Abstract
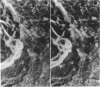
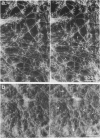
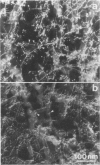
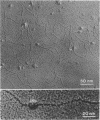
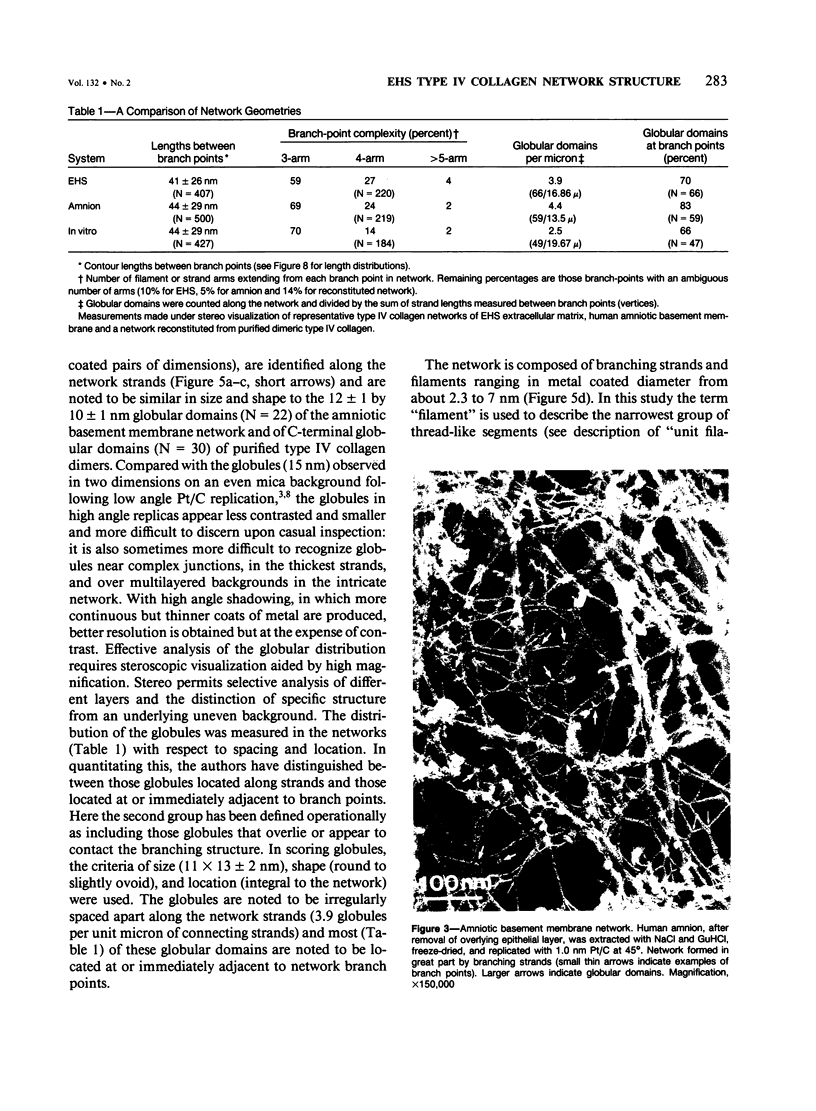
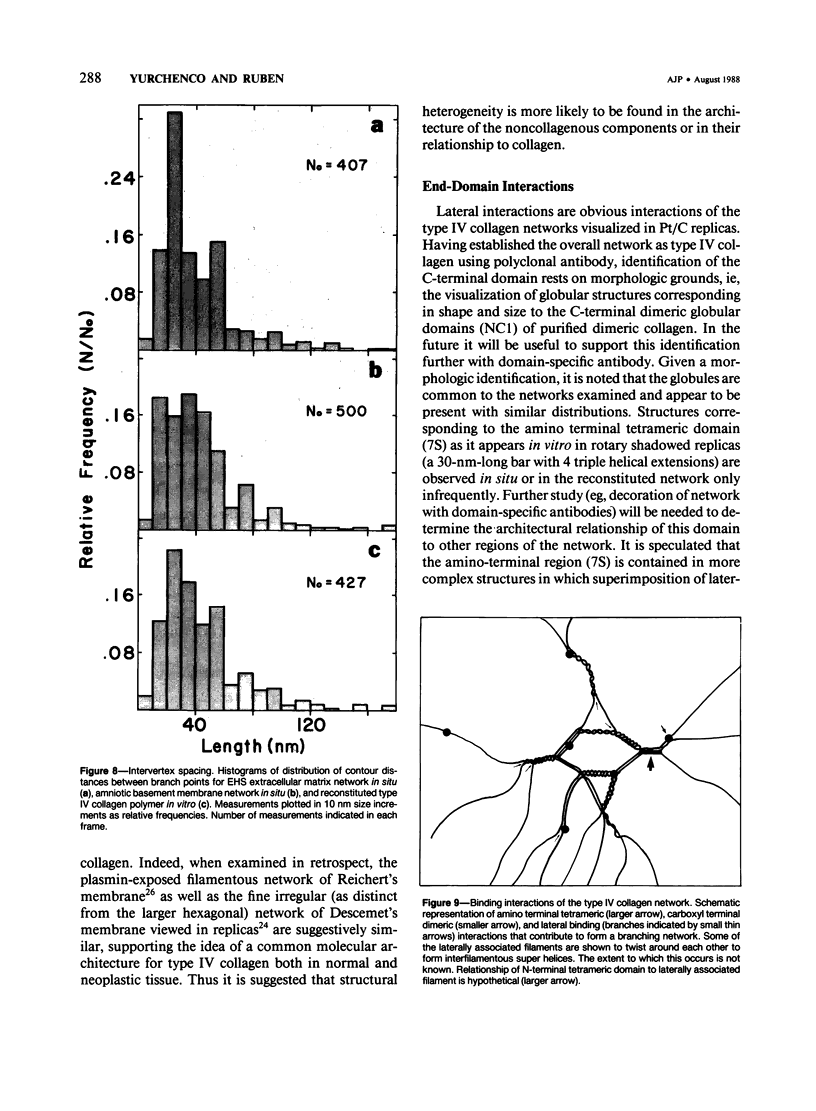
The macromolecular structural organization of the type IV collagen network in the extracellular matrix of the EHS tumor has been investigated using a stereoscopic freeze-dry Pt/C replication technique. This network, which can be specifically decorated with type IV collagen antibody, is formed in great part by the lateral joining of narrow filaments (2.7 nm average metal coated diameter) to form a complex three-dimensional irregular polygonal array of variable diameter branching strands. Globular domains, similar to the C-terminal globular domains of purified type IV dimers, can be identified in the network. In many regions of the network the filaments appear to twist around each other along the strand axis. The network is similar to that visualized in the human amnion as well as to a reconstituted network formed in vitro. These data strongly suggest that the laterally and end-domain-associated network is a widespread supramolecular architecture of type IV collagen in basement membranes.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babel W., Glanville R. W. Structure of human-basement-membrane (type IV) collagen. Complete amino-acid sequence of a 914-residue-long pepsin fragment from the alpha 1(IV) chain. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):545–556. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard K., Gathercole L. J., Bailey A. J. Basement membrane collagen--evidence for a novel molecular packing. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81554-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk D. E., Fitch J. M., Babiarz J. P., Linsenmayer T. F. Collagen type I and type V are present in the same fibril in the avian corneal stroma. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):999–1008. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson E. C., Meezan E., Brendel K., Kenney M. C. Ultrastructural analyses of control and enzyme-treated isolated renal basement membranes. Anat Rec. 1981 Aug;200(4):421–436. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Hayes B. P. Macromolecular organization of collagen fibres in natural and tanned basement membrane. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):263–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Lustig A., Engel J. Structure and interactions of heparan sulfate proteoglycans from a mouse tumor basement membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):145–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Wiedemann H., Timpl R., Odermatt E., Engel J. Electron-microscopical approach to a structural model of intima collagen. Biochem J. 1983 May 1;211(2):303–311. doi: 10.1042/bj2110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville R. W., Qian R. Q., Siebold B., Risteli J., Kühn K. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal aggregation and cross-linking region (7S domain) of the alpha 1 (IV) chain of human basement membrane collagen. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):213–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H., Voss T., Kühn K., Engel J. Localization of flexible sites in thread-like molecules from electron micrographs. Comparison of interstitial, basement membrane and intima collagens. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):325–343. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Leblond C. P. The basement-membrane-like matrix of the mouse EHS tumor: I. Ultrastructure. Am J Anat. 1985 Dec;174(4):373–386. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001740402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Leblond C. P., Laurie G. W. Ultrastructure of Reichert's membrane, a multilayered basement membrane in the parietal wall of the rat yolk sac. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1524–1537. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Alper R., Clark C. C. Biochemistry and metabolism of basement membranes. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;61:167–228. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61998-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Basement membrane: structure function relationships. Ren Physiol. 1981;4(2-3):57–66. doi: 10.1159/000172806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., McGarvey M. L., Liotta L. A., Robey P. G., Tryggvason K., Martin G. R. Isolation and characterization of type IV procollagen, laminin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycan from the EHS sarcoma. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6188–6193. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Gibney E., Fitch J. M., Gross J., Mayne R. Thermal stability of the helical structure of type IV collagen within basement membranes in situ: determination with a conformation-dependent monoclonal antibody. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1405–1409. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan P. S., Spiro R. G. Macromolecular organization of basement membranes. Characterization and comparison of glomerular basement membrane and lens capsule components by immunochemical and lectin affinity procedures. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4328–4336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin R. W., Gehron P., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R., Valentine T., Swarm R. A murine tumor producing a matrix of basement membrane. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):204–220. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Aumailley M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Beck K., Engel J. Laminin-nidogen complex. Extraction with chelating agents and structural characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Yurchenco P. D., Ruben G. C., Engel J., Timpl R. Structure of low density heparan sulfate proteoglycan isolated from a mouse tumor basement membrane. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):297–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risteli J., Bächinger H. P., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. 7-S collagen: characterization of an unusual basement membrane structure. Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H. The fine structure of the bovine Descemet's membrane with special reference to biochemical nature. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;226(2):241–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00218356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D., Glanville R. W., Timpl R., Dixit S. N., Kang A. H. Sequence comparison of pepsin-resistant segments of basement-membrane collagen alpha 1(IV) chains from bovine lens capsule and mouse tumour. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):227–233. doi: 10.1042/bj2200227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Schuppan D., Oberbäumer I., Glanville R. W., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Kühn K. Structure of mouse type IV collagen. Amino-acid sequence of the C-terminal 511-residue-long triple-helical segment of the alpha 2(IV) chain and its comparison with the alpha 1(IV) chain. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebold B., Qian R. A., Glanville R. W., Hofmann H., Deutzmann R., Kühn K. Construction of a model for the aggregation and cross-linking region (7S domain) of type IV collagen based upon an evaluation of the primary structure of the alpha 1 and alpha 2 chains in this region. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Nov 2;168(3):569–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Dziadek M. Structure, development, and molecular pathology of basement membranes. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1986;29:1–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Wiedemann H., van Delden V., Furthmayr H., Kühn K. A network model for the organization of type IV collagen molecules in basement membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):203–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilibary E. C., Charonis A. S. The role of the main noncollagenous domain (NC1) in type IV collagen self-assembly. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2467–2473. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogeli G., Horn E., Carter J., Kaytes P. S. Proposed alignment of helical interruptions in the two subunits of the basement membrane (type IV) collagen. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81334-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber S., Engel J., Wiedemann H., Glanville R. W., Timpl R. Subunit structure and assembly of the globular domain of basement-membrane collagen type IV. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco P. D., Furthmayr H. Self-assembly of basement membrane collagen. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1839–1850. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco P. D., Ruben G. C. Basement membrane structure in situ: evidence for lateral associations in the type IV collagen network. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2559–2568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco P. D., Tsilibary E. C., Charonis A. S., Furthmayr H. Models for the self-assembly of basement membrane. J Histochem Cytochem. 1986 Jan;34(1):93–102. doi: 10.1177/34.1.3510247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]