Abstract
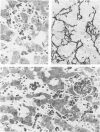
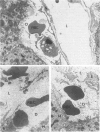
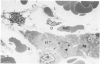
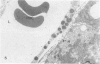
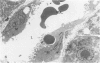
The description of hepatic sinusoidal lesions in a significant number of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients prompted the authors to undertake an ultrastructural study of the sinusoidal barrier abnormalities during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, in order to compare these lesions with those described in other conditions and to discuss their possible origin. In a series of 29 patients with serologic evidence of HIV infection and liver abnormalities, 8 (28%) had sinusoidal lesions. Peliosis hepatis was present in 2 cases, and sinusoidal dilatation in 6. These patients were classified as follows: 3 AIDS, 4 AIDS-related complex, 1 unclassifiable. Ultrastructural lesions of the sinusoidal barrier were observed in all the cases. They closely mimicked the changes previously reported in peliotic and peliotic-like changes of various origins. A striking particularity was, however, the presence of numerous and hyperplastic sinusoidal macrophages. This work suggests that an injury of the endothelial cells, directly or indirectly related to the presence of HIV, may be incriminated in the pathogenesis of sinusoidal lesions during HIV infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardadin K. A., Desmet V. J. Ultrastructural observations on sinusoidal endothelial cells in chronic active hepatitis. Histopathology. 1985 Feb;9(2):171–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1985.tb02433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardadin K. A., Scheuer P. J. Endothelial cell changes in acute hepatitis. A light and electron microscopic study. J Pathol. 1984 Nov;144(3):213–220. doi: 10.1002/path.1711440308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergs V. V., Scotti T. M. Virus-induced peliosis hepatitis in rats. Science. 1967 Oct 20;158(3799):377–378. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3799.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bioulac-Sage P., Roux D., Quinton A., Lamouliatte H., Balabaud C. Ultrastructure of sinusoids in patients with agnogenic myeloid metaplasia. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1986 Oct;18(4):815–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruguera M., Aranguibel F., Ros E., Rodés J. Incidence and clinical significance of sinusoidal dilatation in liver biopsies. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):474–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czapar C. A., Weldon-Linne C. M., Moore D. M., Rhone D. P. Peliosis hepatis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Jul;110(7):611–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darne C., Solal-Celigny P., Herrera A., Ramond M. J., Brun-Vezinet F., Brousse N., Boivin P. Acute myelofibrosis and infection with the lymphadenopathy-associated virus/human T-lymphotropic virus type III. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jan;104(1):130–131. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-1-130_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degott C., Rueff B., Kreis H., Duboust A., Potet F., Benhamou J. P. Peliosis hepatis in recipients of renal transplants. Gut. 1978 Aug;19(8):748–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.8.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes H. P., Popper H., Arnold W., Lobeck H. Histologic observations in human hepatitis non-A, non-B. Hepatology. 1982 Sep-Oct;2(5):562–571. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy L. F., Daum F., Kahn E., Teichberg S., Pahwa R., Fagin J., Kenigsberg K., Kaplan M., Fisher S. E., Pahwa S. Hepatitis in children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Histopathologic and immunocytologic features. Gastroenterology. 1986 Jan;90(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow B. J., Anders K., Layfield L. J., Steinsapir K. D., Gitnick G. L., Lewin K. J. Clinical and pathologic findings of the liver in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 May;83(5):582–588. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.5.582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S. C., Reddy K. R., Gould E. E., McFadden R., O'Brien C., De Medina M., Jeffers L. J., Schiff E. R. The spectrum of liver disease in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Hepatol. 1986;2(3):475–484. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(86)80059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarda L. A., Luna M. A., Smith J. L., Jr, Mansell P. W., Gyorkey F., Roca A. N. Acquired immune deficiency syndrome: postmortem findings. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 May;81(5):549–557. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.5.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):513–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirn A., Gut J. P., Gendrault J. L. Interaction of viruses with sinusoidal cells. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:377–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebovics E., Thung S. N., Schaffner F., Radensky P. W. The liver in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a clinical and histologic study. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):293–298. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Ziegler J. L. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is an opportunistic infection and Kaposi's sarcoma results from secondary immune stimulation. Lancet. 1983 Jul 9;2(8341):78–81. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marche C., Devars J. F., Penalba C., Bouton C., Vittecoq D., Cerf M. Les lésions hépatiques du SIDA. Arch Anat Cytol Pathol. 1984;32(2):120–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanuma Y., Liew C. T., Peters R. L., Govindarajan S. Pathologic features of the liver in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Liver. 1986 Jun;6(3):158–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1986.tb00283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedt G. W., Schinella R. A. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clinicopathologic study of 56 autopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Aug;109(8):727–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. M., Dubuisson L., Quinton A., Bioulac-Sage P., Balabaud C. Benign recurrent cholestasis: a light and electron microscopic study with emphasis on sinusoidal cells. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1987;11(1):11–17. doi: 10.3109/01913128709023178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert C. M., O'Leary T. J., Levens D. L., Simrell C. R., Macher A. M. Autopsy pathology in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1983 Sep;112(3):357–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. C., Kovacs K., Horvath E. Ultrastructure of peliosis hepatis in a percutaneous biopsy. Pathol Eur. 1972;7(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgers J. L., Wieczorek R., Bonetti F., Kaplan K. L., Posnett D. N., Friedman-Kien A. E., Knowles D. M., 2nd The expression of endothelial cell surface antigens by AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Evidence for a vascular endothelial cell origin. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):493–499. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taxy J. B. Peliosis: a morphologic curiosity becomes an iatrogenic problem. Hum Pathol. 1978 May;9(3):331–340. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verme G., Amoroso P., Lettieri G., Pierri P., David E., Sessa F., Rizzi R., Bonino F., Recchia S., Rizzetto M. A histological study of hepatitis delta virus liver disease. Hepatology. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):1303–1307. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi T., Onda H., Tada T., Iijima M., Itoh Y. High incidence of peliosis hepatis in autopsy cases of aplastic anemia with special reference to anabolic steroid therapy. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1984 Sep;34(5):1079–1086. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1984.tb07637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. F., O'Loughlin S. Kaposi's sarcoma: a byproduct of tumour rejection. Lancet. 1975 Oct 11;2(7937):687–689. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90780-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch K., Finkbeiner W., Alpers C. E., Blumenfeld W., Davis R. L., Smuckler E. A., Beckstead J. H. Autopsy findings in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1984 Sep 7;252(9):1152–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK F. G. Peliosis hepatis. Am J Pathol. 1950 Jan;26(1):1-15, incl 2 pl. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafrani E. S., Bernuau D., Feldmann G. Peliosis-like ultrastructural changes of the hepatic sinusoids in human chronic hypervitaminosis A: report of three cases. Hum Pathol. 1984 Dec;15(12):1166–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80311-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafrani E. S., Cazier A., Baudelot A. M., Feldmann G. Ultrastructural lesions of the liver in human peliosis. A report of 12 cases. Am J Pathol. 1984 Mar;114(3):349–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafrani E. S., Degos F., Guigui B., Durand-Schneider A. M., Martin N., Flandrin G., Benhamou J. P., Feldmann G. The hepatic sinusoid in hairy cell leukemia: an ultrastructural study of 12 cases. Hum Pathol. 1987 Aug;18(8):801–807. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zafrani E. S., von Pinaudeau Y., Dhumeaux D. Drug-induced vascular lesions of the liver. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Mar;143(3):495–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]