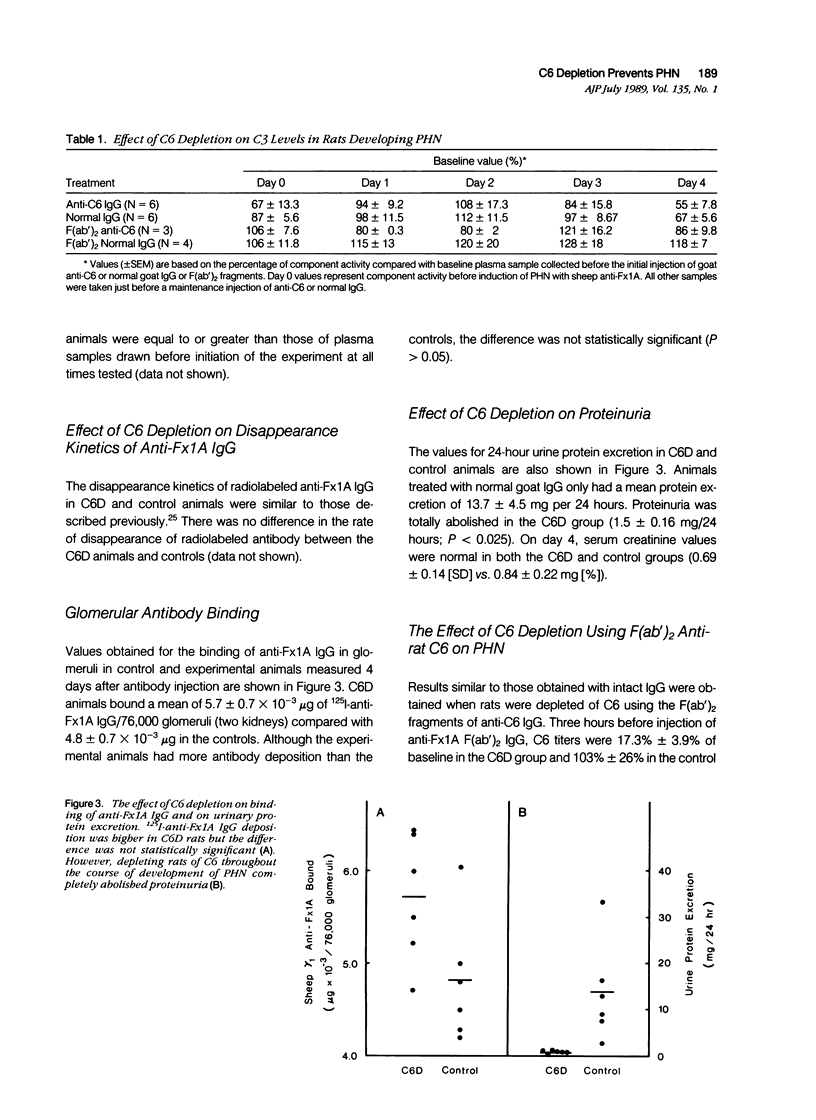
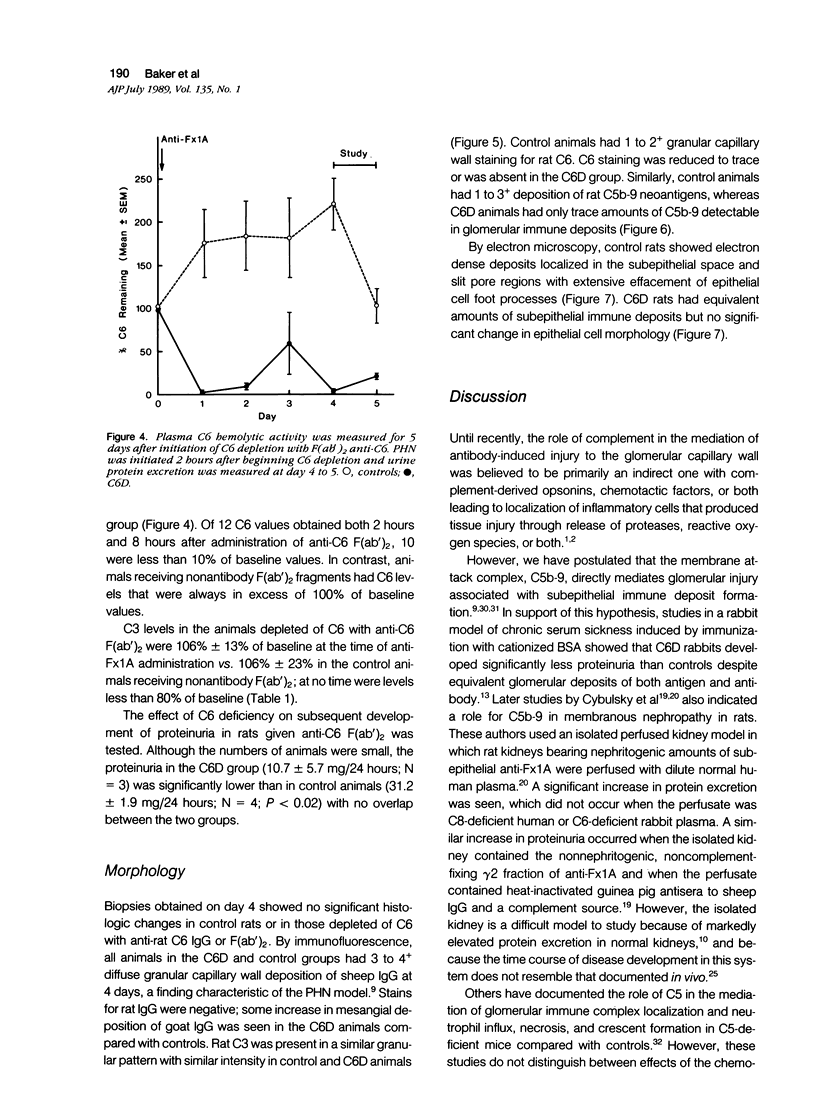
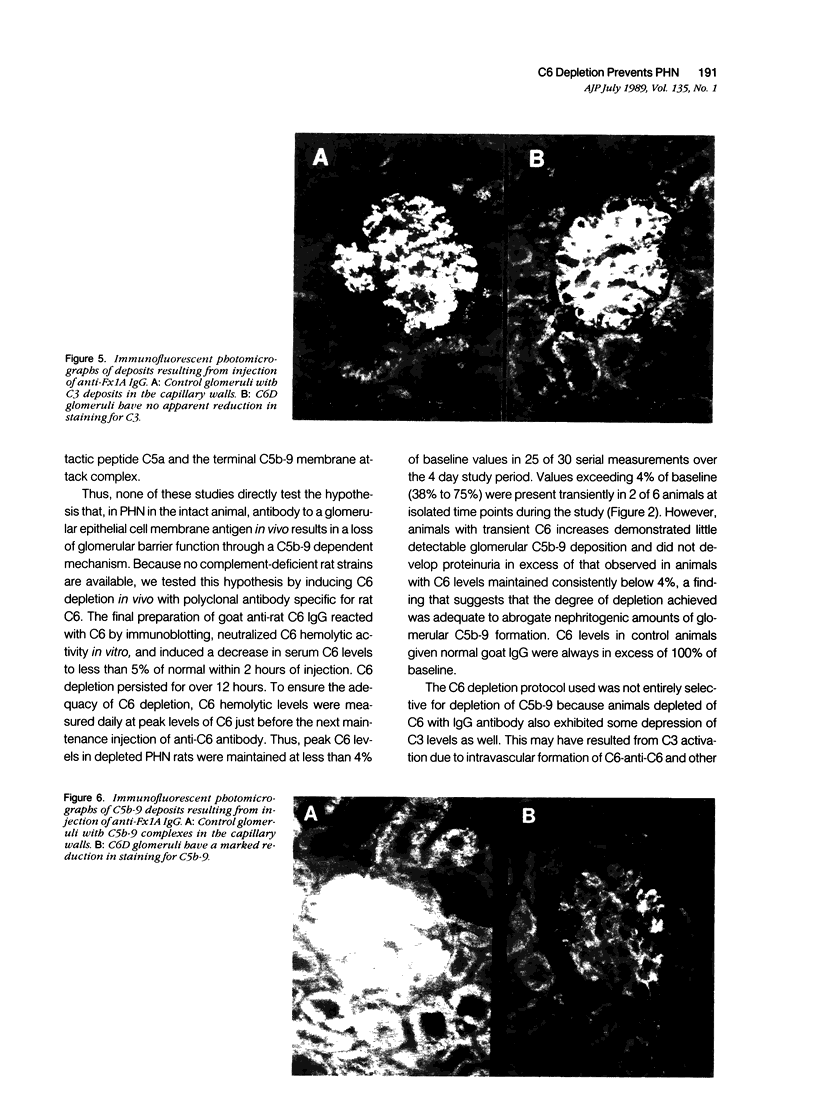
Abstract
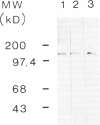
To study the possible role of the complement membrane attack complex, C5b-9, in an experimental rat model that is morphologically indistinguishable from membranous nephropathy in man (passive Heymann nephritis [PHN]), an antibody to rat C6 was used to deplete C6 levels to less than 5% of pretreatment values (C6D) during disease development. C3, C7, C8, and C9 levels were not different in C6D and control rats. After injection of nephritogenic quantities of 125I-anti-Fx1A antibody, the kinetics of disappearance of labeled IgG from the blood were identical in the complement deficient and sufficient groups, and glomerular deposition of 125I-antibody was the same in both groups at 5 days. Glomerular deposits of sheep IgG and C3 were also similar in C6D and controls, but glomerular deposits of C6 and C5b-9 neoantigens were markedly reduced or absent in C6 depleted rats. However, despite equivalent antibody deposits, proteinuria was abolished in C6D rats compared with normocomplementemic controls. Similar results were obtained when F(ab')2 anti-rat C6 IgG was used to deplete C6 during development of PHN. These results demonstrate that C6 is required for the development of the increased glomerular permeability that occurs in PHN, presumably because C6 is required for formation of C5b-9. We conclude that glomerular injury in the PHN model of membranous nephropathy in the rat is mediated by C5b-9.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann U. Apparent escape rate of RIHSA and 51Cr-labeled erythrocytes from the blood of volume-expanded rats. Am J Physiol. 1978 May;234(5):F386–F392. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.5.F386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler S., Baker P. J., Johnson R. J., Ochi R. F., Pritzl P., Couser W. G. Complement membrane attack complex stimulates production of reactive oxygen metabolites by cultured rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):762–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI112372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler S., Baker P. J., Pritzl P., Couser W. G. Detection of terminal complement components in experimental immune glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1984 Dec;26(6):830–837. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler S., Salant D. J., Dittmer J. E., Rennke H. G., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G. Mediation of proteinuria in membranous nephropathy due to a planted glomerular antigen. Kidney Int. 1983 Jun;23(6):807–815. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G. Membrane attack complex of complement as a pathologic mediator. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):237–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Noble B., Andres G. A., Koffler D. Immunopathogenesis of Heymann's nephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Dec;33(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Tucker B. J., Wilson C. B. The acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody upon glomerular filtration in the rat. The influence of dose and complement depletion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):910–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI109016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. A ROLE OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:99–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camussi G., Brentjens J. R., Noble B., Kerjaschki D., Malavasi F., Roholt O. A., Farquhar M. G., Andres G. Antibody-induced redistribution of Heymann antigen on the surface of cultured glomerular visceral epithelial cells: possible role in the pathogenesis of Heymann glomerulonephritis. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2409–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. Mediation of immunologic glomerular injury. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):949–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Baker P. J., Adler S. Complement and the direct mediation of immune glomerular injury: a new perspective. Kidney Int. 1985 Dec;28(6):879–890. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Steinmuller D. R., Stilmant M. M., Salant D. J., Lowenstein L. M. Experimental glomerulonephritis in the isolated perfused rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1275–1287. doi: 10.1172/JCI109248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky A. V., Quigg R. J., Salant D. J. The membrane attack complex in complement-mediated glomerular epithelial cell injury: formation and stability of C5b-9 and C5b-7 in rat membranous nephropathy. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1511–1516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Glassock R. J., Dixon F. J. Autologous immune complex nephritis induced with renal tubular antigen. I. Identification and isolation of the pathogenetic antigen. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):555–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Dalmasso A. P., Kim Y., Tsai C. H., Scheinman J. I., Gewurz H., Michael A. F. Neoantigen of the polymerized ninth component of complement. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody and immunohistochemical localization in renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):560–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI111004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Jennette J. C. Immune complex induced glomerular lesions in C5 sufficient and deficient mice. Kidney Int. 1986 Nov;30(5):678–686. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk R. J., Sisson S. P., Dalmasso A. P., Kim Y., Michael A. F., Vernier R. L. Ultrastructural localization of the membrane attack complex of complement in human renal tissues. Am J Kidney Dis. 1987 Feb;9(2):121–128. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(87)80089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbai F. B., Gushwa L. C., Wilson C. B., Blantz R. C. An evaluation of the development of experimental membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1987 Jun;31(6):1267–1278. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbai F. B., Mundy C. A., Wilson C. B., Blantz R. C. An evaluation of the role of complement depletion in experimental membranous nephropathy in the rat. Lab Invest. 1988 May;58(5):539–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groggel G. C., Adler S., Rennke H. G., Couser W. G., Salant D. J. Role of the terminal complement pathway in experimental membranous nephropathy in the rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):1948–1957. doi: 10.1172/JCI111159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groggel G. C., Salant D. J., Darby C., Rennke H. G., Couser W. G. Role of terminal complement pathway in the heterologous phase of antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis. Kidney Int. 1985 Apr;27(4):643–651. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMER D. K., DIXON F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis. II. Immunologic events in the pathogenesis of nephrotoxic serum nephritis in the rat. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:1019–1034. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D., Cochrane C. G. Glomerular basement membrane damage in immunological glomerulonephritis. Immunology. 