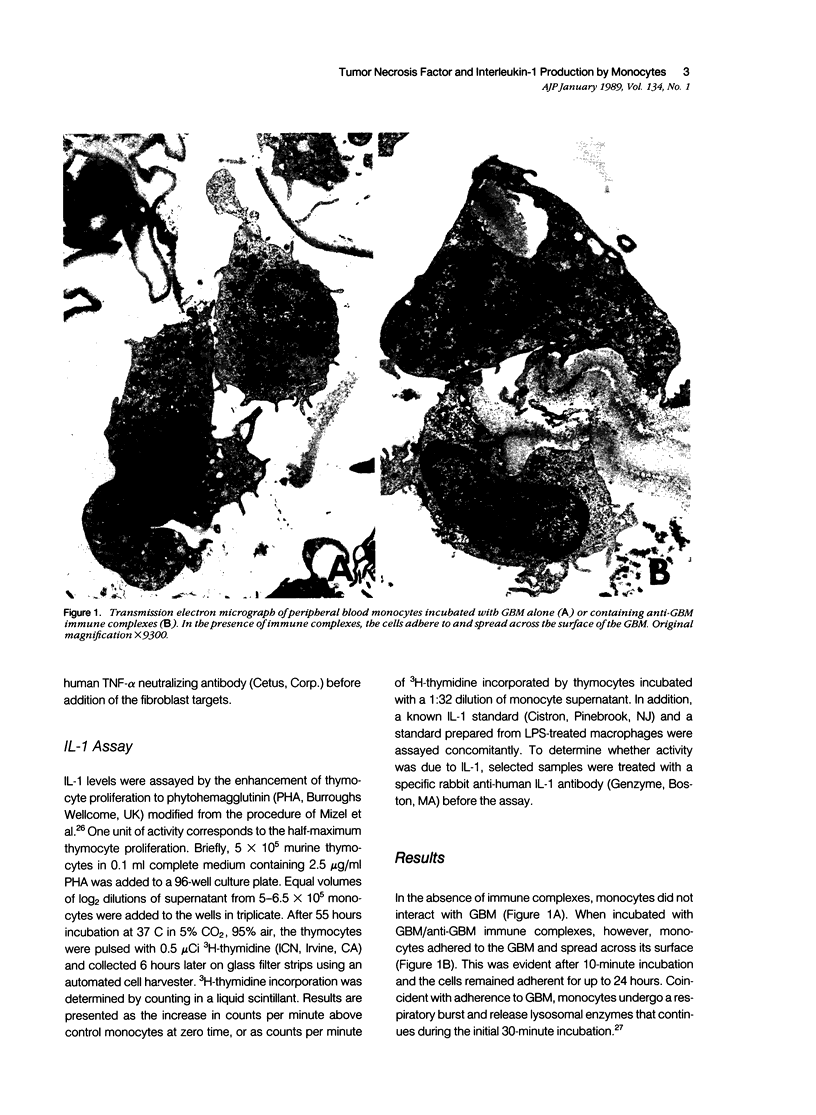
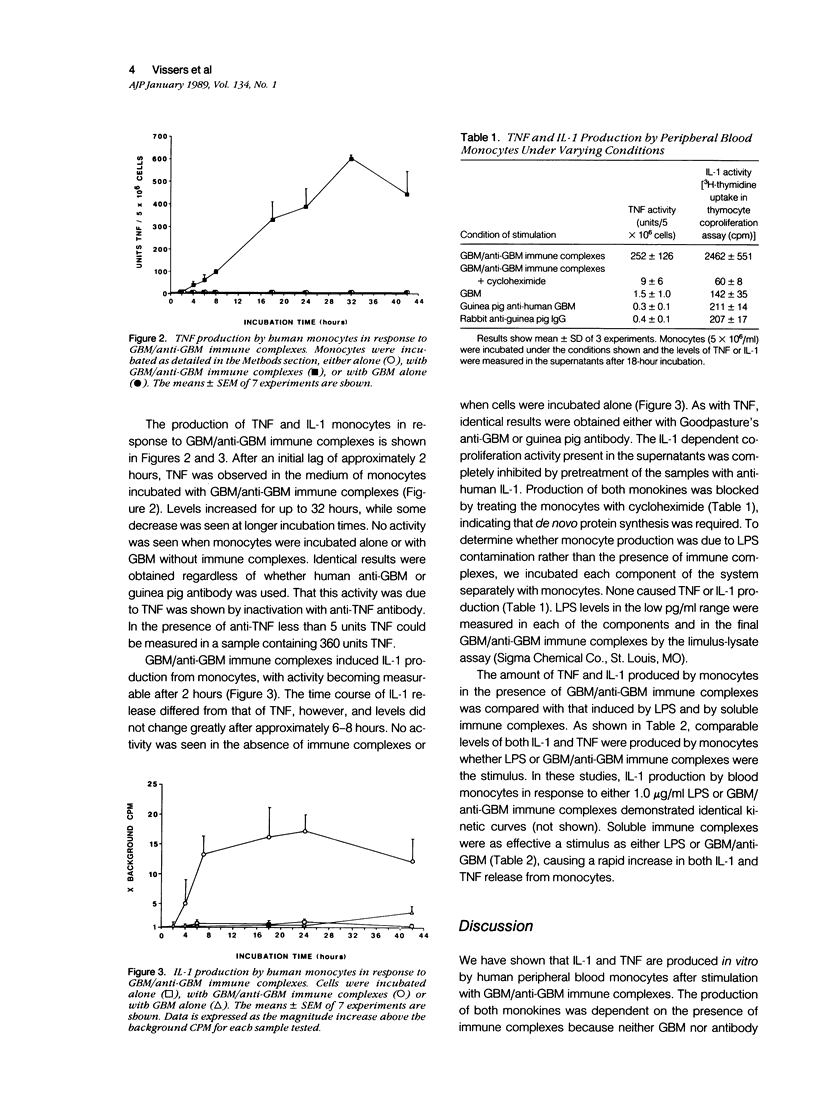
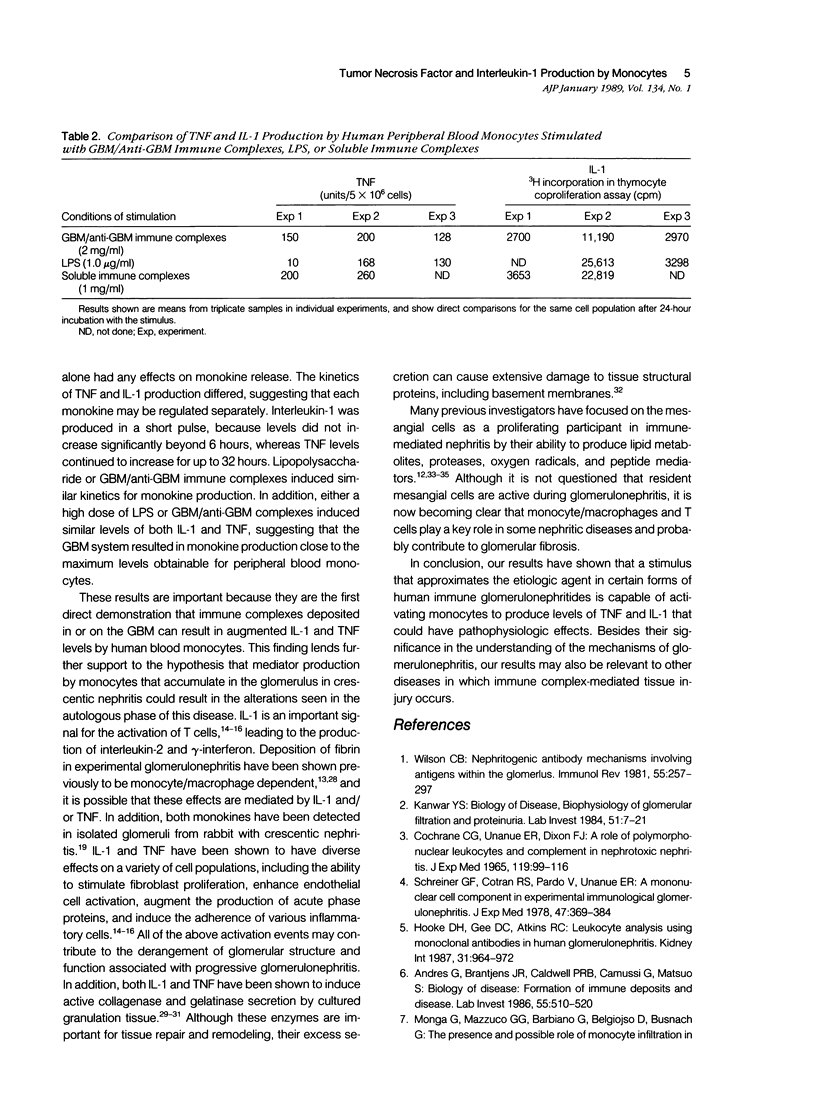
Abstract
The ability of human peripheral blood monocytes to produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) in an in vitro model of immune complex-mediated glomerulonephritis was investigated. When isolated monocytes were incubated with human glomerular basement membrane (GBM) containing anti-GBM immune complexes, both TNF and IL-1 were produced and secreted into the medium. The time course of secretion differed, with IL-1 production being maximal after approximately 8 hours, whereas TNF levels continued to rise for 30 hours. The activities of the monocyte-derived TNF and IL-1 were inhibitable by specific antibodies. No effect was seen when monocytes were incubated separately with either GBM alone or anti-GBM IgG. The levels of TNF and IL-1 released were comparable with those induced by high concentrations of LPS, indicating that production was close to the maximal levels reported for these cells. High levels of TNF and IL-1 also were produced in response to soluble immune complexes. The results show that monocytes can produce significant levels of TNF and IL-1 in response to both surface-bound and soluble immune complexes and provide support for the participation of these monokines in glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres G., Brentjens J. R., Caldwell P. R., Camussi G., Matsuo S. Formation of immune deposits and disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):510–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. A ROLE OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:99–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson E. C., Brendel K., Hjelle J. T., Meezan E. Ultrastructural and biochemical analyses of isolated basement membranes from kidney glomeruli and tubules and brain and retinal microvessels. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Jan;62(1):26–53. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer G., Phan S. H., Wiggins R. C. Analysis of renal fibrosis in a rabbit model of crescentic nephritis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):998–1006. doi: 10.1172/JCI113710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles M. H., Glauert A. M. The response of human monocytes to interaction with immobilized immune complexes. J Cell Sci. 1984 Oct;71:141–157. doi: 10.1242/jcs.71.