Abstract
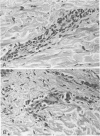
The presence of an erythematous skin rash and hemorrhagic complications in acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) suggest that the vasculature may be involved in the immunopathologic process. We reviewed endothelial and vascular histopathologic changes on light microscopy and on immunoperoxidase stained sections of skin biopsies obtained from 41 HLA-identical allogeneic marrow transplant recipients with at least grade 2 GVHD. Biopsies taken from 14 allogeneic HLA-identical bone marrow transplant recipients who never developed GVHD were used as controls. Sections were evaluated for evidence of immunologic vascular injury using the rank file analysis of histologic features, expression of HLA-DR antigen, and the distribution of fibrin and factor VIII-related antigen (F VIII RAg). Patients with acute GVHD had significantly greater intimal lymphocytic infiltrates, perivascular nuclear dust deposition, perivascular F VIII Rag extravasation and deposition and vascular proliferation than controls. We find significantly greater endothelial injury in GVHD patients, which may represent primary immunologic injury to the vasculature. The clinical findings in acute GVHD probably result from cumulative endothelial as well as epithelial injury.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belch J. J., Zoma A. A., Richards I. M., McLaughlin K., Forbes C. D., Sturrock R. D. Vascular damage and factor-VIII-related antigen in the rheumatic diseases. Rheumatol Int. 1987;7(3):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00270462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschorner W. E., Farmer E. R., Saral R., Stirling W. L., Santos G. W. Epithelial class II antigen expression in cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1987 Aug;44(2):237–243. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198708000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beschorner W. E., Shinn C. A., Hess A. D., Suresch D. L., Santos G. W. Immune-related injury to endothelium associated with acute graft-versus-host disease in the rat. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 3):3025–3027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Katz S. I. Cell-mediated immunity in cutaneous disease. Hum Pathol. 1986 Feb;17(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Katz S. I. Immunopathology of cutaneous graft-versus-host disease. Am J Dermatopathol. 1987 Aug;9(4):343–348. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198708000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Katz S. I. Keratinocytes synthesize Ia antigen in acute cutaneous graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2741–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Shimada S., Kovac Z., Katz S. I. Immunologic aspects of acute cutaneous graft-versus-host disease: decreased density and antigen-presenting function of Ia+ Langerhans cells and absent antigen-presenting capacity of Ia+ keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Mar;86(3):226–234. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G. J., Reynolds E. S., Galvanek E. G., Braun W. E., Dammin G. J. Human renal allografts. The role of vascular injury in early graft failure. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971 Jan;50(1):29–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. B., Dvorak H. F. Role of the clotting system in cell-mediated hypersensitivity. II. Kinetics of fibrinogen/fibrin accumulation and vascular permeability changes in tuberculin and cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity reactions. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):377–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
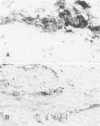
- Colvin R. B., Johnson R. A., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak H. F. Role of the clotting system in cell-mediated hypersensitivity. I. Fibrin deposition in delayed skin reactions in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):686–698. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda R., Alberti M., Caocci L., Putzolu G., Mannucci P. M. An increased factor VIII antigen as an indicator of endothelial damage in measles. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):805–810. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotran R. S. American Association of Pathologists president's address. New roles for the endothelium in inflammation and immunity. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):407–413. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtade E. T., Tsuda T., Thomas C. R., Dannenberg A. M. Capillary density in developing and healing tuberculous lesions produced by BCG in rabbits. A quantitative study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Feb;78(2):243–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak A. M., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak H. F. Morphology of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions in man. II. Ultrastructural alterations affecting the microvasculature and the tissue mast cells. Lab Invest. 1976 Feb;34(2):179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Galli S. J., Dvorak A. M. Cellular and vascular manifestations of cell-mediated immunity. Hum Pathol. 1986 Feb;17(2):122–137. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr Basophilic leukocytes in allergic contact dermatitis. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):235–254. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Barnes B. A., Manseau E. J., Galli S. J. Rejection of first-set skin allografts in man. the microvasculature is the critical target of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):322–337. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Mihm M. C., Jr, Dvorak A. M., Johnson R. A., Manseau E. J., Morgan E., Colvin R. B. Morphology of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions in man. I. Quantitative description of the inflammatory response. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):111–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry B., Halttunen J., Leszczynski D., Schellekens H., vd Meide P. H., Häyry P. Impact of class II major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on the immunogenic potential of isolated rat vascular endothelial cells. Transplantation. 1987 Oct;44(4):499–503. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198710000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. D., Odom R. B. Graft-v-host disease. Arch Dermatol. 