1968 May;14(5):665–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinglais N., Kazatchkine M. D., Bhakdi S., Appay M. D., Mandet C., Grossetete J., Bariety J. Immunohistochemical study of the C5b-9 complex of complement in human kidneys. Kidney Int. 1986 Sep;30(3):399–410. doi: 10.1038/ki.1986.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Betz M., Günther J., Rother K. O., Sterzel B. The complement membrane attack complex stimulates the prostanoid production of cultured glomerular epithelial cells. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;85(1):87–93. doi: 10.1159/000234479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerjaschki D., Farquhar M. G. Immunocytochemical localization of the Heymann nephritis antigen (GP330) in glomerular epithelial cells of normal Lewis rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):667–686. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S. J., Manning D. D. Persistence of passively transferred goat F(ab')2 antibody fragments in the circulation of rodents. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):2339–2343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkinson D. T., Baker P. J., Couser W. G., Johnson R. J., Adler S. Membrane attack complex deposition in experimental glomerular injury. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):121–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Belok S., Madaio M. P., Couser W. G. A new role for complement in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1339–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI109987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Darby C., Couser W. G. Experimental membranous glomerulonephritis in rats. Quantitative studies of glomerular immune deposit formation in isolated glomeruli and whole animals. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):71–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI109837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetsel R. A., Jones M. A., Kolb W. P. Immunoadsorbent affinity purification of the fifth component (C5) of human complement and development of a highly sensitive hemolytic assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(3-4):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Heer E., Daha M. R., Bhakdi S., Bazin H., van Es L. A. Possible involvement of terminal complement complex in active Heymann nephritis. Kidney Int. 1985 Feb;27(2):388–393. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]