activating peptides by LPS-stimulated human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):244–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van't Wout J. W., Van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Dinarello C. A. Protection of neutropenic mice from lethal Candida albicans infection by recombinant interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1143–1146. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpe S. D., Sherry B., Juers D., Davatelis G., Yurt R. W., Cerami A. Identification and characterization of macrophage inflammatory protein 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):612–616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W., Barza M., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. A low dose of recombinant interleukin 1 protects granulocytopenic mice from lethal gram-negative infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1620–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W. The effects of recombinant interleukin-1 and recombinant tumor necrosis factor on non-specific resistance to infection. Biotherapy. 1988;1(1):19–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02170132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



