Abstract
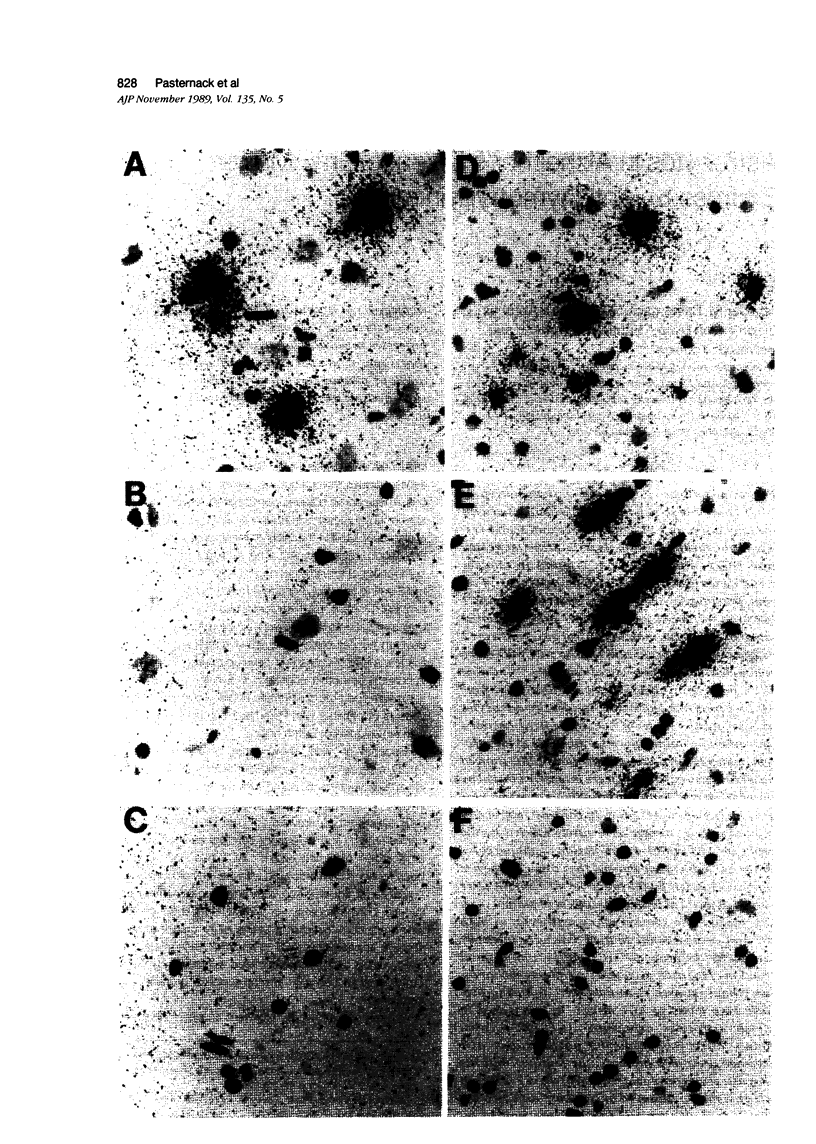
The serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin (ACT) has been shown to be tightly associated with the amyloid found in plaque cores and blood vessels in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although the ACT found in plaques could be derived from the high levels of ACT in serum, previous Northern analysis revealed that ACT mRNA is produced locally in AD gray matter at much higher levels than in control gray matter. To determine which brain cells express ACT mRNA, we conducted in situ hybridization with 35S-labeled cRNA probes on hippocampal sections from four AD and three control cases. To identify astrocytes unequivocally, some of the hybridized sections were immunostained for glial fibrillary acidic protein, which is astrocyte-specific. Our results showed numerous astrocytes that were intensely labeled by the probe for ACT mRNA throughout the subicular gray matter of the AD cases. In contrast, astrocytes in control gray matter were rarely labeled by the probe for ACT mRNA. Examination of plaque cores in the AD subiculum showed that some astrocytes intensely labeled by the probe for ACT mRNA were closely associated with virtually every plaque core. Our results also showed many astrocytes in both AD and control white matter that were intensely labeled by the probe for ACT mRNA, and a small fraction of the astrocytes in a juvenile cerebellar astrocytoma that we examined were found to produce high levels of ACT mRNA. In every area in which astrocytes expressing ACT mRNA were found, astrocytes producing no detectable ACT message were also present. Our findings indicate that astrocytes produce the increased ACT mRNA in AD gray matter observed by Northern analysis, but they also show that ACT mRNA expression by astrocytes is not unique to AD. The presence of astrocytes expressing ACT mRNA near, and extending processes towards, plaque cores strongly suggests that some if not all of the ACT associated with amyloid plaque cores is produced by astrocytes surrounding the cores.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra T., Stackhouse R., Kidd V. J., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Sequence homology between human alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, and antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5055–5061. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Golde T. E., Usiak M. F., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G. In situ hybridization of nucleus basalis neurons shows increased beta-amyloid mRNA in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1227–1231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coria F., Castaño E. M., Frangione B. Brain amyloid in normal aging and cerebral amyloid angiopathy is antigenically related to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):422–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M. Neuronal localization of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA in normal human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3627–3632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Lewis D. A., Bahmanyar S., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Young W. G., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C. Differential regulation of amyloid-beta-protein mRNA expression within hippocampal neuronal subpopulations in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1297–1301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. A., Pasinetti G. M., May P. C., Ponte P. A., Cordell B., Finch C. E. Selective reduction of mRNA for the beta-amyloid precursor protein that lacks a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor motif in cortex from Alzheimer brains. Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;102(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Higgins G. A., Young W. G., Goldgaber D., Gajdusek D. C., Wilson M. C., Morrison J. H. Distribution of precursor amyloid-beta-protein messenger RNA in human cerebral cortex: relationship to neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1691–1695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O., Marcyniuk B., Ravindra C. R. The topography of plaques and tangles in Down's syndrome patients of different ages. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;12(5):447–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1986.tb00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Finch E. A., Dawes L. R. Expression of the Alzheimer amyloid precursor gene transcripts in the human brain. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):669–677. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90166-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Golde T. E., Cohen M. L., Kovacs D. M., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Usiak M. F., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G. Amyloid protein precursor messenger RNAs: differential expression in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1988 Aug 26;241(4869):1080–1084. doi: 10.1126/science.2457949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Podlisny M. B., Witker D. S., Oltersdorf T., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. Antisera to an amino-terminal peptide detect the amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease and recognize senile plaques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):432–437. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Podlisny M. B., Witker D. S., Oltersdorf T., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. The beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer disease has soluble derivatives found in human brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6338–6342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Lipphardt S., Mulvihill P., Kancherla M., Mijares M., Gambetti P., Sharma S., Maggiora L., Cornette J., Lobl T. Amyloid precursor protein in senile plaques of Alzheimer disease. Lancet. 1988 Sep 24;2(8613):746–746. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropper A. H., Williams R. S. Relationship between plaques, tangles, and dementia in Down syndrome. Neurology. 1980 Jun;30(6):639–644. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.6.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Goldgaber D., Burkhart D. S., Gilbert J. R., Gajdusek D. C., Roses A. D. Cellular localization of messenger RNA encoding amyloid-beta-protein in normal tissue and in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2(2):96–111. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198802020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Podlisny M. B., Joachim C. L., Vickers E. A., Lee G., Fritz L. C., Oltersdorf T. Beta-amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease occurs as 110- to 135-kilodalton membrane-associated proteins in neural and nonneural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7341–7345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struble R. G., Cork L. C., Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L. Cholinergic innervation in neuritic plaques. Science. 1982 Apr 23;216(4544):413–415. doi: 10.1126/science.6803359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struble R. G., Price D. L., Jr, Cork L. C., Price D. L. Senile plaques in cortex of aged normal monkeys. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Ghetti B., Terry R. D. Neuritic (senile) plaques and filamentous changes in aged rhesus monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Oct;32(4):566–584. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197310000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duinen S. G., Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis in patients of Dutch origin is related to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5991–5994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





