Abstract
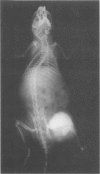
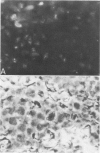
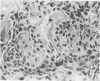
Mice of a transgenic mouse lineage 501, produced by zygotic injection of the parotid alpha-amylase promoter-SV40 T-antigen hybrid gene, developed osteosarcomas at about 15 months of age. The tumors predominantly involved the axial skeleton, were sometimes multiple, and metastasized to the liver. A cell line derived from a primary tumor produced osteosarcomas on transfer to nude mice. The 501 transgenic lineage thus provides a valuable new model for studying the histogenesis of osteosarcomas.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DerKinderen D. J., Koten J. W., Nagelkerke N. J., Tan K. E., Beemer F. A., Den Otter W. Non-ocular cancer in patients with hereditary retinoblastoma and their relatives. Int J Cancer. 1988 Apr 15;41(4):499–504. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox N., Crooke R., Hwang L. H., Schibler U., Knowles B. B., Solter D. Metastatic hibernomas in transgenic mice expressing an alpha-amylase-SV40 T antigen hybrid gene. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):460–463. doi: 10.1126/science.2785714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks L. M., Rowlatt C., Chesterman F. C. Naturally occurring bone tumors in C57BL-Lcrf mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):431–438. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Horowitz J. M., Gerber M. R., Wang X. F., Bogenmann E., Li F. P., Weinberg R. A. Deletions of a DNA sequence in retinoblastomas and mesenchymal tumors: organization of the sequence and its encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9059–9063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Transgenic mice as probes into complex systems. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1265–1275. doi: 10.1126/science.2686032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innes J. R., Ulland B. M., Valerio M. G., Petrucelli L., Fishbein L., Hart E. R., Pallotta A. J., Bates R. R., Falk H. L., Gart J. J. Bioassay of pesticides and industrial chemicals for tumorigenicity in mice: a preliminary note. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Jun;42(6):1101–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., Maltby V., Mock D., Rossant J., Pawson T., Bernstein A. High incidence of lung, bone, and lymphoid tumors in transgenic mice overexpressing mutant alleles of the p53 oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3982–3991. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A. Pathologic effects of different doses of radiostrontium imice. Dose effect relationship in 90Sr-induced bone tumours. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol. 1970 Apr;9(2):155–176. doi: 10.3109/02841867009129097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ootsuyama A., Tanooka H. Induction of osteosarcomas in mouse lumbar vertebrae by repeated external beta-irradiation. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1562–1564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Stewart T. A., Leder A., Sinn E., Muller W., Tepler I., Schmidt E., Leder P. Animal models of human disease. Pathology and molecular biology of spontaneous neoplasms occurring in transgenic mice carrying and expressing activated cellular oncogenes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):39–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Beug H., Graf T., Matthias P., Grez M., Schütz G. Expression of a chicken lysozyme recombinant gene is regulated by progesterone and dexamethasone after microinjection into oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90416-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Garber C., Komitowski D., Müller R., Wagner E. F. Deregulated c-fos expression interferes with normal bone development in transgenic mice. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):412–416. doi: 10.1038/325412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Komitowski D., Schubert F. R., Wagner E. F. c-fos expression induces bone tumors in transgenic mice. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):861–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R. Tumor suppressor genes: the puzzle and the promise. Science. 1989 Dec 15;246(4936):1406–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.2574499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Michiels L., Janowski M., Merregaert J., Erfle V. Expression of protooncogenes in murine osteosarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1986 Jul 15;38(1):67–74. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Sordat B., Schibler U. The two promoters of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a are differentially activated during parotid gland differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):907–912. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]