Abstract
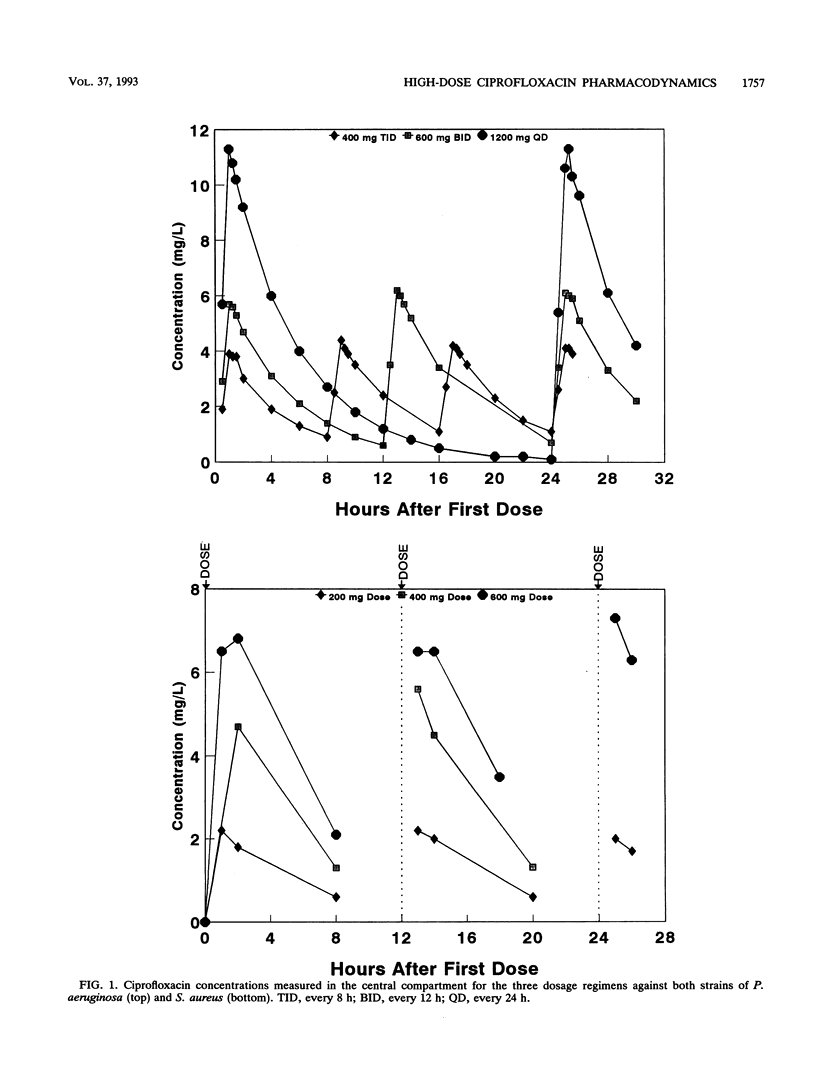
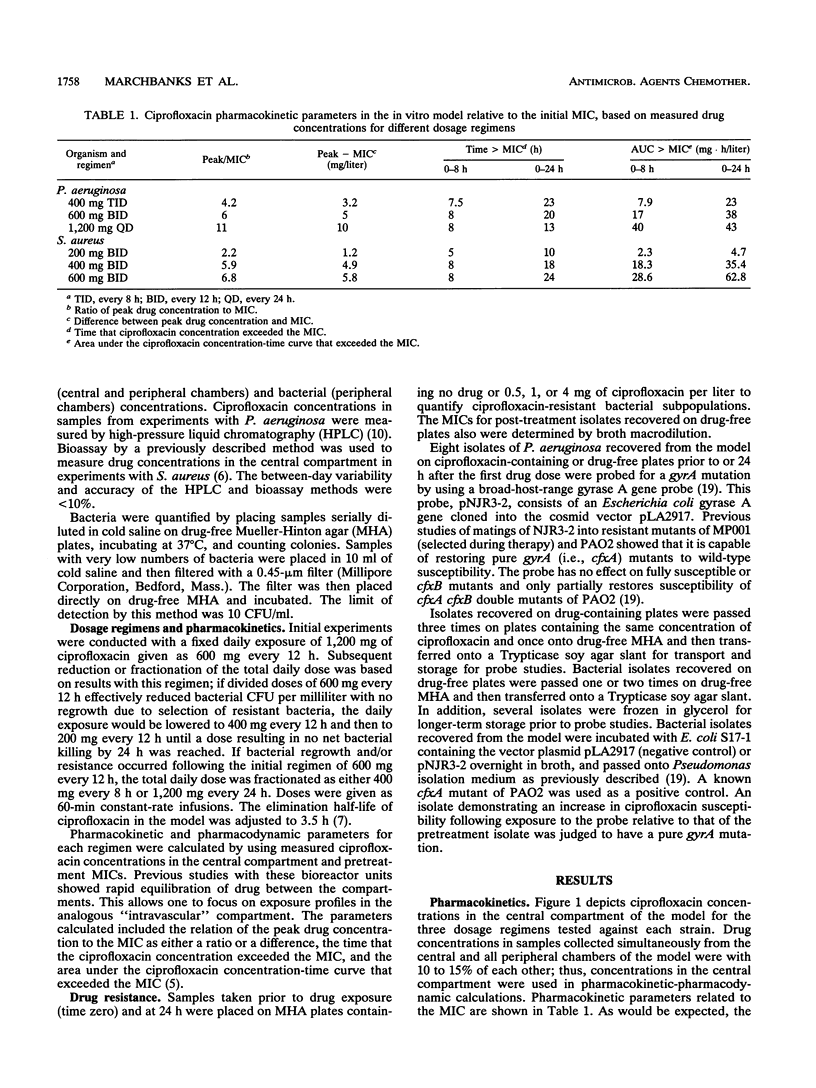
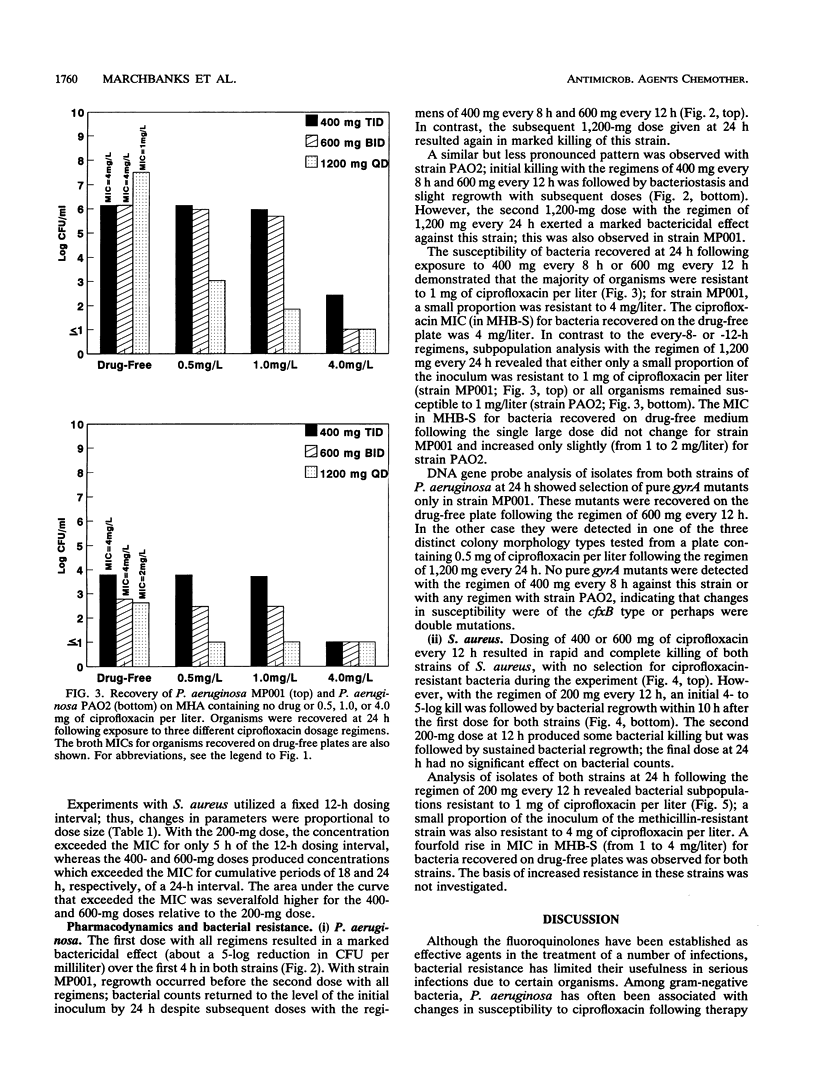
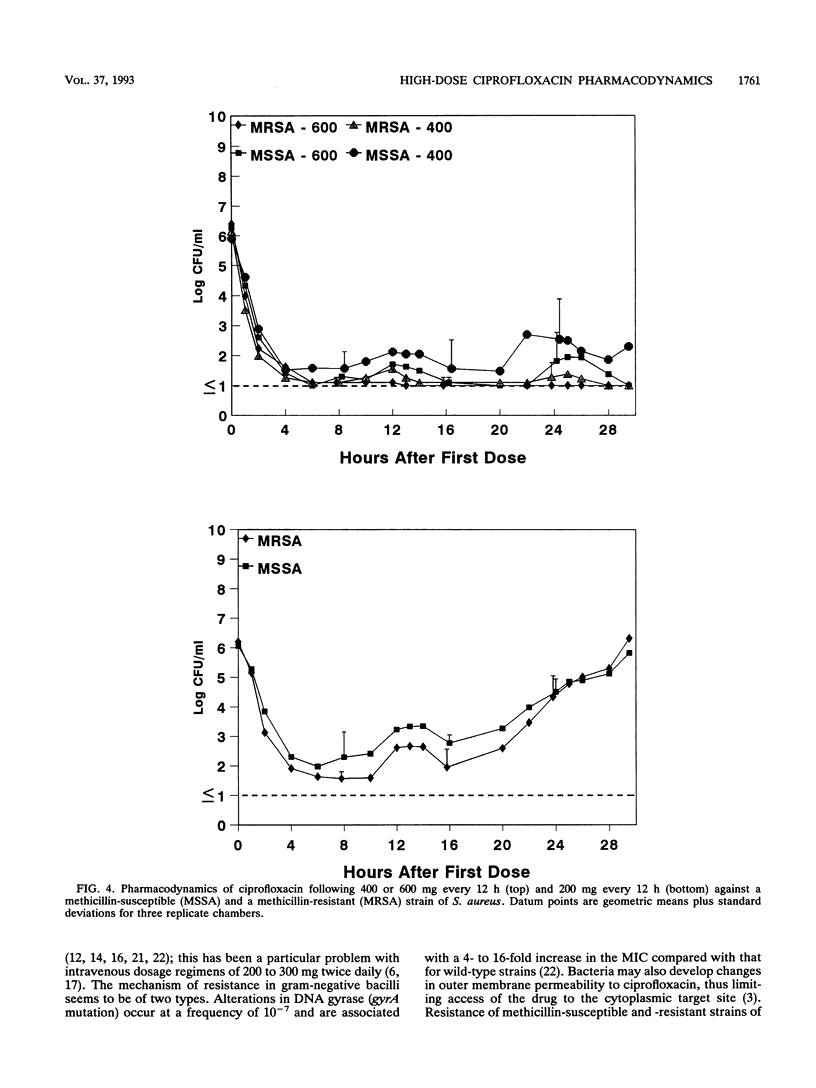
The effect of dose or dose interval on the pharmacodynamics of simulated high-dose intravenous ciprofloxacin therapy on infection due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus was studied in an in vitro hollow-fiber model of infection. Simulated doses of 1,200 mg of ciprofloxacin per day as either 400 mg every 8 h or 600 mg every 12 h against P. aeruginosa resulted in selection of ciprofloxacin-resistant bacteria. The results with one test strain that was isolated from a patient prior to administration of intravenous ciprofloxacin demonstrated selection of a gyrA mutant in the model, as had occurred in vivo. A single 1,200-mg dose every 24 h did not select for bacterial resistance; however, breakthrough regrowth of ciprofloxacin-susceptible bacteria occurred. Dosages of 400 or 600 mg of ciprofloxacin every 12 h effectively reduced bacterial counts of one strain each of methicillin-susceptible or -resistant S. aureus, with no bacterial resistance detected at the end of experiment; in contrast, 200 mg every 12 h resulted in bacterial regrowth due to the selection of drug-resistant bacteria. These data show the need for high-dose intravenous ciprofloxacin, particularly with regimens producing high peak levels, for treatment of infections where selection for bacterial resistance is a clinical problem.