Abstract
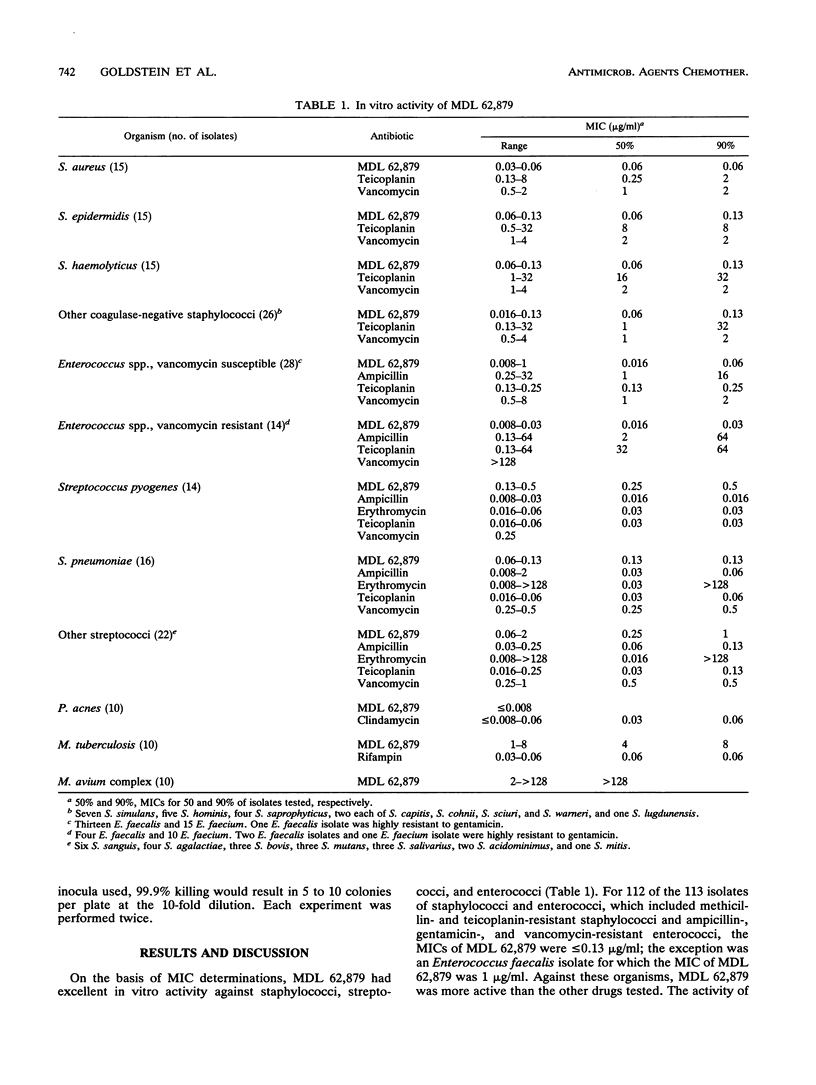
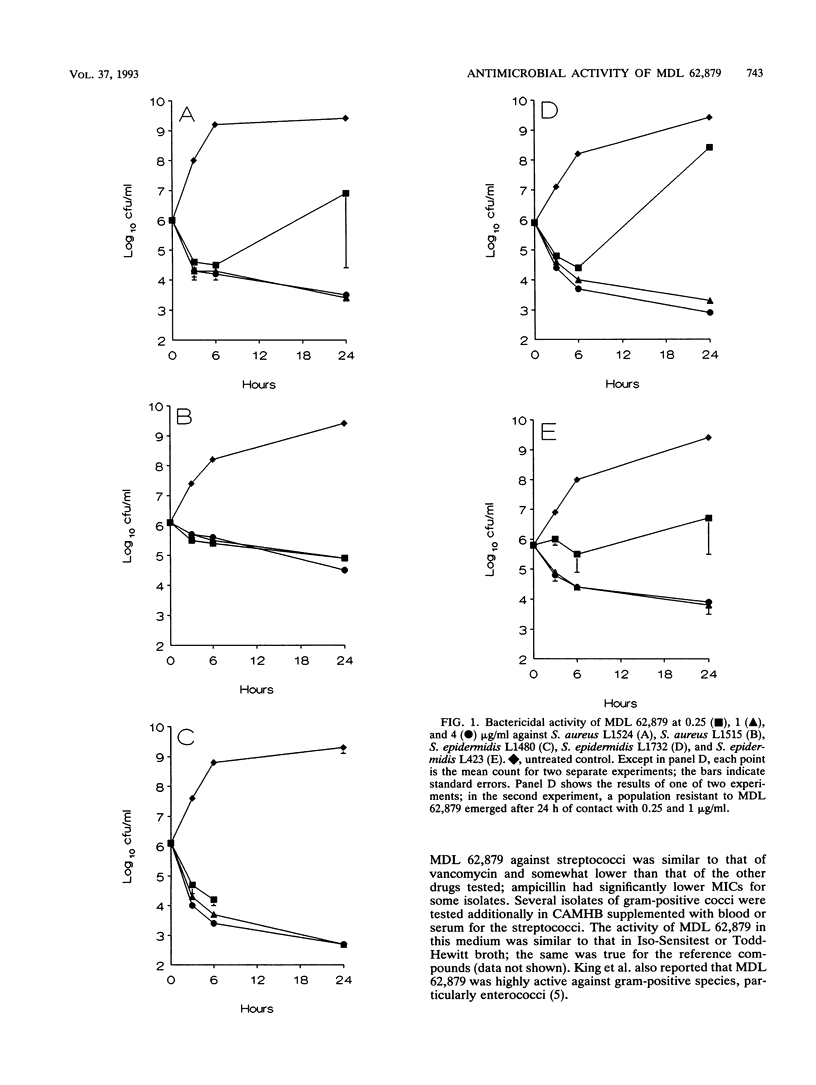
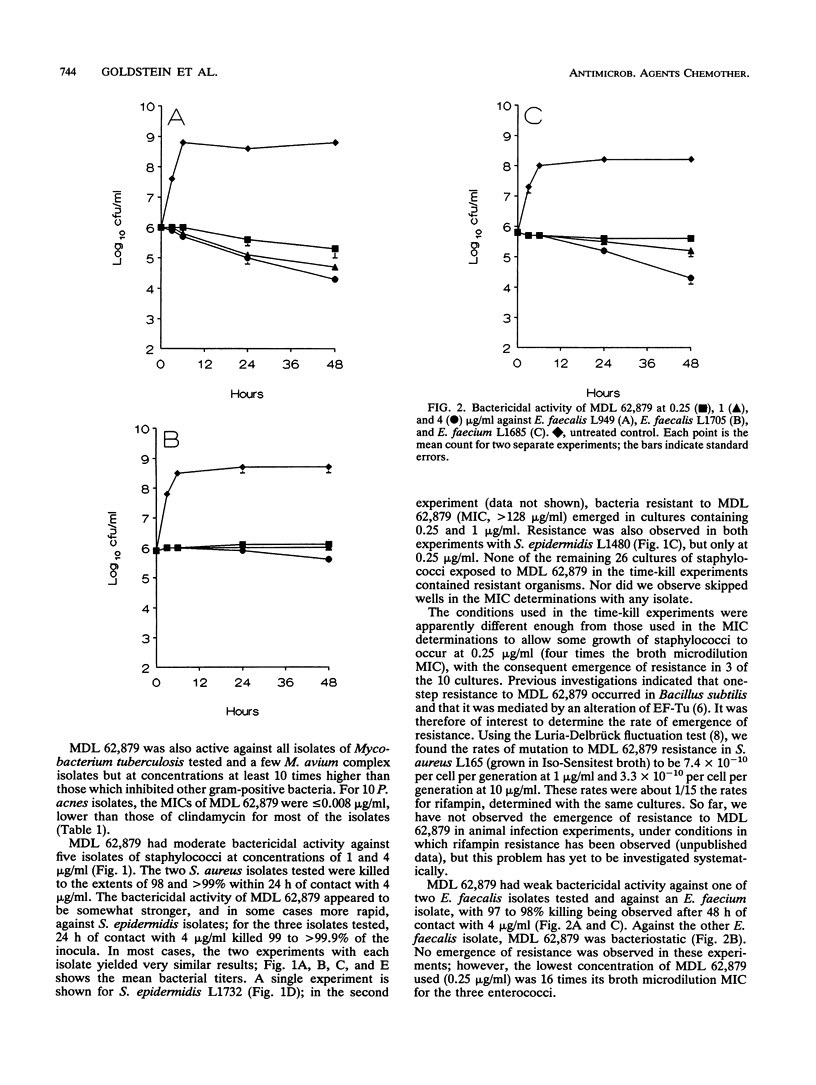
MDL 62,879 (GE2270 A) is a new peptide antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis through an interaction with elongation factor Tu. MDL 62,879 was very active against gram-positive clinical isolates, particularly staphylococci and enterococci, for which MICs for 90% of isolates were < or = 0.13 micrograms/ml. It was equally active against isolates resistant to beta-lactams, erythromycin, gentamicin, and glycopeptides. It also had activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. MDL 62,879 had moderate bactericidal activity against staphylococci.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anborgh P. H., Parmeggiani A. New antibiotic that acts specifically on the GTP-bound form of elongation factor Tu. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):779–784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane C. T., Coleman D. C., Cafferkey M. T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus--a reappraisal. J Hosp Infect. 1991 Nov;19(3):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(91)90218-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Bethune L., Phillips I. In vitro activity of MDL 62,879 (GE2270 A) against aerobic gram-positive and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):746–749. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landini P., Bandera M., Goldstein B. P., Ripamonti F., Soffientini A., Islam K., Denaro M. Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis by elongation-factor-Tu-binding antibiotics MDL 62,879 and efrotomycin. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):649–652. doi: 10.1042/bj2830649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selva E., Beretta G., Montanini N., Saddler G. S., Gastaldo L., Ferrari P., Lorenzetti R., Landini P., Ripamonti F., Goldstein B. P. Antibiotic GE2270 a: a novel inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. I. Isolation and characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1991 Jul;44(7):693–701. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.44.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shlaes D. M. Vancomycin-resistant bacteria. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1992 Apr;13(4):193–194. doi: 10.1086/646508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt B., Collee J. G. Bacterial challenges and evolving antibacterial drug strategy. Postgrad Med J. 1992 Jan;68(795):6–21. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.68.795.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


