Abstract
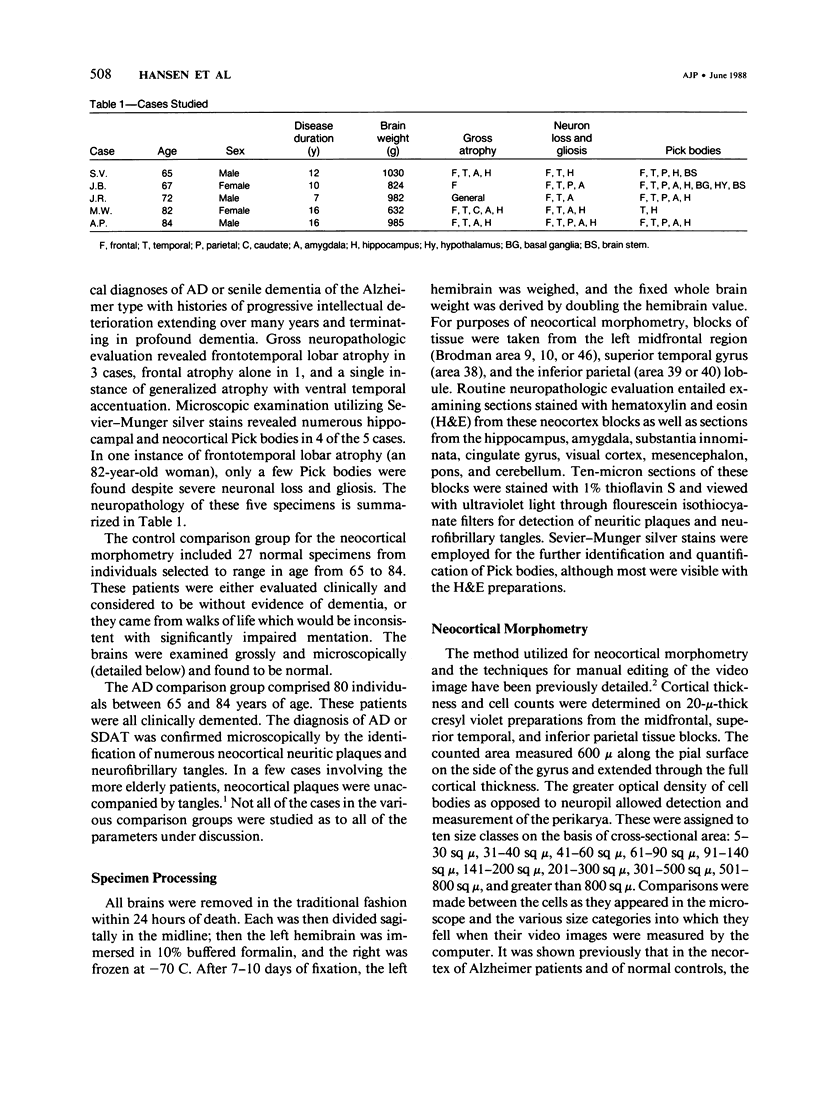
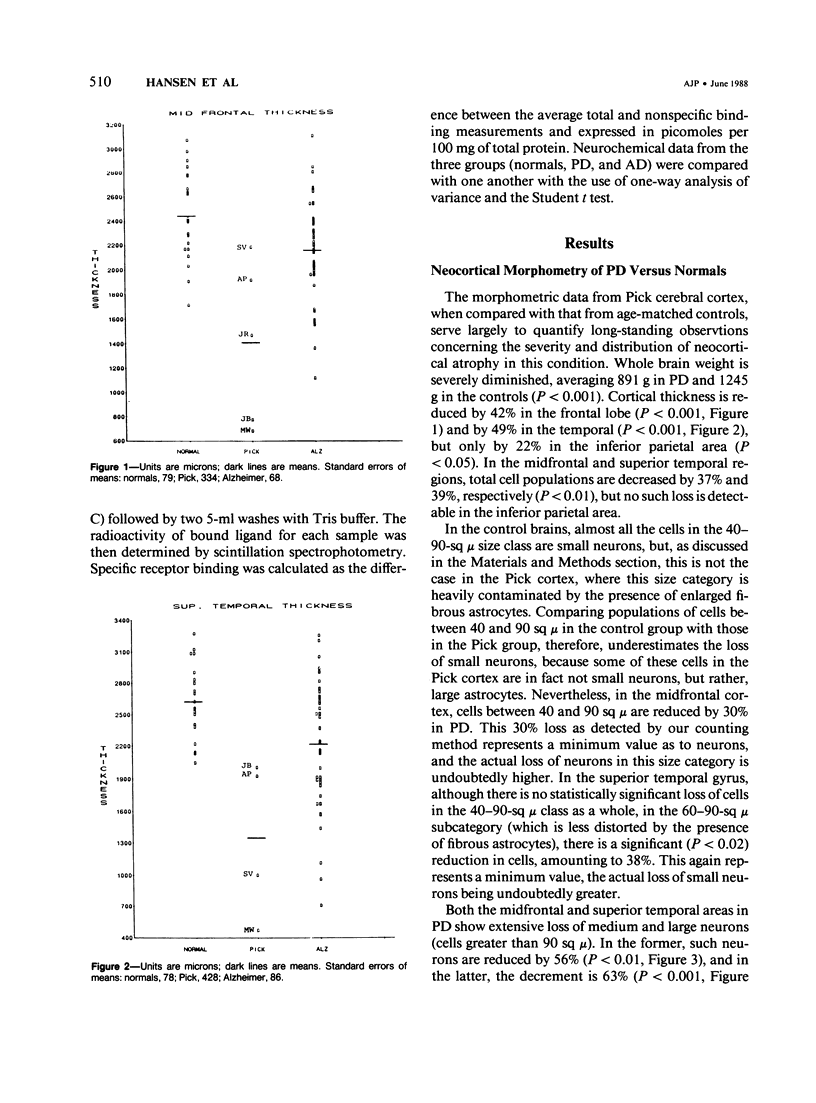
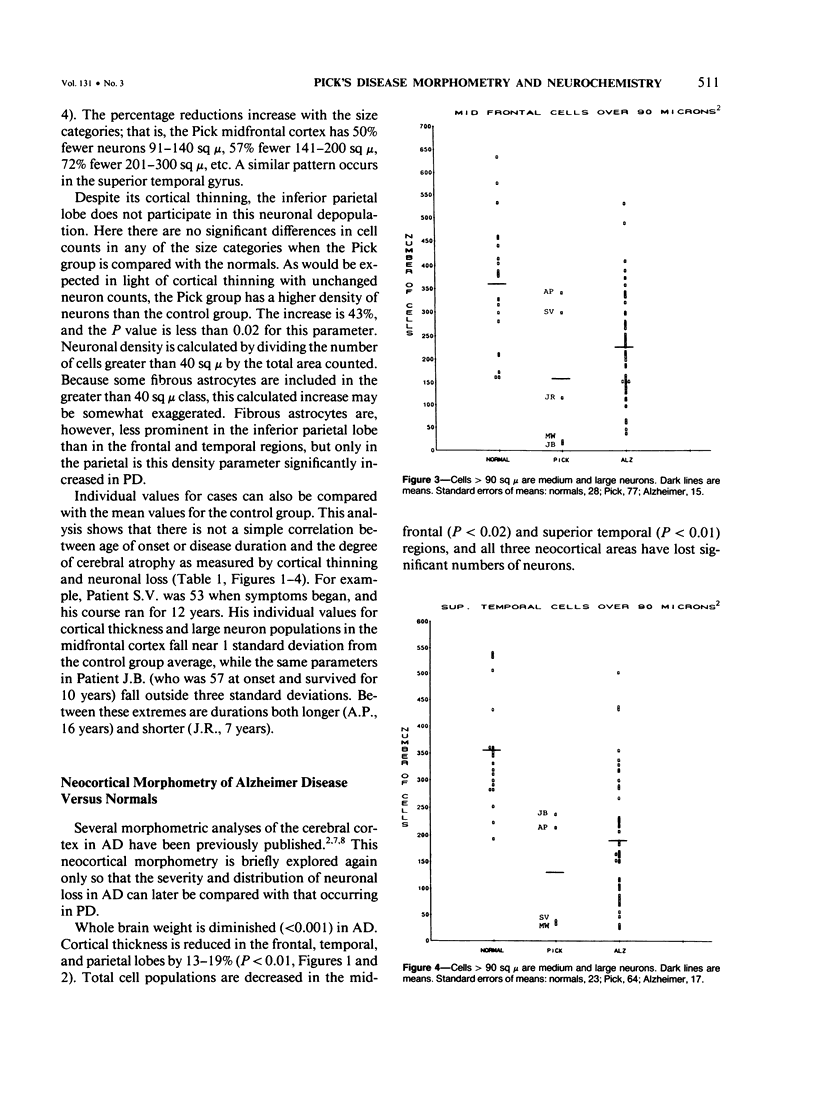
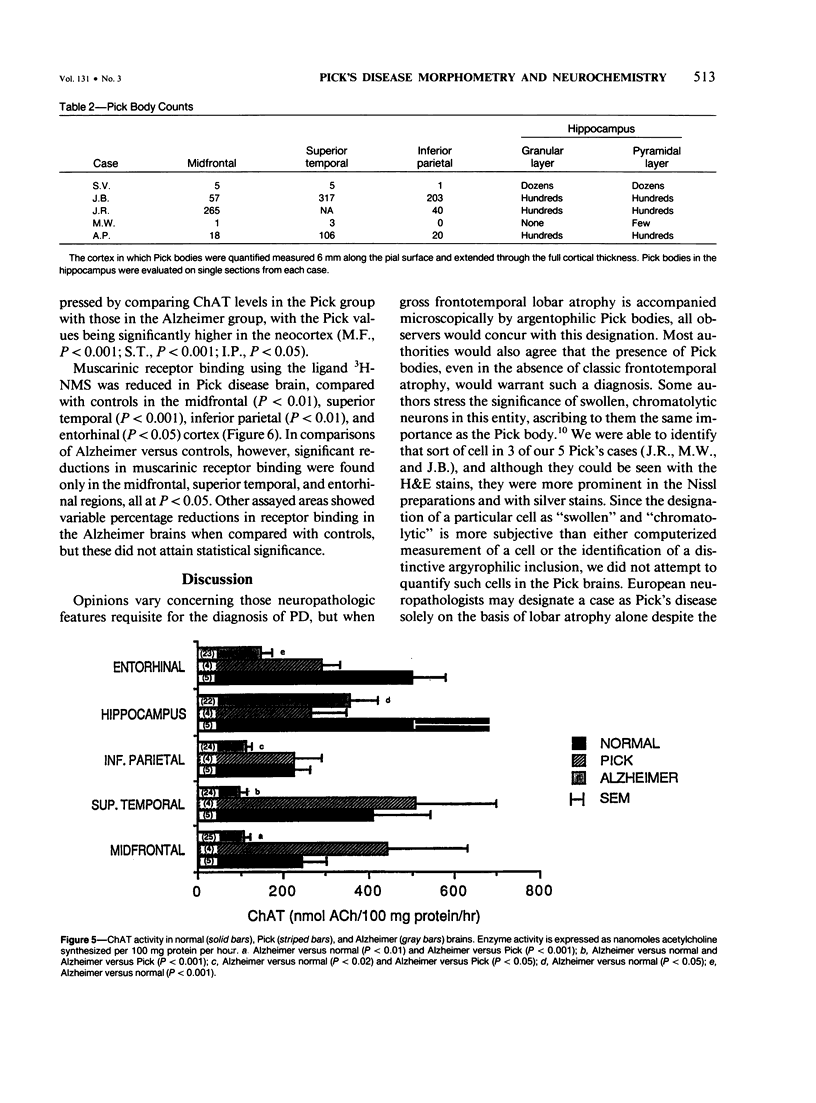
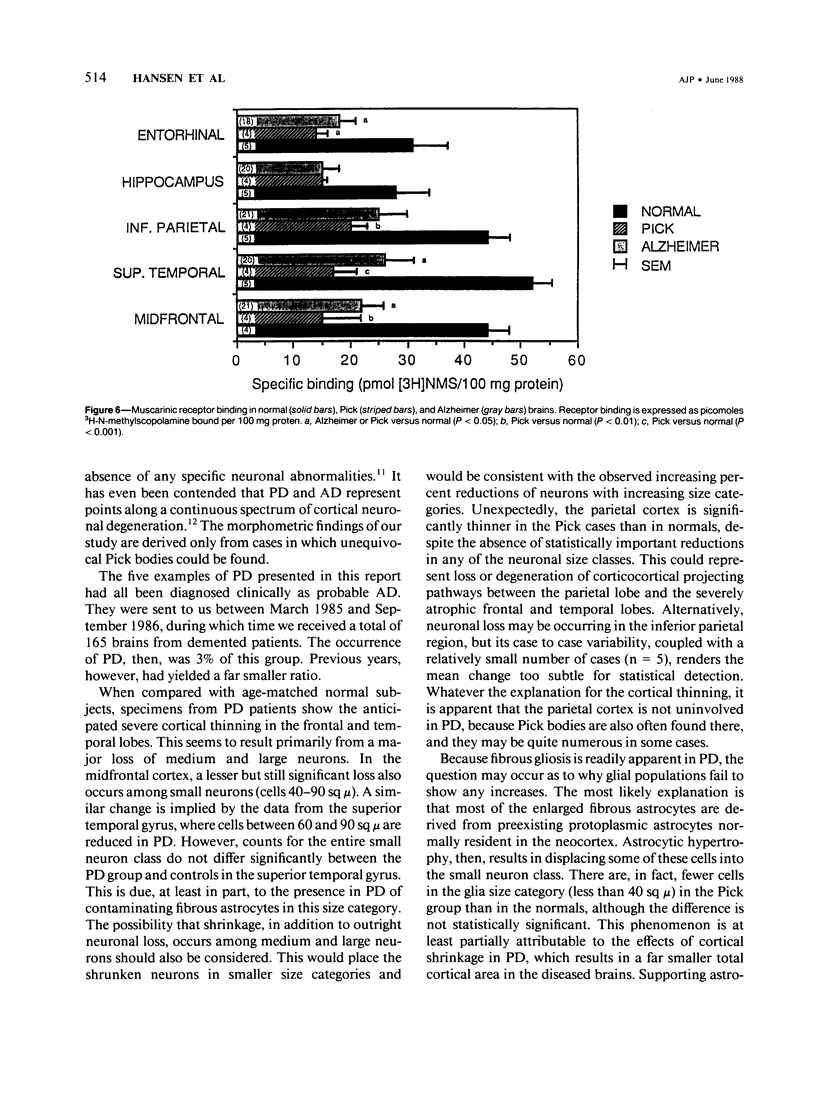
With a computerized image-analysis apparatus for neocortical morphometry and chemical methods for evaluation of the cholinergic system, five brain specimens of Pick's disease (PD) were studied and the results compared to those from specimens of age-matched normal subjects and Alzheimer's disease (AD). The PD specimens showed major reductions in brain weight, frontal and temporal cortical thickness, and large neuron populations, compared with controls. Lesser reductions were seen in small neurons and thickness of the inferior parietal cortex. The authors found no relationship between age of onset or disease duration and either the degree of cortical thinning or neuron loss or the number of Pick bodies in the neocortex and hippocampus. PD specimens were more atrophic than AD brains, having lower brain weights and more fronto-temporal thinning. Large neurons were comparably reduced in the two conditions in the frontal and temporal lobes, but small neuron losses were greater in the PD midfrontal area. Only the AD cases showed loss of large neurons in the inferior parietal region. Levels of choline acetyltransferase were normal in PD and reduced in AD, whereas muscarinic receptor binding was decreased in both.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen D. M., Benton J. S., Spillane J. A., Smith C. C., Allen S. J. Choline acetyltransferase activity and histopathology of frontal neocortex from biopsies of demented patients. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Dec;57(2-3):191–202. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen D. M., Smith C. B., White P., Davison A. N. Neurotransmitter-related enzymes and indices of hypoxia in senile dementia and other abiotrophies. Brain. 1976 Sep;99(3):459–496. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.3.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. W., Manz H. J., White C. L., 3rd, Lehmann J., Miller D., Coyle J. T. Cortical degeneration with swollen chromatolytic neurons: its relationship to Pick's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1986 May;45(3):268–284. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198605000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinidis J., Richard J., Tissot R. Pick's disease. Histological and clinical correlations. Eur Neurol. 1974;11(4):208–217. doi: 10.1159/000114320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Feisullin S. A search for discrete cholinergic nuclei in the human ventral forebrain. J Neurochem. 1982 Dec;39(6):1743–1747. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Maloney A. J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1403–1403. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91936-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. Neurotransmitter-related enzymes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 3;171(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Verth A. H. Regional distribution of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in normal and Alzheimer's-type dementia brains. Brain Res. 1977 Dec 16;138(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90758-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonnum F. Radiochemical micro assays for the determination of choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj1150465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamo H., McGeer P. L., Harrop R., McGeer E. G., Calne D. B., Martin W. R., Pate B. D. Positron emission tomography and histopathology in Pick's disease. Neurology. 1987 Mar;37(3):439–445. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O., Marcyniuk B. A comparison of changes in the nucleus basalis and locus caeruleus in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Feb;47(2):201–203. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O., Marcyniuk B. Changes in nerve cells of the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease and their relationship to ageing and to the accumulation of lipofuscin pigment. Mech Ageing Dev. 1984 Apr-May;25(1-2):189–204. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(84)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O., Marcyniuk B. Some morphometric observations on the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in presenile Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia of Alzheimer type and Down's syndrome in middle age. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Jul;69(3):139–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. C., Cole M., Banker B. Q., Wright D. Hereditary dysphasic dementia and the Pick-Alzheimer spectrum. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):455–466. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountjoy C. Q., Roth M., Evans N. J., Evans H. M. Cortical neuronal counts in normal elderly controls and demented patients. Neurobiol Aging. 1983 Spring;4(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(83)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Garcia D., Ludwin S. K. Classic and generalized variants of Pick's disease: a clinicopathological, ultrastructural, and immunocytochemical comparative study. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):467–480. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. C., Esiri M. M., Hiorns R. W., Wilcock G. K., Powell T. P. Anatomical correlates of the distribution of the pathological changes in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4531–4534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. D., Brogan D., Mirra S. S. The nucleus basalis of Meynert in neurological disease: a quantitative morphological study. Ann Neurol. 1985 Feb;17(2):163–170. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter R., Yen S. H., Terry R. D. Fibrous Astrocytes in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Mar;40(2):95–101. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198103000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Pilleri G. Basal nucleus of Meynert. A neuropathological study in Alzheimer's disease, simple senile dementia, Pick's disease and Huntington's chorea. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):243–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Hansen L. A., DeTeresa R., Davies P., Tobias H., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type without neocortical neurofibrillary tangles. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 May;46(3):262–268. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198705000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Peck A., DeTeresa R., Schechter R., Horoupian D. S. Some morphometric aspects of the brain in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1981 Aug;10(2):184–192. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl G. R., Hilt D. C., Hedreen J. C., Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L. Pick's disease (lobar sclerosis): depletion of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert. Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1470–1473. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P., Hiley C. R., Goodhardt M. J., Carrasco L. H., Keet J. P., Williams I. E., Bowen D. M. Neocortical cholinergic neurons in elderly people. Lancet. 1977 Mar 26;1(8013):668–671. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J. Neurotransmitter receptor alterations in Alzheimer disease: a review. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1987;1(1):9–18. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198701000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Etienne P., Lal S., Nair N. P., Finlayson M. H., Gauthier S., Palo J., Haltia M., Paetau A., Bird E. D. A post-mortem comparison of the cortical cholinergic system in Alzheimer's disease and Pick's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates C. M., Simpson J., Maloney A. F., Gordon A. Neurochemical observations in a case of Pick's disease. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Nov;48(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]