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser J., Stone B. B., Groner M. C., Zinner S. H. Comparative study with enoxacin and netilmicin in a pharmacodynamic model to determine importance of ratio of antibiotic peak concentration to MIC for bactericidal activity and emergence of resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser J., Stone B. B., Zinner S. H. Two compartment kinetic model with multiple artificial capillary units. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):131–137. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Lolans V. T., Jackson G. G. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusano G. L., Johnson D. E., Rosen M., Standiford H. C. Pharmacodynamics of a fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent in a neutropenic rat model of Pseudomonas sepsis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):483–490. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Blaser J., Gilbert D., Mayer K. H., Zinner S. H. Combination therapy with ciprofloxacin plus azlocillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: effect of simultaneous versus staggered administration in an in vitro model of infection. J Infect Dis. 1991 Sep;164(3):499–506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.3.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Ericson J., Zinner S. H. Effect of dose on serum pharmacokinetics of intravenous ciprofloxacin with identification and characterization of extravascular compartments using noncompartmental and compartmental pharmacokinetic models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1782–1786. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of antibiotics with special reference to the fluoroquinolones. Am J Med. 1991 Dec 30;91(6A):45S–50S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90311-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., Harvey L., Hixon D. L., Poretz D. M. Ciprofloxacin therapy of infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):308–310. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Ebert S., Fantin B., Craig W. A. Comparative dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals for beta-lactam, aminoglycoside and quinolone antibiotics against gram-negative bacilli in murine thigh-infection and pneumonitis models. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:179–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masecar B. L., Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Analysis of acquired ciprofloxacin resistance in a clinical strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):281–286. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier F., Zinner S. H., Gaya H., Calandra T., Viscoli C., Klastersky J., Glauser M. Prospective randomized evaluation of ciprofloxacin versus piperacillin plus amikacin for empiric antibiotic therapy of febrile granulocytopenic cancer patients with lymphomas and solid tumors. The European Organization for Research on Treatment of Cancer International Antimicrobial Therapy Cooperative Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):873–878. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michéa-Hamzehpour M., Auckenthaler R., Regamey P., Pechère J. C. Resistance occurring after fluoroquinolone therapy of experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1803–1808. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Reller L. B., Vasil M. L. Development of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem, norfloxacin, and ciprofloxacin during therapy: proof provided by typing with a DNA probe. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):743–748. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peloquin C. A., Cumbo T. J., Nix D. E., Sands M. F., Schentag J. J. Evaluation of intravenous ciprofloxacin in patients with nosocomial lower respiratory tract infections. Impact of plasma concentrations, organism, minimum inhibitory concentration, and clinical condition on bacterial eradication. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Oct;149(10):2269–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. M., Batten J., Hodson M. E. Ciprofloxacin-resistant Pseudomonas. Lancet. 1985 Jun 22;1(8443):1442–1442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91862-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J. Broad-host-range gyrase A gene probe. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1889–1894. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully B. E., Neu H. C., Parry M. F., Mandell W. Oral ciprofloxacin therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1986 Apr 12;1(8485):819–822. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90937-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Bacterial resistance to quinolones: mechanisms and clinical importance. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S960–S968. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., Shih D. J., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Isolation and characterization of an Escherichia coli strain exhibiting partial tolerance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):705–709. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