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foellmer H. G., Sterzel R. B., Kashgarian M. Progressive glomerular sclerosis in experimental antiglomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1986 Jan;7(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(86)80050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J. Macrophage-induced glomerular injury. Cell transfer studies in passive autologous antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-initiated experimental glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):172–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Tipping P. G. Macrophage-induced glomerular fibrin deposition in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1367–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI112112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke D. H., Gee D. C., Atkins R. C. Leukocyte analysis using monoclonal antibodies in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1987 Apr;31(4):964–972. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanwar Y. S. Biophysiology of glomerular filtration and proteinuria. Lab Invest. 1984 Jul;51(1):7–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Heino J., Vuorio E. Interleukin-1 increases collagen production and mRNA levels in cultured skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 6;929(2):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett D. H., Ryan J. L., Sterzel R. B. A thymocyte-activating factor derived from glomerular mesangial cells. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1796–1801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Lovett D. H., Gemsa D., Sterzel R. B., Davies M. Enhancement of glomerular mesangial cell neutral proteinase secretion by macrophages: role of interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):525–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Oppenheim J. J., Rosenstreich D. L. Characterization of lymphocyte-activating factor (LAF) produced by the macrophage cell line, P388D1. I. Enhancement of LAF production by activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa H., Kitagawa H., Aikawa Y. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates gelatinase and collagenase production by granulation tissue in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):791–797. