Abstract
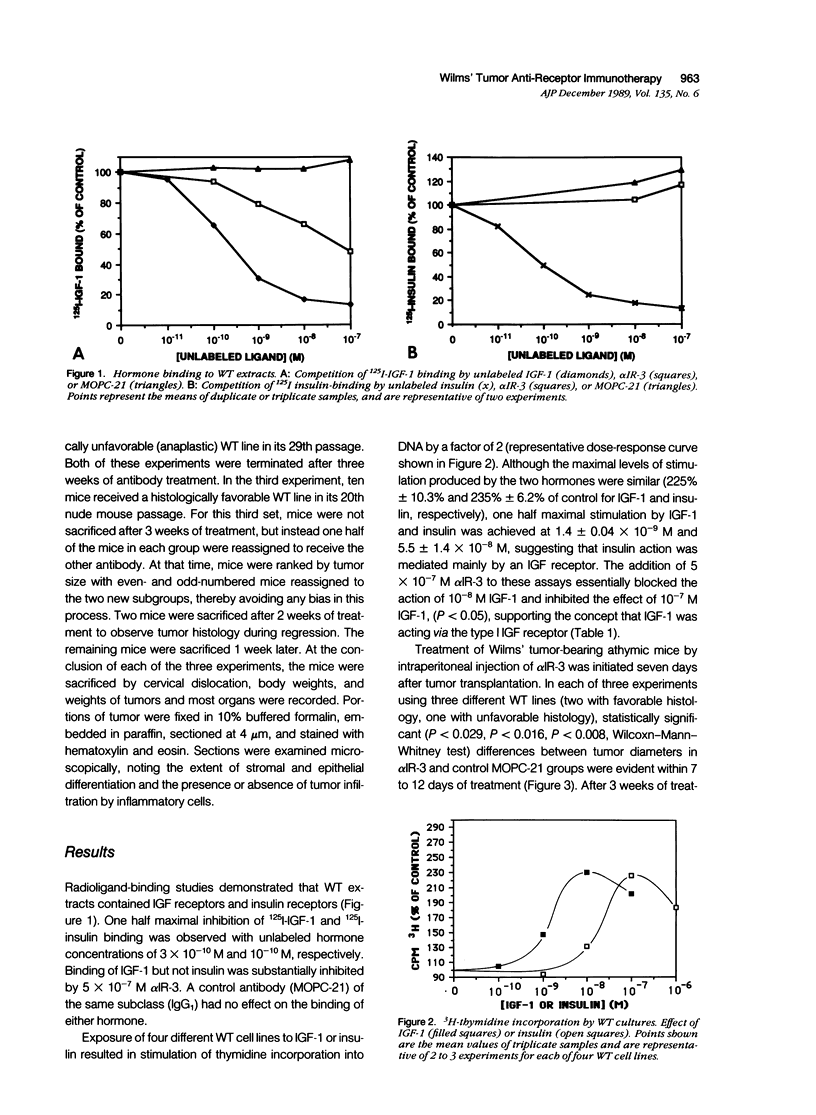
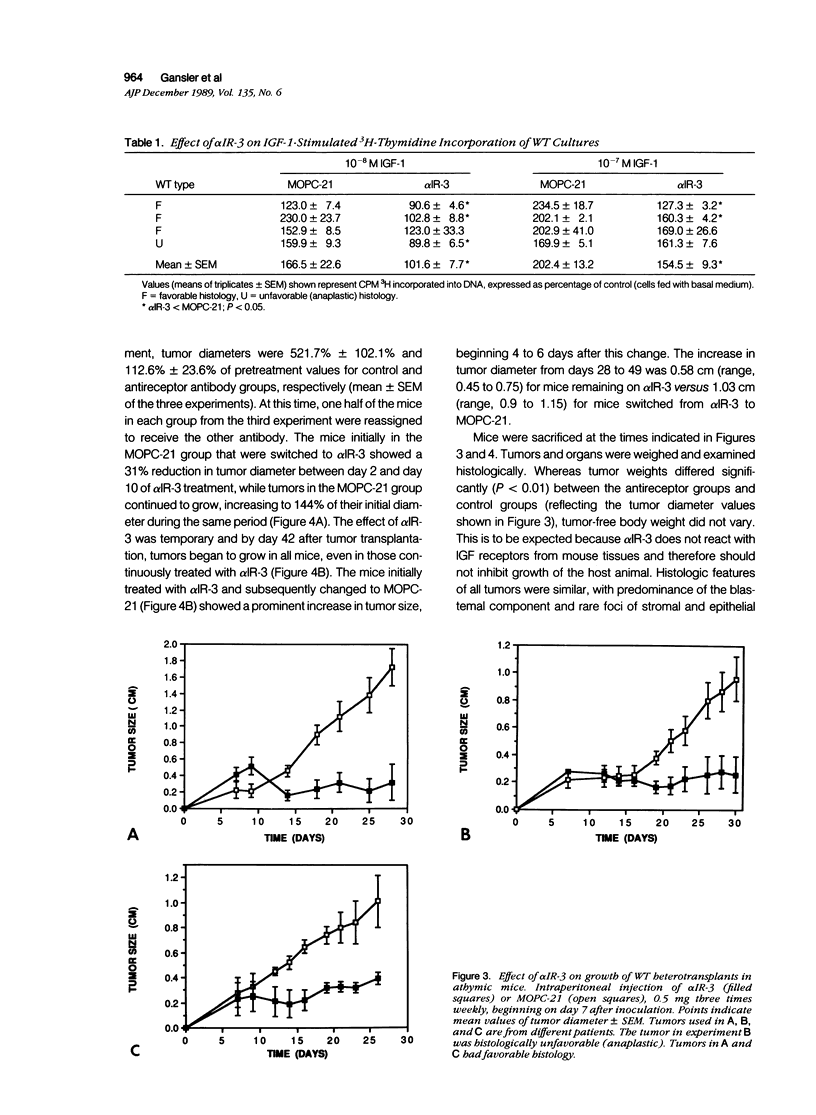
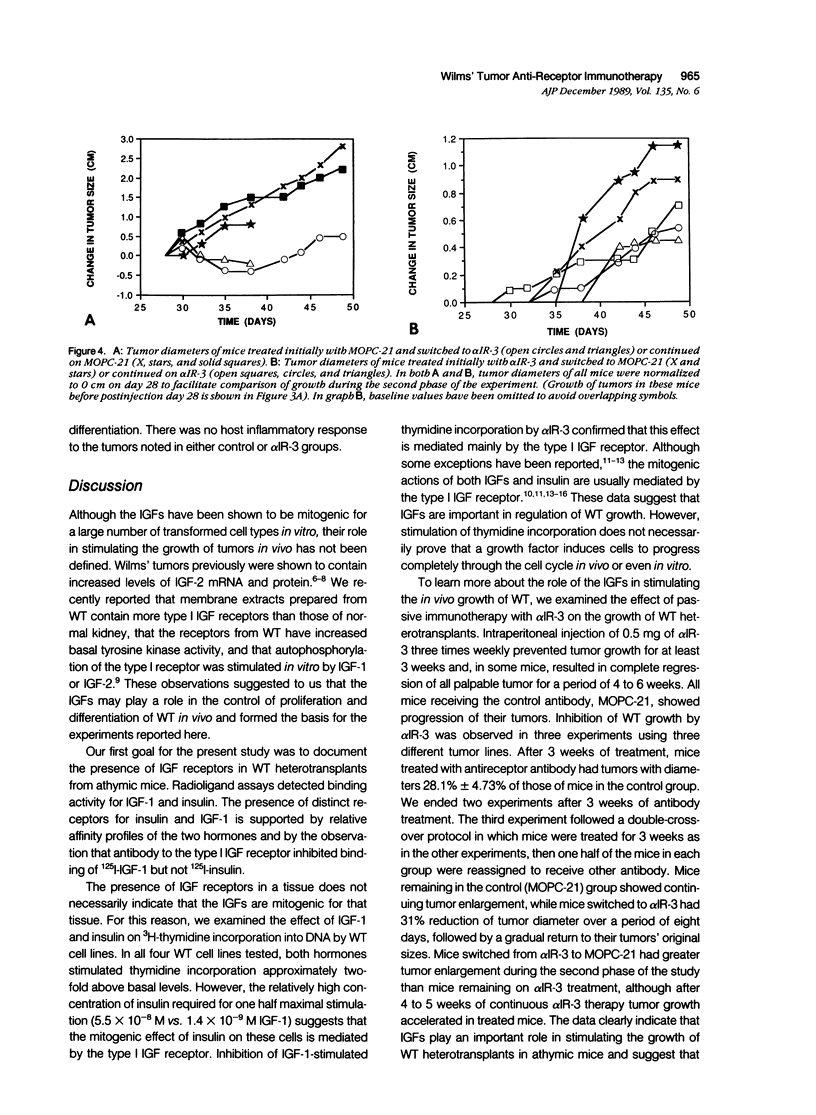
The role of the type I insulinlike growth factor (IGF) receptor in regulating growth of Wilms' tumor (WT) was evaluated by examining the effect of antibody-mediated inhibition of this receptor on tumor growth in cell cultures and as heterotransplants in athymic mice. An antibody to the human type I IGF receptor (alpha IR-3) inhibited 125I-IGF-1 binding and prevented stimulation of thymidine incorporation by IGF-1 in vitro. Intraperitoneal administration of alpha IR-3 to nude mice bearing WT heterotransplants prevented tumor growth for 4 weeks and resulted in partial regression of established tumors. These data indicate the importance of IGF action in control of WT growth in vivo, and suggest potential therapeutic application using antigrowth factor receptor antibodies to block growth factor action.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckwith J. B. Wilms' tumor and other renal tumors of childhood: a selective review from the National Wilms' Tumor Study Pathology Center. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jun;14(6):481–492. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Usher P., Moses A. C. Monoclonal antibody to the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) receptor blocks IGF-I receptor-mediated DNA synthesis: clarification of the mitogenic mechanisms of IGF-I and insulin in human skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W., DiCarlo J. N., Wisehart C. The type II insulin-like growth factor receptor does not mediate deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in human fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1142–1149. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gansler T., Allen K. D., Burant C. F., Inabnett T., Scott A., Buse M. G., Sens D. A., Garvin A. J. Detection of type 1 insulinlike growth factor (IGF) receptors in Wilms' tumors. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):431–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. J., Congleton L., Inabnett T., Gansler T., Sens D. A. Growth characteristics of human Wilms' tumor in nude mice. Pediatr Pathol. 1988;8(6):599–615. doi: 10.3109/15513818809022317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvin A. J., Sullivan J. L., Bennett D. D., Stanley W. S., Inabnett T., Sens D. A. The in vitro growth, heterotransplantation, and immunohistochemical characterization of the blastemal component of Wilms' tumor. Am J Pathol. 1987 Nov;129(2):353–363. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Irminger J. C., Zapf J., Ziegler W. H., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor II in human adrenal pheochromocytomas and Wilms tumors: expression at the mRNA and protein level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1104–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Edman J. C., Standring D. N., Fried V. A., Smith M. C., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Insulin-like growth factor II receptor as a multifunctional binding protein. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):301–307. doi: 10.1038/329301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., Czech M. P. The type II insulin-like growth factor receptor does not mediate increased DNA synthesis in H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12705–12713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve A. E., Eccles M. R., Wilkins R. J., Bell G. I., Millow L. J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II transcripts in Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):258–260. doi: 10.1038/317258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Cowell J., Robertson M. E., Priestley L. M., Wadey R., Hopkins B., Pritchard J., Bell G. I., Rall L. B., Graham C. F. Insulin-like growth factor-II gene expression in Wilms' tumour and embryonic tissues. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):260–262. doi: 10.1038/317260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally M., Li C. H., Hall K. IGF-2 stimulated growth mediated by the somatomedin type 2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):811–816. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90948-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyk J. J., Graves D. C., Casella S. J., Jacobs S. Evidence from monoclonal antibody studies that insulin stimulates deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis through the type I somatomedin receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):639–643. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


