Abstract
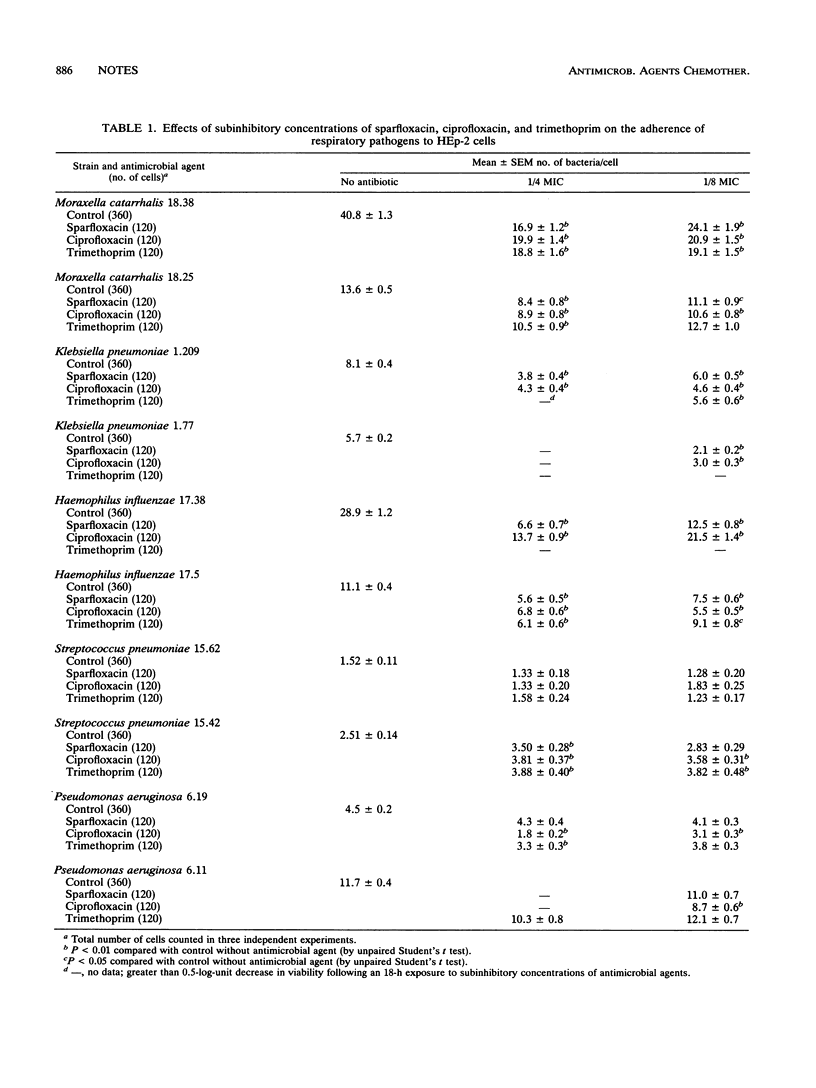
Preincubation with subinhibitory concentrations of sparfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, and trimethoprim decreased the adherence of the respiratory pathogens Klebsiella pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis to human larynx carcinoma HEp-2 cells. Subinhibitory concentrations of sparfloxacin did not change the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Streptococcus pneumoniae 15.62, but adhesion of S. pneumoniae 15.42 was significantly enhanced by subinhibitory antimicrobial concentrations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Eriksson B., Falsen E., Fogh A., Hanson L. A., Nylén O., Peterson H., Svanborg Edén C. Adhesion of Streptococcus pneumoniae to human pharyngeal epithelial cells in vitro: differences in adhesive capacity among strains isolated from subjects with otitis media, septicemia, or meningitis or from healthy carriers. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):311–317. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.311-317.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson B., Svanborg-Edén C. Attachment of Streptococcus pneumoniae to human pharyngeal epithelial cells. Respiration. 1989;55 (Suppl 1):49–52. doi: 10.1159/000195751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Dudas K. C., Stack R. R., Klohs W., LaScolea L. J., Murphy T. F., Mylotte J. M. Fimbriation of Haemophilus species isolated from the respiratory tract of adults. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):40–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr B., Walsh J. B., Coakley D., Scott T., Mulvihill E., Keane C. Effect of age on adherence of Branhamella catarrhalis to buccal epithelial cells. Gerontology. 1989;35(2-3):127–129. doi: 10.1159/000213010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnottes J. F., Diallo N., Moret G., Santonja R. Effects of subinhibitory concentrations of pefloxacin on the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus to human cells. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1987;13(2):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnottes J. F., Le Roy D., Diallo N. Effect of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of pefloxacin on the piliation and adherence of E. coli. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1988;14(10):629–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden C. S., Eriksson B., Hanson L. A. Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):767–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.767-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilsdorf J. R., Jesperson J. M. Effect of antibiotics on adherence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):370–374. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Sakakura Y., Jin C. S. Adherence of Haemophilus influenzae to nasal, nasopharyngeal and buccal epithelial cells from patients with otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1990;247(2):122–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00183182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovarik J. M., Hoepelman I. M., Verhoef J. Influence of fluoroquinolones on expression and function of P fimbriae in uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):684–688. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianou P. E., Bassaris H. P., Votta E. G., Papavassiliou J. T. Interaction of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of clindamycin and gram-negative aerobic organisms: effects on adhesion and polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Apr;15(4):481–487. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Nakata K., Kurobe N., Kouno K., Sakaguchi Y., Kashimoto S., Yoshida H., Kojima T., Ohue T. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of AT-4140, a new broad-spectrum quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1167–1173. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzzo C., Debbia E. A., Satta G. Identification of the major adherence ligand of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the receptor for coliphage T7 and alteration of Klebsiella adherence properties by lysogenic conversion. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):562–571. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.562-571.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R., Houdret N., Koo L., Lamblin G., Roussel P. Differences in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mucin glycopeptides from sputa of patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic bronchitis. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3066–3071. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3066-3071.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal R. The role of bacterial adhesion in cystic fibrosis including the staphylococcal aspect. Infection. 1990 Jan-Feb;18(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01644188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sable N. S., Connor E. M., Hall C. B., Loeb M. R. Variable adherence of fimbriated Haemophilus influenzae type b to human cells. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):119–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.119-123.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Bacterial adhesion: modulation by antibiotics which perturb protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1603–1608. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schifferli D. M., Beachey E. H. Bacterial adhesion: modulation by antibiotics with primary targets other than protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1609–1613. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinger D. S., Reed W. P. Pneumococcal adherence to human epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):545–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.545-548.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Geme J. W., 3rd, Falkow S. Loss of capsule expression by Haemophilus influenzae type b results in enhanced adherence to and invasion of human cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1325–1333. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1325-1333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenfors L. E., Räisänen S. Is attachment of bacteria to the epithelial cells of the nasopharynx the key to otitis media? Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1991 Jul;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(91)90091-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd T. R., Franklin A., Mankinen-Irvin P., Gurman G., Irvin R. T. Augmented bacterial adherence to tracheal epithelial cells is associated with gram-negative pneumonia in an intensive care unit population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath S., Guay C. M., Ramphal R. Effects of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on the adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tracheobronchial mucin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 May;19(5):579–583. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.5.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser M. R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Beumer H., Hoepelman I. M., Verhoef J. Comparative in vitro antibacterial activity of sparfloxacin (AT-4140; RP 64206), a new quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):858–868. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosbeck K., Mett H., Huber U., Bohn J., Petignat M. Effects of low concentrations of antibiotics on Escherichia coli adhesion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):864–869. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