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders E., Davies M., Coles G. A. On the pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis: a clinico-pathological study indicating that neutrophils attack and degrade glomerular basement membrane. Ren Physiol. 1980;3(1-6):355–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D., Satriano J. A., Hagege J., Perez J., Baud L. Effect of platelet-activating factor and serum-treated zymosan on prostaglandin E2 synthesis, arachidonic acid release, and contraction of cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1172/JCI111309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Pardo V., Unanue E. R. A mononuclear cell component in experimental immunological glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):369–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedor J. R., Carey S. W., Emancipator S. N. Immune complexes bind to cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells to stimulate superoxide release. Evidence for an Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3751–3757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striker G. E., Striker L. J. Glomerular cell culture. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):122–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Holdsworth S. R. The participation of macrophages, glomerular procoagulant activity, and factor VIII in glomerular fibrin deposition. Studies on anti-GBM antibody-induced glomerulonephritis in rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1986 Jul;124(1):10–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. Gelatinase contributes to the degradation of glomerular basement membrane collagen by human neutrophils. Coll Relat Res. 1988 Mar;8(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(88)80023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C., Hunt J. S. Degradation of glomerular basement membrane by human neutrophils in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 19;804(2):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vissers M. C., Winterbourn C. C. The effect of oxidants on neutrophil-mediated degradation of glomerular basement membrane collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 19;889(3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B. Nephritogenic antibody mechanisms involving antigens within the glomerulus. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:257–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



