Abstract
Scintiscanning to detect the uptake of bone-seeking radioactive isotopes by soft tissue is a promising technique for the in vivo study of visceral calcification. Visceral uptake of such radioisotopes was studied in 40 patients: 22 undergoing long-term dialysis, 9 with malignant disease and hypercalcemia and 9 with primary hyperparathyroidism and hypercalcemia.
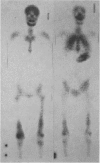
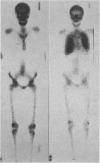
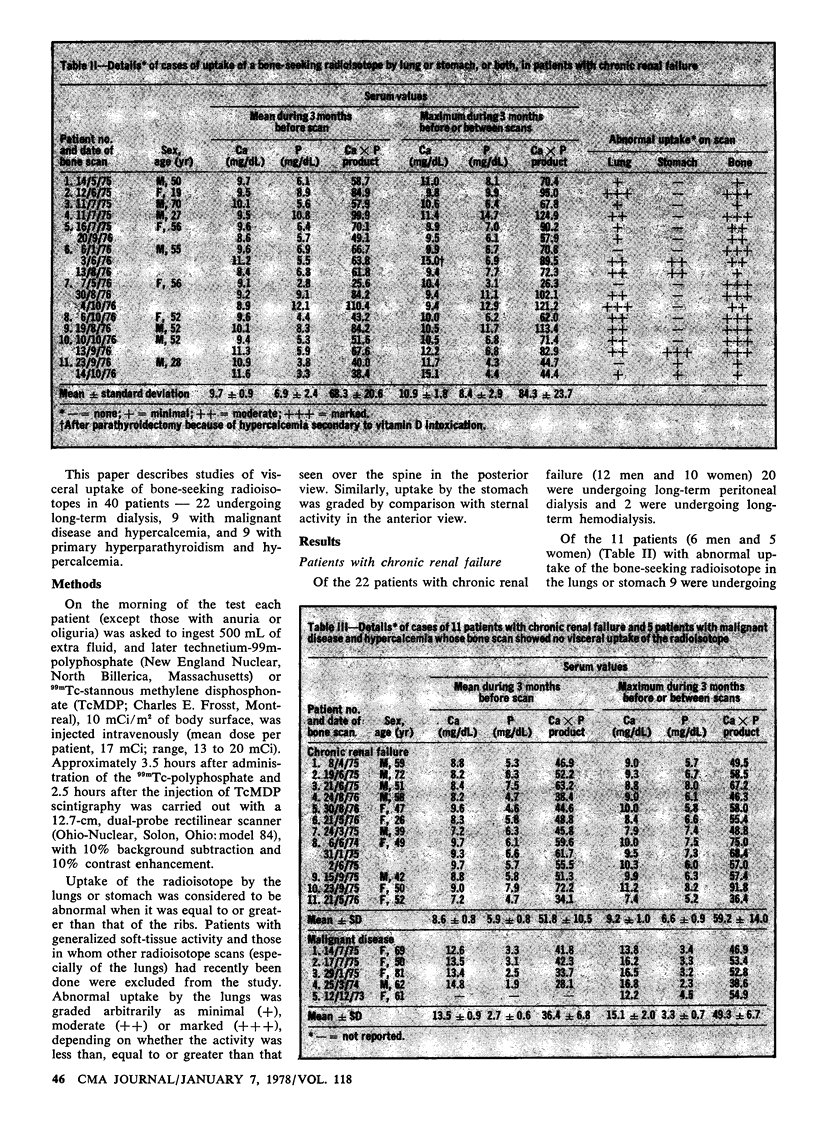
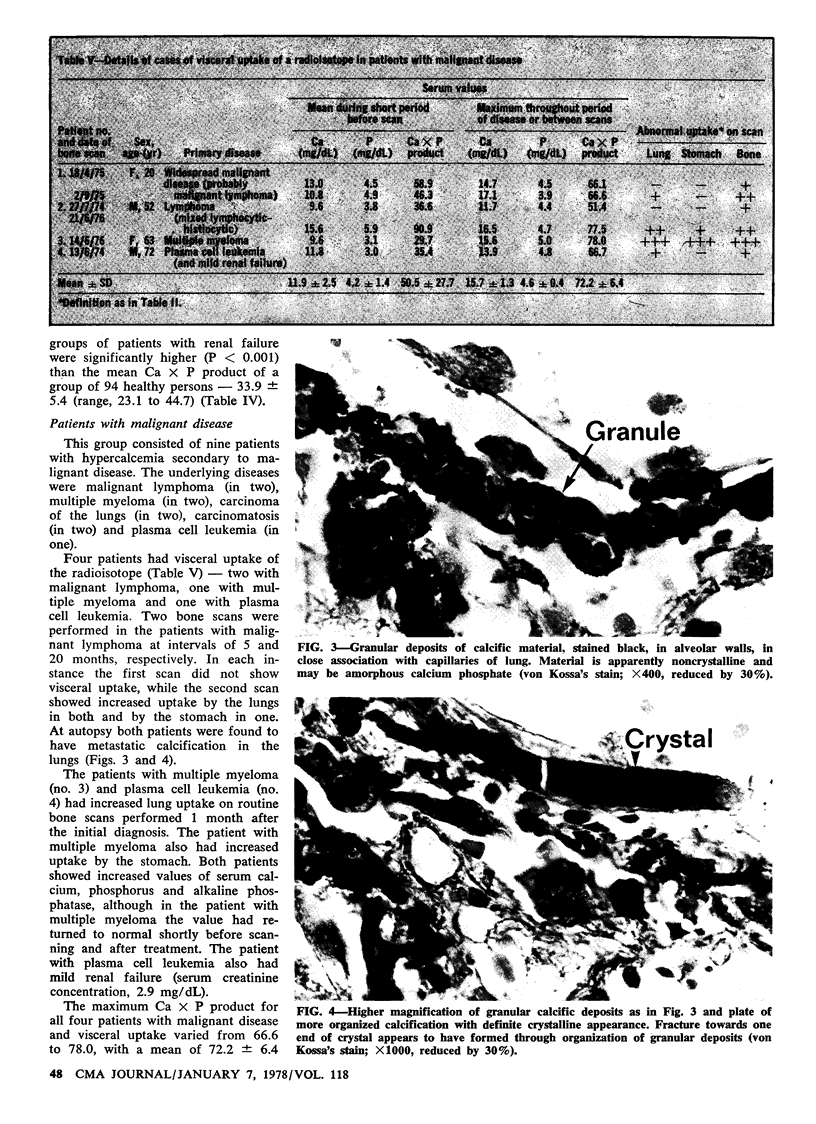
Fifteen patients, 11 undergoing dialysis and 4 with malignant disease, had radioisotope uptake in the lungs, and 5, 3 undergoing dialysis and 2 with malignant disease, had uptake in the stomach. None of the patients with primary hyperparathyroidism had visceral uptake, nor did the patients with uptake have radiologic evidence of pulmonary or gastric calcification. The dialysis patients with visceral uptake had a mean calcium × phosphate product of 84.3 ± 23.7 (standard deviation), which was significantly greater (P < 0.001) than that of patients without such uptake (59.2 ± 14.0). Similarly, in patients with malignant disease and visceral uptake the Ca × P product was 72.2 ± 6.4 — significantly greater (P < 0.005) than that of patients without such uptake (49.3 ± 6.7).
These findings indicate that scintiscanning for the visceral uptake of a bone-seeking radioisotope is a simple and effective technique for the in vivo study of visceral calcification. An elevation in the Ca × P product seems to be the single most important factor in the production of visceral calcification.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfrey A. C., Solomons C. C., Ciricillo J., Miller N. L. Extraosseous calcification. Evidence for abnormal pyrophosphate metabolism in uremia. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):692–699. doi: 10.1172/JCI108326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri T. K., Muilenburg M. I., Christie J. H. Abnormal deposition of radiostrontium in lungs. Chest. 1972 Feb;61(2):190–192. doi: 10.1378/chest.61.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conger J. D., Hammond W. S., Alfrey A. C., Contiguglia S. R., Stanford R. E., Huffer W. E. Pulmonary calcification in chronic dialysis patients. Clinical and pathologic studies. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Sep;83(3):330–336. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-3-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devacaanthan K., Yap A. U., Chayes Z., Stein R. M. Pulmonary calcification in chronic renal failure: use of diphosphonate scintiscan as a diagnostic tool. Clin Nephrol. 1976 Nov;6(5):488–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grames G. M., Sauser D. D., Jansen C., Soderblom R. E., Hodgkin J. E., Stilson M. S. Radionuclide detection of diffuse interstitial pulmonary calcification. JAMA. 1974 Nov 18;230(7):992–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert L. A., Lemann J., Jr, Petersen J. R., Lennon E. J. Studies of the mechanism by which phosphate infusion lowers serum calcium concentration. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1886–1894. doi: 10.1172/JCI105493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Bisaz S., Fleisch H. The binding of pyrophosphate and two diphosphonates by hydroxyapatite crystals. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973 Mar 30;11(4):269–280. doi: 10.1007/BF02547227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B., Baum G. L., Bogaty G., McCoy M. D., Tucker M. So-called "metastatic" calcification of the lung. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):188–196. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin A. F. Uptake of 99mTc bone-scanning agent by lungs with metastatic calcification. J Nucl Med. 1975 Apr;16(4):322–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moinuddin M., Rockett J. F., Waber A. Letter: Scanning for pulmonary calcification. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Feb;84(2):224–225. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-2-224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. G. Metastatic calcification detected through scanning with 99mTc-polyphosphate. J Nucl Med. 1974 Nov;15(11):1057–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian G., McAfee J. G. A new complex of 99mTc for skeletal imaging. Radiology. 1971 Apr;99(1):192–196. doi: 10.1148/99.1.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]