Abstract
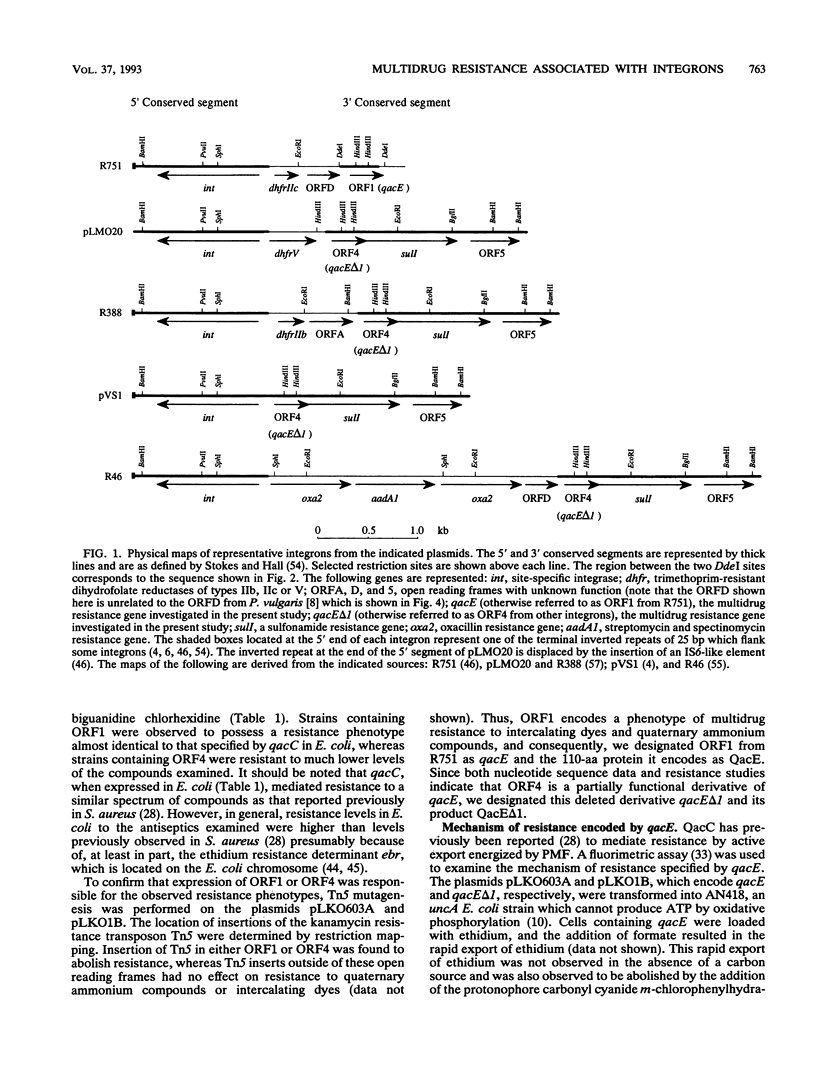
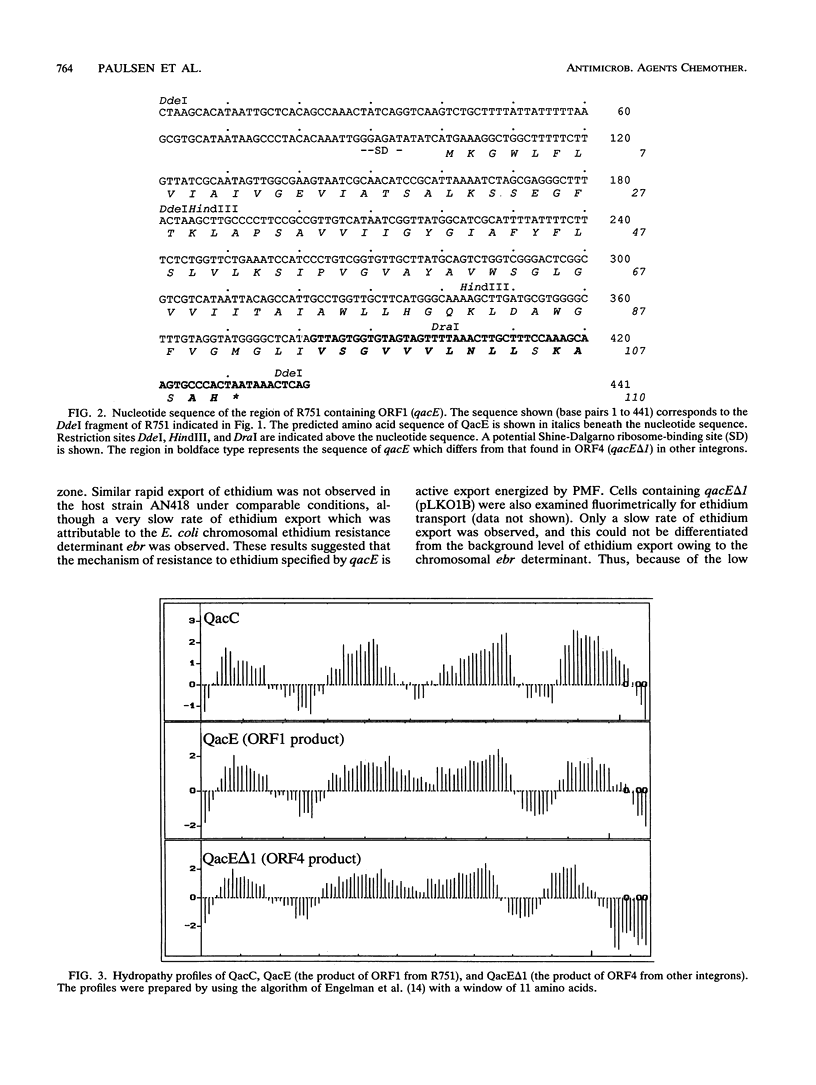
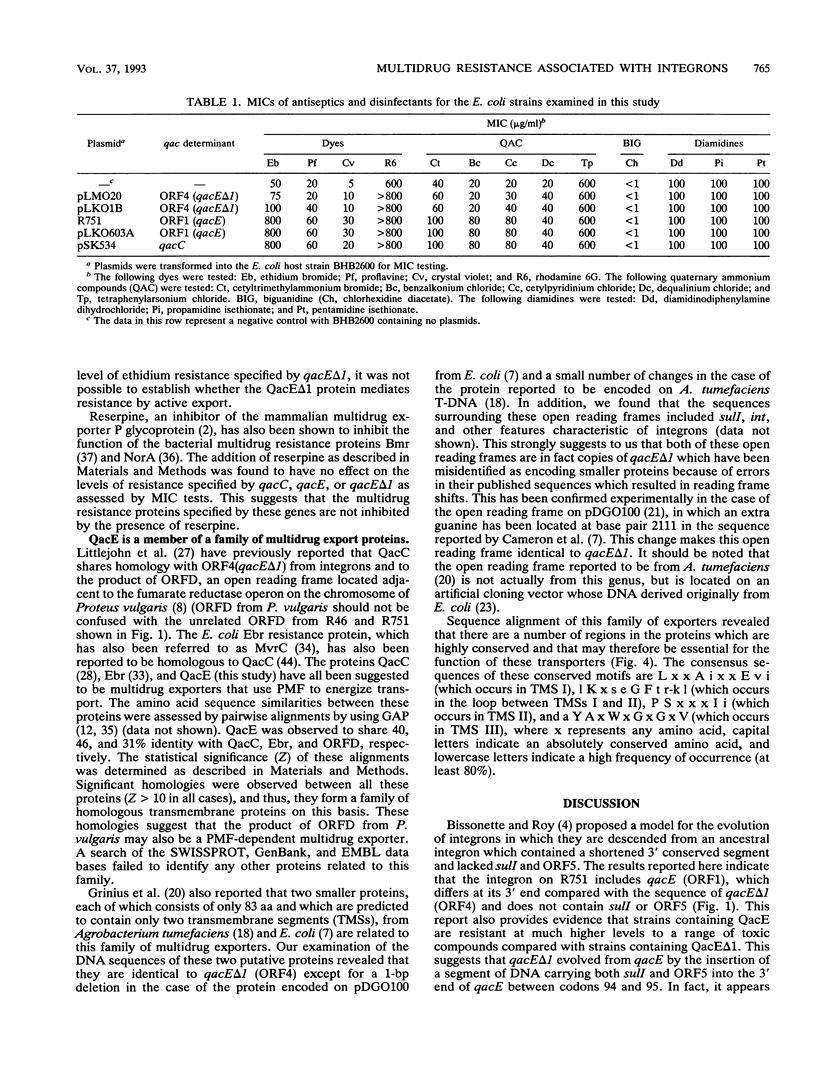
Nucleotide sequence analysis of ORF1 from the integron on the broad-host-range plasmid R751 revealed that the first 94 of 110 codons of ORF1 from R751 are identical to ORF4, an open reading frame from the 3' conserved segment of other integrons found in gram-negative bacteria, after which point they diverged completely. The predicted products of both ORF1 and ORF4 share homology with the multidrug exporter QacC. Phenotypic analysis revealed that ORF1 specifies a resistance profile to antiseptics and disinfectants almost identical to that of qacC, whereas ORF4 specifies much lower levels of resistance to these compounds. ORF4, whose product lacks the C-terminal 16 amino acids of the ORF1 protein, may have evolved by the interruption of ORF1 from the insertion of a DNA segment carrying a sulI sulfonamide resistance determinant. Hence, ORF1 was designated qacE, and its partially functional deletion derivative, ORF4, was designated qacE delta 1. Fluorimetric experiments indicated that the mechanism of resistance mediated by QacE, the protein specified by qacE, is active export energized by proton motive force. Amino acid sequence comparisons revealed that QacE is related to a family of small multidrug export proteins with four transmembrane segments.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P., Landy A., Abremski K., Egan J. B., Haggard-Ljungquist E., Hoess R. H., Kahn M. L., Kalionis B., Narayana S. V., Pierson L. S., 3rd The integrase family of site-specific recombinases: regional similarities and global diversity. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):433–440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Cirtain M. C., Glover C. J., Felsted R. L., Safa A. R. Effects of indole alkaloids on multidrug resistance and labeling of P-glycoprotein by a photoaffinity analog of vinblastine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):959–966. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81321-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. E., Davies J., Allet B., Rochaix J. D. Transposition of R factor genes to bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette L., Roy P. H. Characterization of In0 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa plasmid pVS1, an ancestor of integrons of multiresistance plasmids and transposons of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1248–1257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1248-1257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. L., Misra T. K., Winnie J. N., Schmidt A., Seiff M., Silver S. The nucleotide sequence of the mercuric resistance operons of plasmid R100 and transposon Tn501: further evidence for mer genes which enhance the activity of the mercuric ion detoxification system. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00330531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron F. H., Groot Obbink D. J., Ackerman V. P., Hall R. M. Nucleotide sequence of the AAD(2'') aminoglycoside adenylyltransferase determinant aadB. Evolutionary relationship of this region with those surrounding aadA in R538-1 and dhfrII in R388. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8625–8635. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis of the frd operon encoding the fumarate reductase of Proteus vulgaris. Extensive sequence divergence of the membrane anchors and absence of an frd-linked ampC cephalosporinase gene. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Sep 15;167(3):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. M., Hall R. M. Site-specific deletion and rearrangement of integron insert genes catalyzed by the integron DNA integrase. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1574–1585. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1574-1585.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. B., Downie J. A., Gibson F., Radik J. Genetic complementation between two mutant unc alleles (unc A401 and unc D409) affecting the Fl portion of the magnesium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase of Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 15;170(3):593–598. doi: 10.1042/bj1700593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flensburg J., Steen R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the trimethoprim resistant dihydrofolate reductase encoded by R plasmid R751. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5933–5933. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Thompson J. K., Cowman A. F., Kemp D. J. Amplification of the multidrug resistance gene in some chloroquine-resistant isolates of P. falciparum. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen G., Herman L., Breyne P., Gielen J., Van Montagu M., Depicker A. Cloning and sequence analysis of truncated T-DNA inserts from Nicotiana tabacum. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90382-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. K., Baker M. E., Rouch D. A., Page M. G., Skurray R. A., Paulsen I. T., Chater K. F., Baldwin S. A., Henderson P. J. Membrane transport proteins: implications of sequence comparisons. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):684–695. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90090-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L., Dreguniene G., Goldberg E. B., Liao C. H., Projan S. J. A staphylococcal multidrug resistance gene product is a member of a new protein family. Plasmid. 1992 Mar;27(2):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90012-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. M., Brookes D. E., Stokes H. W. Site-specific insertion of genes into integrons: role of the 59-base element and determination of the recombination cross-over point. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1941–1959. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman L. M., Van Montagu M. C., Depicker A. G. Isolation of tobacco DNA segments with plant promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4486–4492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Stoffel W. PROFILEGRAPH: an interactive graphical tool for protein sequence analysis. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Aug;8(4):331–337. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.4.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobanputra R. S., Datta N. Trimethoprim R factors in enterobacteria from clinical specimens. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):169–177. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlejohn T. G., DiBerardino D., Messerotti L. J., Spiers S. J., Skurray R. A. Structure and evolution of a family of genes encoding antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Gene. 1991 May 15;101(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90224-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlejohn T. G., Paulsen I. T., Gillespie M. T., Tennent J. M., Midgley M., Jones I. G., Purewal A. S., Skurray R. A. Substrate specificity and energetics of antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Aug 15;74(2-3):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90439-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon B. R., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Analysis of plasmids in nosocomial strains of multiple-antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):817–826. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., de la Cruz F. Genetic elements involved in Tn21 site-specific integration, a novel mechanism for the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1275–1281. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., de la Cruz F. Transposon Tn21 encodes a RecA-independent site-specific integration system. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Feb;211(2):320–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00330610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. J., Shapiro J. A. Genetic organization of the broad-host-range IncP-1 plasmid R751. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1362–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1362-1373.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M. The phosphonium ion efflux system of Escherichia coli: relationship to the ethidium efflux system and energetic studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3187–3193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimyo M., Hongo E., Hama-Inaba H., Machida I. Cloning and characterization of the mvrC gene of Escherichia coli K-12 which confers resistance against methyl viologen toxicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3159–3165. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A., Bidnenko V. E., Chen L. B. Efflux-mediated multidrug resistance in Bacillus subtilis: similarities and dissimilarities with the mammalian system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4781–4785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A. The multidrug efflux transporter of Bacillus subtilis is a structural and functional homolog of the Staphylococcus NorA protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):484–485. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Yoshida M., Nishimura M., Nishikawa M., Nishiyama M., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. A leptomycin B resistance gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a protein similar to the mammalian P-glycoproteins. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):761–769. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Bissonnette L., Roy P. H. Precise insertion of antibiotic resistance determinants into Tn21-like transposons: nucleotide sequence of the OXA-1 beta-lactamase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7378–7382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M., Roy P. H. Homology of ORFs from Tn2603 and from R46 to site-specific recombinases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):10055–10055. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.10055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purewal A. S., Jones I. G., Midgley M. Cloning of the ethidium efflux gene from Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90127-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purewal A. S. Nucleotide sequence of the ethidium efflux gene from Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Aug 1;66(2):229–231. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90338-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D. A., Cram D. S., DiBerardino D., Littlejohn T. G., Skurray R. A. Efflux-mediated antiseptic resistance gene qacA from Staphylococcus aureus: common ancestry with tetracycline- and sugar-transport proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2051–2062. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupert C. S. Determination of plasmid molecular weights from ultraviolet sensitivities. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):471–472. doi: 10.1038/272471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasatsu M., Shima K., Shibata Y., Kono M. Nucleotide sequence of a gene that encodes resistance to ethidium bromide from a transferable plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10103–10103. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A., Sporn P. Tn402: a new transposable element determining trimethoprim resistance that inserts in bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1632–1635. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1632-1635.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Hall R. M. A novel family of potentially mobile DNA elements encoding site-specific gene-integration functions: integrons. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1669–1683. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes H. W., Hall R. M. The integron In1 in plasmid R46 includes two copies of the oxa2 gene cassette. Plasmid. 1992 Nov;28(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90054-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström L., Rådström P., Swedberg G., Sköld O. Site-specific recombination promotes linkage between trimethoprim- and sulfonamide resistance genes. Sequence characterization of dhfrV and sulI and a recombination active locus of Tn21. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):191–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00339581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström L., Vinayagamoorthy T., Sköld O. Novel type of plasmid-borne resistance to trimethoprim. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):60–66. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G., McCarthy B. J., Heffron F. DNA sequence of a plasmid-encoded dihydrofolate reductase. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(4):441–447. doi: 10.1007/BF00428733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennent J. M., Lyon B. R., Gillespie M. T., May J. W., Skurray R. A. Cloning and expression of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid-mediated quaternary ammonium resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennent J. M., Lyon B. R., Midgley M., Jones I. G., Purewal A. S., Skurray R. A. Physical and biochemical characterization of the qacA gene encoding antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jan;135(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. A., Redborg A. H., Konisky J. Plasmid-determined immunity of Escherichia coli K-12 to colicin Ia Is mediated by a plasmid-encoded membrane protein. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):817–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.817-828.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann B., Meyer J. F., Zühlsdorf M. T. Insertions of resistance genes into Tn21-like transposons. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18 (Suppl 100):85–92. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_c.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A., Adachi K., Akasaka T., Ono N., Sawai T. Metal-tetracycline/H+ antiporter of Escherichia coli encoded by a transposon Tn10. Histidine 257 plays an essential role in H+ translocation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6045–6051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