1983 Aug;119(8):683–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemnitz J., Cohnert T., Schäfers H. J., Helmke M., Wahlers T., Herrmann G., Schmidt R. M., Haverich A. A classification of cardiac allograft rejection. A modification of the classification by Billingham. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987 Jul;11(7):503–515. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198707000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Geha R. S., Newburger J. W., Burns J. C., Fiers W., Lapierre L. A., Pober J. S. Two monokines, interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor, render cultured vascular endothelial cells susceptible to lysis by antibodies circulating during Kawasaki syndrome. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1958–1972. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. Y., Moake J. L., Havens P. L., Kim M., Pober J. S. Lytic anti-endothelial cell antibodies in haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Lancet. 1988 Jul 23;2(8604):183–186. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W. Subsets of T cells in the rat mediating lethal graft versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1981 Sep;32(3):222–226. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198109000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messadi D. V., Pober J. S., Fiers W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Murphy G. F. Induction of an activation antigen on postcapillary venular endothelium in human skin organ culture. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1557–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Cavender D., Ziff M. Production of interleukin 1 by human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2486–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. F., Merot Y., Tong A. K., Smith B., Mihm M. C., Jr Depletion and repopulation of epidermal dendritic cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in humans. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Mar;84(3):210–214. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Champagne J., DeClerck Y., Cooper M., Draper V., Walker S. Cellular interactions in graft-v-host disease. Transplant Proc. 1987 Dec;19(6 Suppl 7):52–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault C., Pelletier M., Landry D., Gyger M. Study of Langerhans cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1984 Apr;63(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Allet B., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is an effector of skin and gut lesions of the acute phase of graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Collins T., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Libby P., Reiss C. S. Inducible expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens and the immunogenicity of vascular endothelium. Transplantation. 1986 Feb;41(2):141–146. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198602000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran R. S., Sholley M. M. Endothelial proliferation in the delayed hypersensitivity reaction: an autoradiographic study. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):529–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. G., Blacklock H. A., Janossy G., Gilmore M. J., Price-Jones L., Tidman N., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Skeggs D. B., Panjwani D., Ball S. Depletion of T lymphocytes in donor marrow prevents significant graft-versus-host disease in matched allogeneic leukaemic marrow transplant recipients. Lancet. 1984 Mar 3;1(8375):472–476. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92848-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Chopek M., Chao S., McDonald T., Schwartz S. M. Injury induces increase of von Willebrand factor in rat endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):857–864. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. E., Lerner K. G., Barker E. A., Shulman H. M., Thomas E. D. The skin biopsy in the diagnosis of acute graft-versus-host disease in man. Am J Pathol. 1977 Dec;89(3):621–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidky Y. A., Auerbach R. Lymphocyte-induced angiogenesis: a quantitative and sensitive assay of the graft-vs.-host reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 May 1;141(5):1084–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.5.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin R. E., Santos G. W. The graft versus host reaction in man after bone marrow transplantation: pathology, pathogenesis, clinical features, and implication. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Jul;1(4):472–498. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snover D. C., Freese D. K., Sharp H. L., Bloomer J. R., Najarian J. S., Ascher N. L. Liver allograft rejection. An analysis of the use of biopsy in determining outcome of rejection. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987 Jan;11(1):1–10. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198701000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snover D. C., Weisdorf S. A., Ramsay N. K., McGlave P., Kersey J. H. Hepatic graft versus host disease: a study of the predictive value of liver biopsy in diagnosis. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn L. A., Rubin P., Marder V. J., Wagner D. D. Irradiation induces release of von Willebrand protein from endothelial cells in culture. Blood. 1984 Aug;64(2):567–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., Klempnauer J. Distinct histologic patterns of acute, prolonged, and chronic rejection in vascularized rat pancreas allografts. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):253–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suitters A. J., Lampert I. A. Class II antigen induction in the liver of rats with graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation. 1984 Aug;38(2):194–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker K. Z., Schoefl G. I., Lafferty K. J., Adams E. P. Pathogenesis of the graft-versus-host reaction in chicken embryos. The development of haemorrhagic lesions. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Feb;51(1):93–107. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Moore S. B., Gastineau D. A., Hoagland H. C. Immunologic, clinical, and pathologic aspects of human graft-versus-host disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1983 Sep;58(9):603–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L. Increased factor VIII related antigen in cerebral thrombosis. Thromb Res. 1983 Nov 1;32(3):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]